|
Carbureted Compression Ignition Model Engine
A carbureted compression ignition model engine, popularly known as a model diesel engine, is a simple compression ignition engine made for model propulsion, usually model aircraft but also model boats. These are quite similar to the typical glow-plug engine that runs on a mixture of methanol-based fuels with a hot wire filament to provide ignition. Despite their name, their use of compression ignition, and the use of a kerosene fuel that is similar to diesel, model diesels share very little with full-size diesel engines. Comparison with full-size engines Full-size diesel engines, such as those found in a truck, are fuel injected and either two-stroke or four-stroke. They use compression ignition to ignite the mixture: the compression within the cylinder heats the inlet charge sufficiently to cause ignition, without requiring any external ignition source. A fundamental feature of such engines, unlike petrol (gasoline) engines, is that they draw in air alone and the fuel is only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miniature Two-stroke Diesel Engine 1960
A miniature is a small-scale reproduction, or a small version. It may refer to: * Portrait miniature, a miniature portrait painting * Miniature art, miniature painting, engraving and sculpture * Miniature (chess), a masterful chess game or problem with very few pieces or moves, often comprising spectacular tactical combinations * Miniature (illuminated manuscript), a small painting in an illuminated text ** Arabic miniature, a small painting in an illuminated text ** Armenian miniature, a small painting in an illuminated text ** Persian miniature, a small painting in an illuminated text or album ** Ottoman miniature, a small painting in an illuminated text or album *** Contemporary Turkish Miniature, painting ** Mughal miniature, a small painting in an illuminated text or album * Scale model ** Room box ** Figurine ** Miniature figure (gaming), a small figurine used in role playing games and tabletop wargames * Miniature (alcohol), a very small bottle of an alcoholic drink * Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
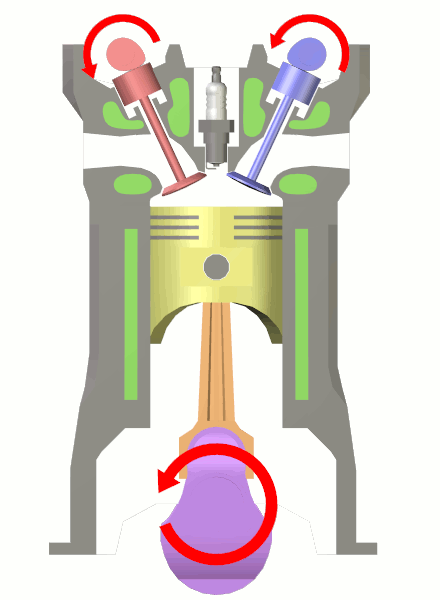
Top Dead Center
In a reciprocating engine, the dead centre is the position of a piston in which it is either farthest from, or nearest to, the crankshaft. The former is known as Top Dead Centre (TDC) while the latter is known as Bottom Dead Centre (BDC). More generally, the dead centre is any position of a crank where the applied force is straight along its axis, meaning no turning force can be applied. Many sorts of machines are crank driven, including unicycles, bicycles, tricycles, various types of machine presses, gasoline engines, diesel engines, steam locomotives, and other steam engines. Crank-driven machines rely on the energy stored in a flywheel to overcome the dead centre, or are designed, in the case of multi-cylinder engines, so that dead centres can never exist on all cranks at the same time. A steam locomotive is an example of the latter, the connecting rods being arranged such that the dead centre for each cylinder occurs out of phase with the other one (or more) cylinde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cetane Number
Cetane number (cetane rating) is an indicator of the combustion speed of diesel fuel and compression needed for ignition. It plays a similar role for diesel as octane rating does for gasoline. The CN is an important factor in determining the quality of diesel fuel, but not the only one; other measurements of diesel fuel's quality include (but are not limited to) energy content, density, lubricity, cold-flow properties and sulphur content.Werner Dabelstein, Arno Reglitzky, Andrea Schütze and Klaus Reders "Automotive Fuels" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', 2007, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Definition The cetane number (or CN) of a fuel is defined by finding a blend of cetane and isocetane with the same ignition delay. Cetane has a cetane number defined to be 100, while isocetane's measured cetane number is 15, replacing the former reference fuel alpha-methylnaphthalene, which was assigned a cetane number of 0. Once the blend is known, the cetane number is calcula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vegetable Oil
Vegetable oils, or vegetable fats, are oils extracted from seeds or from other parts of fruits. Like animal fats, vegetable fats are ''mixtures'' of triglycerides. Soybean oil, grape seed oil, and cocoa butter are examples of seed oils, or fats from seeds. Olive oil, palm oil, and rice bran oil are examples of fats from other parts of fruits. In common usage, vegetable ''oil'' may refer exclusively to vegetable fats which are liquid at room temperature. Vegetable oils are usually edible. Uses In antiquity Oils extracted from plants have been used since ancient times and in many cultures. Archaeological evidence shows that olives were turned into olive oil by 6000 BCE and 4500 BCE in present-day Israel and Palestine. In addition to use as food, fats and oils (both vegetable and mineral) have long been used as fuel, typically in lamps which were a principal source of illumination in ancient times. Oils may have been used for lubrication, but there is no evidence for this. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castor Oil
Castor oil is a vegetable oil pressed from castor beans. It is a colourless or pale yellow liquid with a distinct taste and odor. Its boiling point is and its density is 0.961 g/cm3. It includes a mixture of triglycerides in which about 90% of fatty acids are ricinoleates. Oleic acid and linoleic acid are the other significant components. Castor oil and its derivatives are used in the manufacturing of soaps, lubricants, hydraulic and brake fluids, paints, dyes, coatings, inks, cold-resistant plastics, waxes and polishes, nylon, and perfumes. Etymology The name probably comes from a confusion between the '' Ricinus'' plant that produces it and another plant, the '' Vitex agnus-castus''. An alternative etymology, though, suggests that it was used as a replacement for castoreum. Composition Castor oil is well known as a source of ricinoleic acid, a monounsaturated, 18-carbon fatty acid. Among fatty acids, ricinoleic acid is unusual in that it has a hydroxyl functiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diethyl Ether
Diethyl ether, or simply ether, is an organic compound in the ether class with the formula , sometimes abbreviated as (see Pseudoelement symbols). It is a colourless, highly volatile, sweet-smelling ("ethereal odour"), extremely flammable liquid. It is commonly used as a solvent in laboratories and as a starting fluid for some engines. It was formerly used as a general anesthetic, until non-flammable drugs were developed, such as halothane. It has been used as a recreational drug to cause intoxication. Production Most diethyl ether is produced as a byproduct of the vapor-phase hydration of ethylene to make ethanol. This process uses solid-supported phosphoric acid catalysts and can be adjusted to make more ether if the need arises. Vapor-phase dehydration of ethanol over some alumina catalysts can give diethyl ether yields of up to 95%. Diethyl ether can be prepared both in laboratories and on an industrial scale by the acid ether synthesis. Ethanol is mixed with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group). Ethanol is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. It is a psychoactive recreational drug, the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. It has medical applications as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the synthesis of organic compounds, and as a fuel source. Ethanol also can be dehydrated to make ethylene, an important chemical feedstock. As of 2006, world production of ethanol was , coming mostly from Brazil and the U.S. Etymology ''Ethanol'' is the systematic name defined by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerosene
Kerosene, paraffin, or lamp oil is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid which is derived from petroleum. It is widely used as a fuel in aviation as well as households. Its name derives from el, κηρός (''keros'') meaning "wax", and was registered as a trademark by Canadian geologist and inventor Abraham Gesner in 1854 before evolving into a generic trademark. It is sometimes spelled kerosine in scientific and industrial usage. The term kerosene is common in much of Argentina, Australia, Canada, India, New Zealand, Nigeria, and the United States, while the term paraffin (or a closely related variant) is used in Chile, eastern Africa, South Africa, Norway, and in the United Kingdom. The term lamp oil, or the equivalent in the local languages, is common in the majority of Asia and the Southeastern United States. Liquid paraffin (called mineral oil in the US) is a more viscous and highly refined product which is used as a laxative. Paraffin wax is a waxy solid extracted from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schnuerle Porting
Schnuerle porting is a system to improve efficiency of a valveless two-stroke engine by giving better scavenging. The intake and exhaust ports cut in the cylinder wall are shaped to give a more efficient transfer of intake and exhaust gases. Description Gas flow within the two-stroke engine is even more critical than for a four-stroke engine, as the two flows are both entering and leaving the combustion chamber simultaneously. A well-defined flow pattern is required, avoiding any turbulent mixing. The efficiency of the two-stroke engine depends on effective scavenging, the more complete replacement of the old spent charge with a fresh charge. Apart from large diesels with separate superchargers, two-stroke engines are generally piston-ported and use their crankcase beneath the piston for the compression needed to fill the cylinder with fuel/air mixture. The cylinder has a transfer port (inlet from crankcase to cylinder) and an exhaust port cut into it. These are opened, as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio-controlled Model
A radio-controlled model (or RC model) is a model that is steerable with the use of radio control. All types of model vehicles have had RC systems installed in them, including ground vehicles, boats, planes, helicopters and even submarines and scale railway locomotives. History Radio control has been around since Nikola Tesla demonstrated a remote control boat in 1898. World War II saw increased development in radio control technology. The Luftwaffe used controllable winged bombs for targeting Allied ships. During the 1930s the Good brothers Bill and Walt pioneered vacuum tube based control units for R/C hobby use. Their "Guff" radio controlled plane is on display at the National Aerospace museum. Ed Lorenze published a design in Model Airplane News that was built by many hobbyists. Later, after WW2, in the late 1940s to mid 1950 many other R/C designs emerged and some were sold commercially, Berkeley's Super Aerotrol, was one such example. Originally simple 'on-off' syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power-to-weight Ratio
Power-to-weight ratio (PWR, also called specific power, or power-to-mass ratio) is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measurement of actual performance of any engine or power source. It is also used as a measurement of performance of a vehicle as a whole, with the engine's power output being divided by the weight (or mass) of the vehicle, to give a metric that is independent of the vehicle's size. Power-to-weight is often quoted by manufacturers at the peak value, but the actual value may vary in use and variations will affect performance. The inverse of power-to-weight, weight-to-power ratio (power loading) is a calculation commonly applied to aircraft, cars, and vehicles in general, to enable the comparison of one vehicle's performance to another. Power-to-weight ratio is equal to thrust per unit mass multiplied by the velocity of any vehicle. Power-to-weight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutions Per Minute
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines. Standards ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionless unit equal to 1, which it refers to as a revolution, but does not define the revolution as a unit. It defines a unit of rotational frequency equal to s−1. The superseded standard ISO 80000-3:2006 did however state with reference to the unit name 'one', symbol '1', that "The special name revolution, symbol r, for this unit is widely used in specifications on rotating machines." The International System of Units (SI) does not recognize rpm as a unit, and defines the unit of frequency, Hz, as equal to s−1. :\begin 1~&\text &&=& 60~&\text \\ \frac~&\text &&=& 1~&\text \end A corresponding but distinct quantity for describing rotation is angular velocity, for which the SI unit is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |