|
Cancer (disease)
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as '' Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CT Scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry (medical), gantry to measure X-ray Attenuation#Radiography, attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce Tomography, tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is Contraindication, contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diet (nutrition)
In nutrition, diet is the sum of food consumed by a person or other organism. The word diet often implies the use of specific intake of nutrition for health or weight-management reasons (with the two often being related). Although humans are omnivores, each culture and each person holds some food preferences or some food taboos. This may be due to personal tastes or ethical reasons. Individual dietary choices may be more or less healthy. Complete nutrition requires ingestion and absorption of vitamins, minerals, essential amino acids from protein and essential fatty acids from fat-containing food, also food energy in the form of carbohydrate, protein, and fat. Dietary habits and choices play a significant role in the quality of life, health and longevity. Health A healthy diet can improve and maintain health, which can include aspects of mental and physical health. Specific diets, such as the DASH diet, can be used in treatment and management of chronic conditions. Die ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cancer Types
The following is a list of cancer types. Cancer is a group of diseases that involve abnormal increases in the number of cells, with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Not all tumors or lumps are cancerous; benign tumors are not classified as being cancer because they do not spread to other parts of the body. There are over 100 different known cancers that affect humans. Cancers are often described by the body part that they originated in. However, some body parts contain multiple types of tissue, so for greater precision, cancers are additionally classified by the type of cell that the tumor cells originated from. These types include: * ''Carcinoma'': Cancers derived from epithelial cells. This group includes many of the most common cancers that occur in older adults. Nearly all cancers developing in the breast, prostate, lung, pancreas, and colon are carcinomas. * ''Sarcoma'': Cancers arising from connective tissue (i.e. bone, cartilage, fat, ner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defecation
Defecation (or defaecation) follows digestion, and is a necessary process by which organisms eliminate a solid, semisolid, or liquid waste material known as feces from the digestive tract via the anus. The act has a variety of names ranging from the common, like pooping or crapping, to the technical, e.g. bowel movement, to the obscene ('' shitting''), to the euphemistic ("dropping a deuce" or "taking a dump"). The topic, usually avoided among polite company, can become the basis for some potty humour. Humans expel feces with a frequency varying from a few times daily to a few times weekly. Waves of muscular contraction (known as '' peristalsis'') in the walls of the colon move fecal matter through the digestive tract towards the rectum. Undigested food may also be expelled this way, in a process called ''egestion''. When birds defecate, they also expel urine and urates in the same mass, whereas other animals may also urinate at the same time, but spatially separat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer Signs And Symptoms
Cancer symptoms are changes in the body caused by the presence of cancer. They are usually caused by the effect of a cancer on the part of the body where it is growing, although the disease can cause more general symptoms such as weight loss or tiredness. There are more than 100 different types of cancer with a wide range of signs and symptoms which can manifest in different ways. Signs and Symptoms Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Cancer can be difficult to diagnose because its signs and symptoms are often nonspecific, meaning they may be general phenomena that do not point directly to a specific disease process. In medicine, a sign is an objective piece of data that can be measured or observed, as in a high body temperature (fever), a rash, or a bruise. A symptom, by contrast, is the subjective experience that may signify a disease, illness or injury, such as pain, dizziness, or fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benign Tumor
A benign tumor is a mass of cells (tumor) that does not invade neighboring tissue or metastasize (spread throughout the body). Compared to malignant (cancerous) tumors, benign tumors generally have a slower growth rate. Benign tumors have relatively well differentiated cells. They are often surrounded by an outer surface (fibrous sheath of connective tissue) or stay contained within the epithelium. Common examples of benign tumors include moles and uterine fibroids. Some forms of benign tumors may be harmful to health. Benign tumor growth causes a mass effect that can compress neighboring tissues. This can lead to nerve damage, blood flow reduction ( ischemia), tissue death (necrosis), or organ damage. The health effects of benign tumor growth may be more prominent if the tumor is contained within an enclosed space such as the cranium, respiratory tract, sinus, or bones. For example, unlike most benign tumors elsewhere in the body, benign brain tumors can be life-thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. Cancer occurs after cells are genetically altered to proliferate rapidly and indefinitely. This uncontrolled proliferation by mitosis produces a primary heterogeneic tumour. The cells which constitute the tumor eventually undergo metaplasia, followed by dysplasia then anaplasia, resulting in a malignant phenotype. This malignancy allows for invasion into the circulation, followed by invasion to a second site for tumorigenesis. Some cancer cells known as circulating tumor cells acquire the ability to penetrate the walls of lymphatic or blood vessels, after which they a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
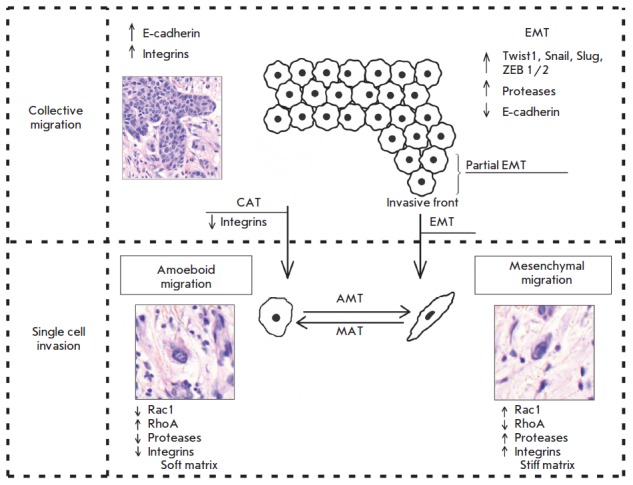
Invasion (cancer)
For cancer, invasion is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. It is generally distinguished from metastasis, which is the spread of cancer cells through the circulatory system or the lymphatic system to more distant locations. Yet, lymphovascular invasion is generally the first step of metastasis. Introduction Numerous studies have confirmed the existence of two main patterns of cancer cell invasion by cell migration: collective cell migration and individual cell migration, by which tumor cells overcome barriers of the extracellular matrix and spread into surrounding tissues. Each pattern of cell migration displays specific morphological features and the biochemical/molecular genetic mechanisms underlying cell migration. Two types of migrating tumor cells, mesenchymal (fibroblast-like) and amoeboid, are observed in each pattern of cancer cell invasion. This review describes the key differences between the variants of cancer cell migra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Growth
Cell growth refers to an increase in the total mass of a cell, including both cytoplasmic, nuclear and organelle volume. Cell growth occurs when the overall rate of cellular biosynthesis (production of biomolecules or anabolism) is greater than the overall rate of cellular degradation (the destruction of biomolecules via the proteasome, lysosome or autophagy, or catabolism). Cell growth is not to be confused with cell division or the cell cycle, which are distinct processes that can occur alongside cell growth during the process of cell proliferation, where a cell, known as the mother cell, grows and divides to produce two daughter cells. Importantly, cell growth and cell division can also occur independently of one another. During early embryonic development ( cleavage of the zygote to form a morula and blastoderm), cell divisions occur repeatedly without cell growth. Conversely, some cells can grow without cell division or without any progression of the cell cycl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five-year Survival
The five-year survival rate is a type of survival rate for estimating the prognosis of a particular disease, normally calculated from the point of diagnosis. Lead time bias from earlier diagnosis can affect interpretation of the five-year survival rate. There are absolute and relative survival rates, but the latter are more useful and commonly used. Relative and absolute rates Five-year relative survival rates are more commonly cited in cancer statistics. Five-year absolute survival rates may sometimes also be cited. * Five-year ''absolute'' survival rates describe the percentage of patients alive five years after the disease is diagnosed. * Five-year ''relative'' survival rates describe the percentage of patients with a disease alive five years after the disease is diagnosed, divided by the percentage of the general population of corresponding sex and age alive after five years. Typically, cancer five-year relative survival rates are well below 100%, reflecting excess mortali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy or molecularly targeted therapy is one of the major modalities of medical treatment ( pharmacotherapy) for cancer, others being hormonal therapy and cytotoxic chemotherapy. As a form of molecular medicine, targeted therapy blocks the growth of cancer cells by interfering with specific targeted molecules needed for carcinogenesis and tumor growth, rather than by simply interfering with all rapidly dividing cells (e.g. with traditional chemotherapy). Because most agents for targeted therapy are biopharmaceuticals, the term ''biologic therapy'' is sometimes synonymous with ''targeted therapy'' when used in the context of cancer therapy (and thus distinguished from chemotherapy, that is, cytotoxic therapy). However, the modalities can be combined; antibody-drug conjugates combine biologic and cytotoxic mechanisms into one targeted therapy. Another form of targeted therapy involves the use of nanoengineered enzymes to bind to a tumor cell such that the body's natura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms ( palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |