|
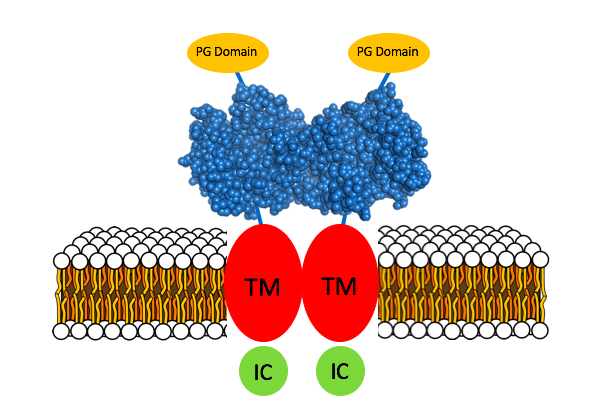
Carbonic Anhydrase 9
Carbonic anhydrase IX (CA9/CA IX) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CA9'' gene. It is one of the 14 carbonic anhydrase isoforms found in humans and is a transmembrane dimeric Metalloprotein, metalloenzyme with an extracellular active site that facilitates acid secretion in the gastrointestinal tract. CA IX is overexpressed in many types of cancer including clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) as well as carcinomas of the cervix, breast and lung where it promotes tumor growth by enhancing tumor acidosis. Function Carbonic anhydrases (CAs) are a large family of zinc metalloenzymes that catalyze the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide. They participate in a variety of biological processes, including respiration, calcification, acid-base balance, bone resorption, and the formation of aqueous humor, cerebrospinal fluid, saliva, and gastric acid. They show extensive diversity in tissue distribution and in their subcellular localization. CA IX is mainly expressed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caix Pymol H Bonding
Caix (; pcd, Tchai) is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France. Its 13th-16th century church is a listed monument. Geography Caix is situated on the D28 road, some southeast of Amiens. First World War In the First World War Caix was under German occupation for most of the period. It was recaptured by the 1st Canadian Division on 8 August 1918.The First World War Remembered, Gary Sheffield Population See also *Communes of the Somme department The following is a list of the 772 communes of the Somme department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020): [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
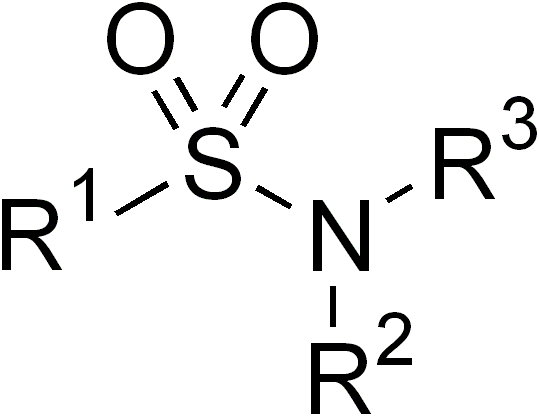
Sulfonamide
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. Because of the rigidity of the functional group, sulfonamides are typically crystalline; for this reason, the formation of a sulfonamide is a classic method to convert an amine into a crystalline derivative which can be identified by its melting point. Many important drugs contain the sulfonamide group. A sulfonamide (compound) is a chemical compound that contains this group. The general formula is or , where each R is some organic group; for example, "methanesulfonamide" (where R = methane, R' = R" = hydrogen) is . Any sulfonamide can be considered as derived from a sulfonic acid by replacing a hydroxyl group () with an amine group. In medicine, the term "sulfonamide" is sometimes used as a synonym for sulfa drug, a derivative or var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Girentuximab
Girentuximab (trade name Rencarex) is a chimeric IgG1 monoclonal antibody to carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX). CAIX is expressed on the surface of most renal cancer cells and is hypothesized to be on the surface of other tumor cells. It is investigational agent in clinical trials for renal cell carcinoma. Its development was suspended as a "naked" or unconjugated antibody during phase III trials due to efficacy. Girentuximab was originally developed by Wilex AG, Germany. It was granted fast track status and orphan drug designation by the FDA for renal cancer. In January 2017, Telix Pharmaceuticals Limited, an Australian biotechnology company, announced that it had in-licensed Girentuximab for use as a radioimmunoconjugate. It triggers antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). When it binds to its antigen ( carbonic anhydrase IX), it activates natural killer cell Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells or large granular lymphocytes (LGL), are a type of cytotoxic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
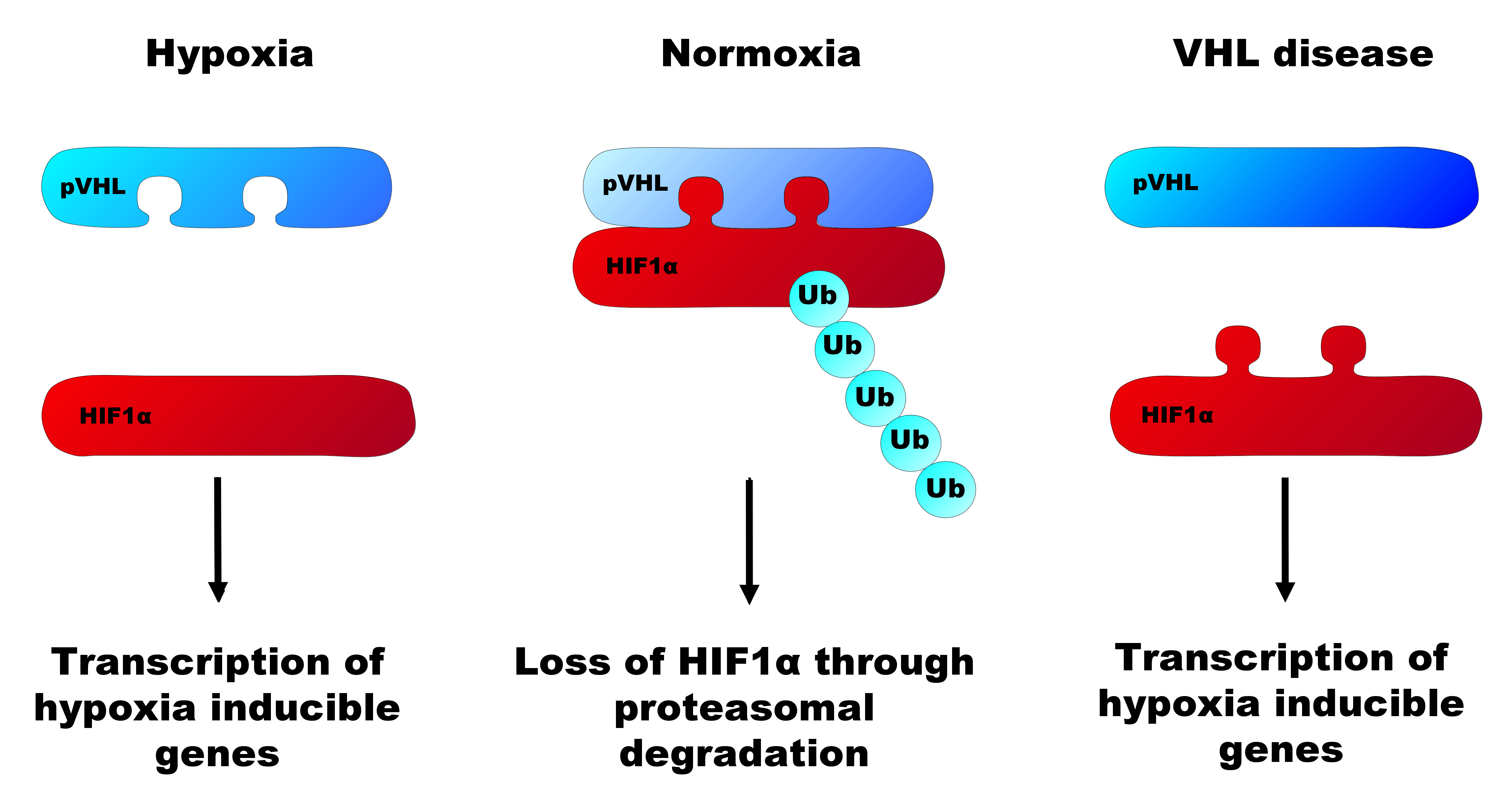
Von Hippel–Lindau Tumor Suppressor
) hockey league, Supreme Hockey League The Von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor also known as pVHL is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''VHL'' gene. Mutations of the VHL gene are associated with Von Hippel–Lindau disease. Function The protein encoded by the VHL gene is the substrate recognition component of a protein complex that includes elongin B, elongin C, and cullin-2, and possesses E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. This complex is involved in the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), which are transcription factors that play a central role regulating gene expression in response to changing oxygen levels. RNA polymerase II subunit POLR2G/RPB7 is also reported to be a target of this protein. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been observed. The resultant protein is produced in two forms, an 18 kDa and a 30 kDa protein that functions as a tumor suppressor. The main action of the VH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clear-cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma (CCRCC) is a type of renal-cell carcinoma. Genetics Cytogenetics * Alterations of chromosome 3p segments occurs in 70–90% of CCRCCs * Inactivation of von Hippel–Lindau disease ( VHL) gene by gene mutation and promoter hypermethylation * Gain of chromosome 5q * Loss of chromosomes 8p, 9p, and 14q Molecular genetics Several frequently mutated genes were discovered in CCRCC: VHL, KDM6A/UTX, SETD2, KDM5C/JARID1C and MLL2. PBRM1 is also commonly mutated in CCRCC. Histogenesis CCRCC is derived from the proximal convoluted tubule. Microscopy Generally, the cells have a clear cytoplasm, are surrounded by a distinct cell membrane and contain round and uniform nuclei. Microscopically, CCRCCs are graded by the ISUP/WHO as follows: Updated: Jul 02, 2019 * Grade 1: Inconspicuous and basophilic nucleoli at magnification of 400 times * Grade 2: Clearly visible and eosinophilic nucleoli at magnification of 400 times * Grade 3: Clearly visible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectodomain
An ectodomain is the domain of a membrane protein that extends into the extracellular space (the space outside a cell). Ectodomains are usually the parts of proteins that initiate contact with surfaces, which leads to signal transduction.A notable example of an ectodomain is the S protein, commonly known as the spike protein, of the viral particle responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The ectodomain region of the spike protein (S) is essential for attachment and eventual entry of the viral protein into the host cell. Ectodomains play a crucial part in the signaling pathways of viruses. Recent findings have indicated that certain antibodies including the anti-receptor binding domain (anti-RBD) or anti-spike ectodomain (anti-ECD) IgG titers can act as virus neutralization titers (VN titers) which can be identified in individuals with diseases, dyspnea and hospitalizations. In perspective of severe acute respiratory syndrome corona virus 2 (SARS-Cov-2) these specific ectodomains ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metalloproteinase
A metalloproteinase, or metalloprotease, is any protease enzyme whose catalytic mechanism involves a metal. An example is ADAM12 which plays a significant role in the fusion of muscle cells during embryo development, in a process known as myogenesis. Most metalloproteases require zinc, but some use cobalt. The metal ion is coordinated to the protein via three ligands. The ligands coordinating the metal ion can vary with histidine, glutamate, aspartate, lysine, and arginine. The fourth coordination position is taken up by a labile water molecule. Treatment with chelating agents such as EDTA leads to complete inactivation. EDTA is a metal chelator that removes zinc, which is essential for activity. They are also inhibited by the chelator orthophenanthroline. Classification There are two subgroups of metalloproteinases: * Exopeptidases, metalloexopeptidases ( EC number: 3.4.17). * Endopeptidases, metalloendopeptidases (3.4.24). Well known metalloendopeptidases include ADAM pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HIF1A
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha, also known as HIF-1-alpha, is a subunit of a heterodimeric transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) that is encoded by the ''HIF1A'' gene. The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2019 was awarded for the discovery of HIF. HIF1A is a basic helix-loop-helix PAS domain containing protein, and is considered as the master transcriptional regulator of cellular and developmental response to hypoxia. The dysregulation and overexpression of ''HIF1A'' by either hypoxia or genetic alternations have been heavily implicated in cancer biology, as well as a number of other pathophysiologies, specifically in areas of vascularization and angiogenesis, energy metabolism, cell survival, and tumor invasion. Two other alternative transcripts encoding different isoforms have been identified. Structure HIF1 is a heterodimeric basic helix-loop-helix structure that is composed of HIF1A, the alpha subunit (this protein), and the aryl hydrocarbon rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a sequence of DNA to which proteins bind to initiate transcription of a single RNA transcript from the DNA downstream of the promoter. The RNA transcript may encode a protein (mRNA), or can have a function in and of itself, such as tRNA or rRNA. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand). Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long, the sequence of which is highly dependent on the gene and product of transcription, type or class of RNA polymerase recruited to the site, and species of organism. Promoters control gene expression in bacteria and eukaryotes. RNA polymerase must attach to DNA near a gene for transcription to occur. Promoter DNA sequences provide an enzyme binding site. The -10 sequence is TATAAT. -35 sequences are conserved on average, but not in most promoters. Artificial promoters with conserved -10 and -35 elements transcribe more slowly. All D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CA IX
Carbonic anhydrase IX (CA9/CA IX) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CA9'' gene. It is one of the 14 carbonic anhydrase isoforms found in humans and is a transmembrane dimeric metalloenzyme with an extracellular active site that facilitates acid secretion in the gastrointestinal tract. CA IX is overexpressed in many types of cancer including clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) as well as carcinomas of the cervix, breast and lung where it promotes tumor growth by enhancing tumor acidosis. Function Carbonic anhydrases (CAs) are a large family of zinc metalloenzymes that catalyze the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide. They participate in a variety of biological processes, including respiration, calcification, acid-base balance, bone resorption, and the formation of aqueous humor, cerebrospinal fluid, saliva, and gastric acid. They show extensive diversity in tissue distribution and in their subcellular localization. CA IX is mainly expressed in the gastrointe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O-linked Glycosylation
''O''-linked glycosylation is the attachment of a sugar molecule to the oxygen atom of serine (Ser) or threonine (Thr) residues in a protein. ''O''-glycosylation is a post-translational modification that occurs after the protein has been synthesised. In eukaryotes, it occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus and occasionally in the cytoplasm; in prokaryotes, it occurs in the cytoplasm. Several different sugars can be added to the serine or threonine, and they affect the protein in different ways by changing protein stability and regulating protein activity. O-glycans, which are the sugars added to the serine or threonine, have numerous functions throughout the body, including trafficking of cells in the immune system, allowing recognition of foreign material, controlling cell metabolism and providing cartilage and tendon flexibility. Because of the many functions they have, changes in O-glycosylation are important in many diseases including cancer, diabetes and Alzheimer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |