|
Camptothecin
Camptothecin (CPT) is a topoisomerase inhibitor. It was discovered in 1966 by M. E. Wall and M. C. Wani in systematic screening of natural products for anticancer drugs. It was isolated from the bark and stem of ''Camptotheca acuminata'' (Camptotheca, Happy tree), a tree native to China used in traditional Chinese medicine. It has been used clinically more recently in China for the treatment of gastrointestinal tumors. CPT showed anticancer activity in preliminary clinical trials, especially against breast, ovarian, colon, lung, and stomach cancers. However, it has low solubility and adverse effects have been reported when used therapeutically, so synthetic and medicinal chemists have developed numerous syntheses of camptothecin and various derivatives to increase the benefits of the chemical, with good results. Four CPT analogues have been approved and are used in cancer chemotherapy today, topotecan, irinotecan, belotecan, and trastuzumab deruxtecan. Camptothecin has also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topoisomerase Inhibitor
Topoisomerase inhibitors are chemical compounds that block the action of topoisomerases, which are broken into two broad subtypes: type I topoisomerases (TopI) and type II topoisomerases (TopII). Topoisomerase plays important roles in cellular reproduction and DNA organization, as they mediate the cleavage of single and double stranded DNA to relax supercoils, untangle catenanes, and condense chromosomes in eukaryotic cells. Topoisomerase inhibitors influence these essential cellular processes. Some topoisomerase inhibitors prevent topoisomerases from performing DNA strand breaks while others, deemed topoisomerase poisons, associate with topoisomerase-DNA complexes and prevent the re-ligation step of the topoisomerase mechanism. These topoisomerase-DNA-inhibitor complexes are cytotoxic agents, as the un-repaired single- and double stranded DNA breaks they cause can lead to apoptosis and cell death. Because of this ability to induce apoptosis, topoisomerase inhibitors have gained int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irinotecan
Irinotecan, sold under the brand name Camptosar among others, is a medication used to treat colon cancer, and small cell lung cancer. For colon cancer it is used either alone or with fluorouracil. For small cell lung cancer it is used with cisplatin. It is given intravenously. Common side effects include diarrhea, vomiting, bone marrow suppression, hair loss, shortness of breath, and fever. Other severe side effects include blood clots, colon inflammation, and allergic reactions. Those with two copies of the UGT1A1*28 gene variant are at higher risk for side effects. Use during pregnancy can result in harm to the baby. Irinotecan is a topoisomerase inhibitor—it blocks the topoisomerase I enzyme, resulting in DNA damage and cell death. Irinotecan was approved for medical use in the United States in 1996. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is made from the natural compound camptothecin which is found in the Chinese ornamental tree ''Campt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topotecan
Topotecan, sold under the brand name Hycamtin among others, is a chemotherapeutic agent medication that is a topoisomerase inhibitor. It is a synthetic, water-soluble analog of the natural chemical compound camptothecin. It is used in the form of its hydrochloride salt to treat ovarian cancer, lung cancer and other cancer types. After GlaxoSmithKline received final FDA approval for topotecan on October 15, 2007, it became the first topoisomerase I inhibitor for oral use. Uses * Ovarian cancer (FDA May 1996). * Cervical cancer (FDA June 2006). * Small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) (FDA Oct 2007). Experimental uses As of 2016, experiments were under way for Neuroblastoma, Brainstem glioma, Ewing's sarcoma and Angelman's syndrome. In addition, topotecan is experimentally treating Non-small cell lung cancer, Colorectal Cancer, Breast cancer, Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, Endometrial cancer, and Oligodendroglioma. Angelman's syndrome Angelman's syndrome is a neuro-genetic di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camptotheca Acuminata
''Camptotheca'' (happy tree, cancer tree, or tree of life) is a genus of medium-sized deciduous trees growing to tall, native to southern China and Tibet. The genus is usually included in the tupelo family Nyssaceae, but sometimes included (with the tupelos) in the dogwood family Cornaceae. The name "happy tree" is a direct translation of the Chinese name xǐ shù (Simplified Chinese:喜树). There are two species: *''Camptotheca acuminata'' Decne. *''Camptotheca lowreyana'' S.Y.Li The bark and stems of ''C. acuminata'' contain the alkaloid camptothecin. Several chemical derivatives of camptothecin are under investigation for or used as drugs for cancer treatment, including irinotecan, topotecan, rubitecan. ''C. acuminata'' also contains the chemical compounds trifolin and hyperoside Hyperoside is a chemical compound. It is the 3-''O''-galactoside of quercetin. Natural occurrences Hyperoside has been isolated from ''Drosera rotundifolia'', from the Lamiaceae ''Stachys sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belotecan
Belotecan is a drug used in chemotherapy. It is a semi-synthetic camptothecin analogue indicated for small-cell lung cancer and ovarian cancer, approved in South Korea under the trade name Camtobell, presented in 2 mg vials for injection. The drug has been marketed by ChongKunDang Pharmaceuticals since 2003. Mechanism of action Belotecan blocks topoisomerase I DNA topoisomerases (or topoisomerases) are enzymes that catalyze changes in the topological state of DNA, interconverting relaxed and supercoiled forms, linked (catenated) and unlinked species, and knotted and unknotted DNA. Topological issues i ... with a pIC50 of 6.56, stabilizing the cleavable complex of topoisomerase I-DNA, which inhibits the religation of single-stranded DNA breaks generated by topoisomerase I; lethal double-stranded DNA breaks occur when the topoisomerase I-DNA complex is encountered by the DNA replication machinery, DNA replication is disrupted, and the tumor cell undergoes apoptosis. Topoiso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms ( palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chonemorpha Fragrans
''Chonemorpha fragrans'', the frangipani vine or climbing frangipani, is a plant species in the genus ''Chonemorpha''. It is a vigorous, generally evergreen, climbing shrub producing stems or more long that can climb to the tops of the tallest trees in the forests of Southeast Asia. It has scented, white flowers and large shiny leaves. and it is native to China, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, Sri Lanka and Thailand. It is very commonly used in Ayurveda (an Indian traditional medicine) and it is also cultivated mostly worldwide in frost-free places. Description ''Chonemorpha fragrans'' is a vigorous climber, reaching up to .T. Pullaiah, P.B. Raghavendra, S. Karuppusamy, V. Raveendran and M. Anuradha It can also grow or spread to about wide, depending on the support. It has a rusty brown,P.K. Warrier, V.P.K. Nambiar and C. Ramankutty or grey barked stem which is numerously lenticelled.K. Vanangamudi, V. Anbukkarasi and M. Prabhu The bark can produce fibre of good qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bark (botany)
Bark is the outermost layers of stems and roots of woody plants. Plants with bark include trees, woody vines, and shrubs. Bark refers to all the tissues outside the vascular cambium and is a nontechnical term. It overlays the wood and consists of the inner bark and the outer bark. The inner bark, which in older stems is living tissue, includes the innermost layer of the periderm. The outer bark on older stems includes the dead tissue on the surface of the stems, along with parts of the outermost periderm and all the tissues on the outer side of the periderm. The outer bark on trees which lies external to the living periderm is also called the rhytidome. Products derived from bark include bark shingle siding and wall coverings, spices and other flavorings, tanbark for tannin, resin, latex, medicines, poisons, various hallucinogenic chemicals and cork. Bark has been used to make cloth, canoes, and ropes and used as a surface for paintings and map making. A number of plants a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drugs (journal)
''Drugs'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal published by Adis International (Springer Nature) that covers topics in drug A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via insuffla ...s and therapeutics. Besides research articles, the journal also publishes "Adis Drug Evaluations and AdisInsight Reports", evidence-based, single-agent reviews. Abstracting and indexing ''Drugs'' is abstracted and indexed in: According to the '' Journal Citation Reports'' it received an impact factor of 11.431, ranking it 2nd out of 94 journals in the category "Toxicology" and ranking it 13th out of 279 journals in the category "Pharmacology & Pharmacy" References External links * {{Official, https://www.springer.com/adis/journal/40265 Pharmacology journals Toxicology journals English-language journa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
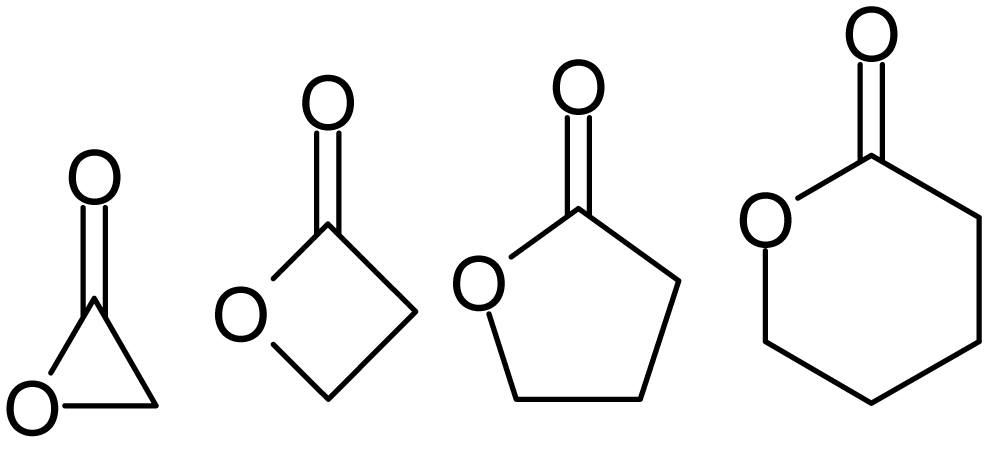
Lactone
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure (), or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring. Lactones are formed by intramolecular esterification of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids, which takes place spontaneously when the ring that is formed is five- or six-membered. Lactones with three- or four-membered rings (α-lactones and β-lactones) are very reactive, making their isolation difficult. Special methods are normally required for the laboratory synthesis of small-ring lactones as well as those that contain rings larger than six-membered. Nomenclature Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy groups. Both the negatively charged anion , called hydroxide, and the neutral radical , known as the hydroxyl radical, consist of an unbonded hydroxy group. According to IUPAC definitions, the term ''hydroxyl'' refers to the hydroxyl radical () only, while the functional group is called a ''hydroxy group''. Properties Water, alcohols, carboxylic acids, and many other hydroxy-containing compounds can be readily deprotonated due to a large difference between the electronegativity of oxygen (3.5) and that of hydrogen (2.1). Hydroxy-containing compounds engage in intermolecular hydrogen bonding increasing the electrostatic attraction between molecules and thus to higher boiling and melting points than found for compounds that lack this f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Carbon
In the nomenclature of organic chemistry, a locant is a term to indicate the position of a functional group or substituent within a molecule. Numeric locants The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recommends the use of numeric prefixes to indicate the position of substituents, generally by identifying the parent hydrocarbon chain and assigning the carbon atoms based on their substituents in order of precedence. For example, there are at least two isomers of the linear form of pentanone, a ketone that contains a chain of exactly five carbon atoms. There is an oxygen atom bonded to one of the middle three carbons (if it were bonded to an end carbon, the molecule would be an aldehyde, not a ketone), but it is not clear where it is located. In this example, the carbon atoms are numbered from one to five, which starts at one end and proceeds sequentially along the chain. Now the position of the oxygen atom can be defined as on carbon atom number two, three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |