|
Casualty Estimation
Casualty estimation often refers to the process of statistically estimating the number of injuries or deaths in a battle or natural disaster that has already occurred. Estimates based on detailed information on individual deaths, but also extending to statistical extrapolations, became known as casualty recording in the early twenty-first century. Casualty prediction is the process of estimating the number of injuries or deaths that might occur in a planned or potential battle or natural disaster. Measures used to imply casualties include: * Reported number of kills * Number of enemy individual weapons captured after engagement * Number of tanks and aircraft lost * Remote sensing of mass graves Methods Measurement and signature intelligence alone cannot give a reasonable estimate of casualties. What Spectroscopic MASINT can do is help find mass graves. Geophysical MASINT can help localize metal and possibly bodies at that site. TECHINT is needed if there are weapons or artifacts t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casualty Recording
Casualty recording is the systematic and continuous process of documenting individual direct deaths from armed conflict or widespread violence. It aims to create a comprehensive account of all deaths within a determined scope, usually bound by time and location. Parameters At minimum, casualty recording typically involves documenting the date and location of a violent incident; the number of people killed; the means of violence or category of weapon used; and the party responsible. Casualty recording differs from casualty tracking by military actors to track the effects of their operations on the civilian population for the purpose of improving their procedures and reducing civilian casualties. A defining feature of casualty recording is that it is victim-centric and seeks to establish the identity of every fatality including name, age, sex, and other relevant demographic details. Where relevant to the conflict context, this may also include ethnicity and religious or politic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casualty Prediction
Casualty prediction is the science of predicting the number of deaths or injuries that may result from an epidemic, natural disaster or act of war such as the explosion of a nuclear weapon, chemical weapon or biological weapon. (Casualty estimation is the process of estimating the number of injuries or deaths in a battle or natural disaster that has already occurred.) The New York University Large Scale Emergency Readiness Project applies agent-based modelling to simulate the effects of a large-scale disaster. Their initial project focused on modelling a 1998 Brazilian food-poisoning incident involving 8,000 injuries and 16 deaths. Blast casualty prediction is routinely performed in the planning of military operations. For example, a cruise missile attack was considered by the United States in 1998 for Tarnak Farms in order to kill Osama bin Laden. However, not enough was known about the collateral damage effects of cruise missiles on mud huts. At the time there were estim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
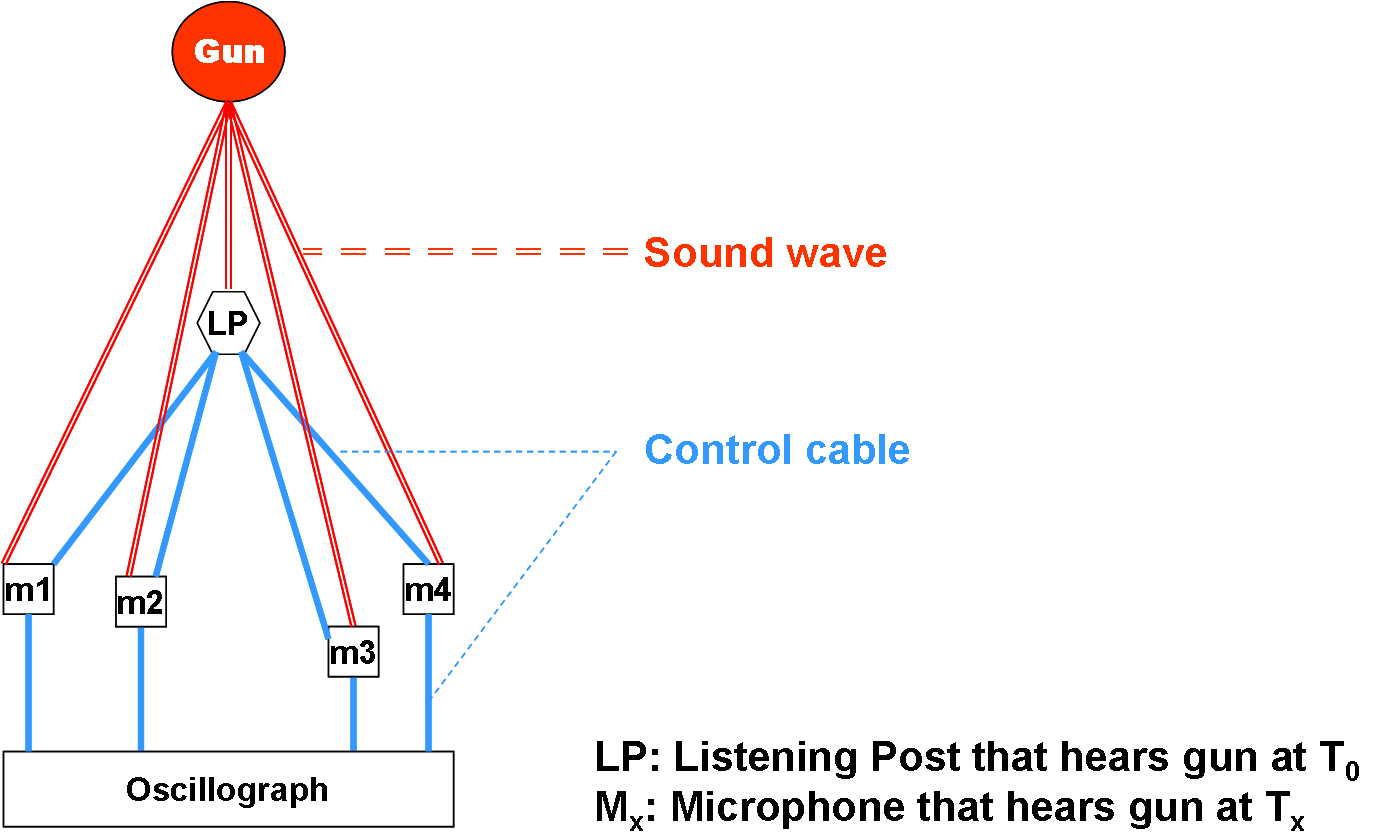
MASINT
Measurement and signature intelligence (MASINT) is a technical branch of intelligence gathering, which serves to detect, track, identify or describe the distinctive characteristics (signatures) of fixed or dynamic target sources. This often includes radar intelligence, acoustic intelligence, nuclear intelligence, and chemical and biological intelligence. MASINT is defined as scientific and technical intelligence derived from the analysis of data obtained from sensing instruments for the purpose of identifying any distinctive features associated with the source, emitter or sender, to facilitate the latter's measurement and identification. MASINT specialists themselves struggle with providing simple explanations of their field. One attempt calls it the "CSI" of the intelligence community, in imitation of the television series ''CSI: Crime Scene Investigation''. Another possible definition calls it "astronomy except for the direction of view." The allusion here is to observational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electro-optical MASINT
Electro-optical MASINT is a subdiscipline of Measurement and Signature Intelligence, (MASINT) and refers to intelligence gathering activities which bring together disparate elements that do not fit within the definitions of Signals Intelligence (SIGINT), Imagery Intelligence (IMINT), or Human Intelligence (HUMINT). Electro-optical MASINT and IMINT have some similarities, but is distinct from it. IMINT's primary goal to create a picture, composed of visual elements understandable to a trained user. Electro-optical MASINT helps validate that picture, so that, for example, the analyst can tell if an area of green is vegetation or camouflage paint. Electro-optical MASINT also generates information on phenomena that emit, absorb, or reflect electromagnetic energy in the infrared, visible light, or ultraviolet spectra, phenomena where a "picture" is less important than the amount or type of energy reported. For example, a class of satellites, originally intended to give early warning of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophysical MASINT
Geophysical MASINT is a branch of Measurement and Signature Intelligence (MASINT) that involves phenomena transmitted through the earth (ground, water, atmosphere) and manmade structures including emitted or reflected sounds, pressure waves, vibrations, and magnetic field or ionosphere disturbances. According to the United States Department of Defense, MASINT has technically derived intelligence (excluding traditional imagery IMINT and signals intelligence SIGINT) that – when collected, processed, and analyzed by dedicated MASINT systems – results in intelligence that detects, tracks, identifies or describes the signatures (distinctive characteristics) of fixed or dynamic target sources. MASINT was recognized as a formal intelligence discipline in 1986. Another way to describe MASINT is a "non-literal" discipline. It feeds on a target's unintended emissive by-products, the "trails" - the spectral, chemical or RF that an object leaves behind. These trails form distinct signature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TECHINT
Techint is an Argentine conglomerate founded in Milan in 1945 by Italian industrialist Agostino Rocca and headquartered in Milan (Italy) and Buenos Aires (Argentina). As of 2019 the Techint Group is composed of six main companies in the following areas of business: engineering, construction, steel, mining, oil & gas, industrial plants, healthcare. Techint, with its subsidiaries, is the largest steel making company in Argentina. Techint claims to be the world's largest manufacturer of seamless steel tubes, mainly used in the oil industry. History Agostino Rocca, an executive at Ansaldo and later at Dalmine and SIAC (steel and iron industries) founded ''Compagnia Tecnica Internazionale'' (Italian for "Technical International Company") in Milan in September 1945, but developed its main activity worldwide. The original company name was changed after to ''Techint'', its abbreviated telex code.http://www.techint.com/~/media/TechintCom/Brochures/techint bilancio.ashx The company beg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. The north was supported by the Soviet Union, China, and other communist states, while the south was United States in the Vietnam War, supported by the United States and other anti-communism, anti-communist Free World Military Forces, allies. The war is widely considered to be a Cold War-era proxy war. It lasted almost 20 years, with direct U.S. involvement ending in 1973. The conflict also spilled over into neighboring states, exacerbating the Laotian Civil War and the Cambodian Civil War, which ended with all three countries becoming communist states by 1975. After the French 1954 Geneva Conference, military withdrawal from Indochina in 1954 – following their defeat in the First Indochina War – the Viet Minh to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Hackworth
David Haskell Hackworth (November 11, 1930 – May 4, 2005), also known as Hack, was a prominent journalist, military journalist and a famous former United States Army colonel who was decorated in both the Korean War and Vietnam War. Hackworth is known for his role in the creation and command of Tiger Force, a military unit which was formed in South Vietnam to apply guerrilla warfare tactics against Viet Cong guerrilla fighters. Hackworth is also known for his accusation in 1996 that Chief of Naval Operations Admiral Jeremy Michael Boorda, Mike Boorda was wearing two unauthorized service ribbon devices on two of his uniform's awards denoting valor in combat. Although Admiral Boorda had served off the coast of Vietnam in the 1960s and believed he was authorized to wear the two wartime decorations for meritorious service, he did not meet the Navy's requirements. Boorda committed suicide during Hackworth's investigation. It came out in 1997 that Hackworth claimed he had earned tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquakes
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time period. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. The word ''tremor'' is also used for non-earthquake seismic rumbling. At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and displacing or disrupting the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause a tsunami. Earthquakes ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Defense
Civil defense ( en, region=gb, civil defence) or civil protection is an effort to protect the citizens of a state (generally non-combatants) from man-made and natural disasters. It uses the principles of emergency operations: prevention, mitigation, preparation, response, or emergency evacuation and recovery. Programs of this sort were initially discussed at least as early as the 1920s and were implemented in some countries during the 1930s as the threat of war and aerial bombardment grew. Civil-defense structures became widespread after authorities recognised the threats posed by nuclear weapons. Since the end of the Cold War, the focus of civil defense has largely shifted from responding to military attack to dealing with emergencies and disasters in general. The new concept is characterised by a number of terms, each of which has its own specific shade of meaning, such as ''crisis management'', '' emergency management'', ''emergency preparedness'', ''contingency planning' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Count
A body count is the total number of people killed in a particular event. In combat, a body count is often based on the number of confirmed kills, but occasionally only an estimate. Often used in reference to military combat, the term can also refer to any situation involving multiple killings, such as the actions of death squads or serial killers. The military gathers such figures for a variety of reasons, such as determining the need for continuing operations, estimating efficiency of new and old weapons systems, and planning follow-up operations. The term has since been used to describe the number of sexual partners a person has engaged with. Military use Body count figures have a long history in military planning and propaganda. Sassanian Empire According to Procopius, when the Persians were about to march to a war, the king would sit on the throne and many baskets would be set before him. The men of the army would pass along the baskets one by one, each throwing one arro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loss Exchange Ratio
Loss exchange ratio is a figure of merit in attrition warfare. It is usually relevant to a condition or state of war where one side depletes the resources of another through attrition. Specifically and most often used as a comparator in aerial combat, where it is known as a kill-ratio. Historical applications Loss exchange ratio has played a significant role in past wars, especially those that have devolved into stalemate and become wars of attrition. For example, the German objective at the Battle of Verdun (1916) during World War I was not the seizure of any strategic objective, but rather to inflict an LER of 2:1 on the French forces and thereby cripple the French army. During the First Indochina War, Võ Nguyên Giáp, the leader of the Việt Minh, told his French opposite number that "you can kill ten of my men for every one I kill of yours, and at that rate, I will still triumph." In fact, the LER was approximately 3:1 in favor of the French, and they did indeed withdraw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |