|
Calponin 1
Calponin 1 is a basic smooth muscle protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CNN1'' gene. The ''CNN1'' gene is located at 19p13.2-p13.1 in the human chromosomal genome and contains 7 exons, encoding the protein calponin 1, an actin filament-associated regulatory protein. Human calponin 1 is a 33.2-KDa protein consists of 297 amino acids with an isoelectric point of 9.1, thus calponin 1 is also known as basic calponin. Evolution Three homologous genes, ''Cnn1'', ''Cnn2'' and ''Cnn3'', have evolved in vertebrates, encoding three isoforms of calponin: calponin 1, calponin 2, calponin 3, respectively. Protein sequence alignment shows that calponin 1 is highly conserved in mammals but more diverged among lower vertebrates. Smooth muscle-specific expression The expression of CNN1 is specific to differentiated mature smooth muscle cells, suggesting a role in contractile functions. Calponin 1 is up-regulated in smooth muscle tissues during postnatal development with a higher conten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
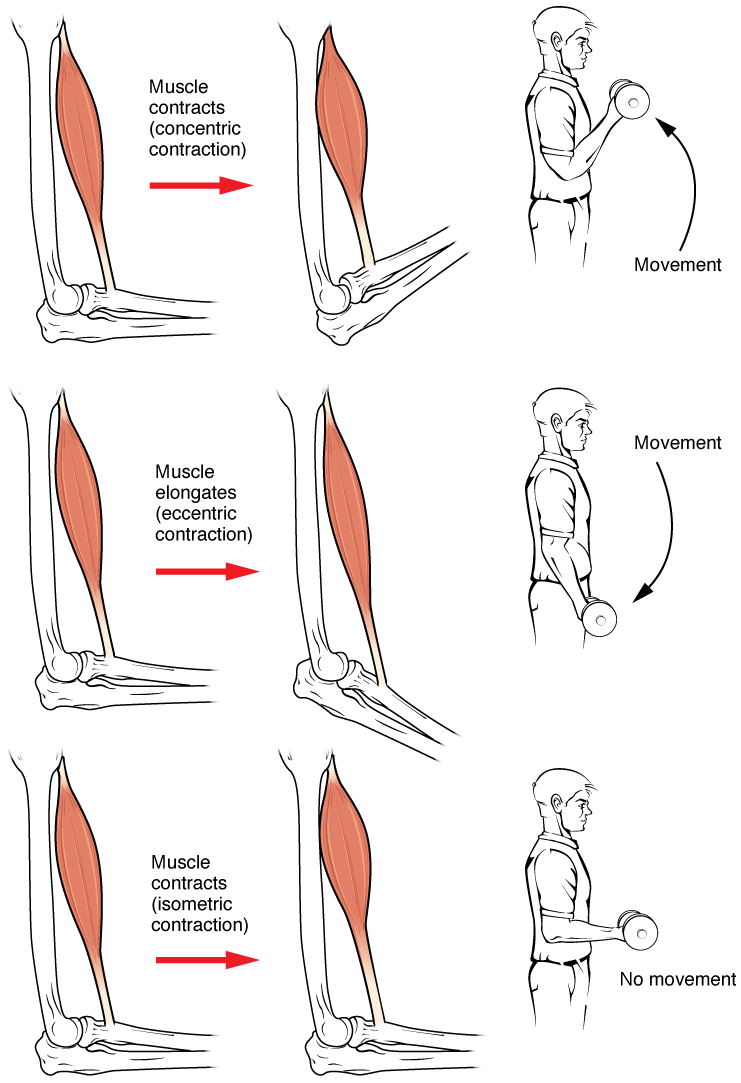
Muscle Contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding something heavy in the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state. For the contractions to happen, the muscle cells must rely on the interaction of two types of filaments which are the thin and thick filaments. Thin filaments are two strands of actin coiled around each, and thick filaments consist of mostly elongated proteins called myosin. Together, these two filaments form myofibrils which are important organelles in the skeletal muscle system. Muscle contraction can also be described based on two variables: length and tension. A muscle contraction is described as isometric if the muscle tension changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium-ATPase
In enzymology, a Mg2+-importing ATPase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :ATP + H2O + Mg2+out \rightleftharpoons ADP + phosphate + Mg2+in The 3 substrates of this enzyme are ATP, H2O, and Mg2+, whereas its 3 products are ADP, phosphate, and Mg2+. This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, specifically those acting on acid anhydrides to catalyse transmembrane movement of substances. The systematic name of this enzyme class is ATP phosphohydrolase (Mg2+-importing). The ''mgtA'' gene which encodes this enzyme is thought to be regulated by a magnesium responsive RNA element. A human enzyme was found in erythrocytes Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ... but the observation could not be confirmed. References :* :* EC 3.6.3 Enzymes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer, monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many forms of polymerization and different systems exist to categorize them. In chemical compounds, polymerization can occur via a variety of reaction mechanisms that vary in complexity due to the functional groups present in the reactants and their inherent steric effects. In more straightforward polymerizations, alkenes form polymers through relatively simple free-radical reaction, radical reactions; in contrast, reactions involving substitution at a carbonyl group require more complex synthesis due to the way in which reactants polymerize. Alkanes can also be polymerized, but only with the help of strong acids. As alkenes can polymerize in somewhat straightforward radical reactions, they form useful compounds such as polyethylene and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Transducing Adaptor Protein
Signal transducing adaptor proteins (STAPs) are proteins that are accessory to main proteins in a signal transduction pathway. Adaptor proteins contain a variety of protein-binding modules that link protein-binding partners together and facilitate the creation of larger signaling complexes. These proteins tend to lack any intrinsic enzymatic activity themselves, instead mediating specific protein–protein interactions that drive the formation of protein complexes. Examples of adaptor proteins include MYD88, Grb2 and SHC1. Signaling components Much of the specificity of signal transduction depends on the recruitment of several signalling components such as protein kinases and G-protein GTPases into short-lived active complexes in response to an activating signal such as a growth factor binding to its receptor. Domains Adaptor proteins usually contain several domains within their structure (e.g., Src homology 2 (SH2) and SH3 domains) that allow specific interactions with sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule donates a phosphate group to the substrate molecule. This transesterification produces a phosphorylated substrate and ADP. Conversely, it is referred to as dephosphorylation when the phosphorylated substrate donates a phosphate group and ADP gains a phosphate group (producing a dephosphorylated substrate and the high energy molecule of ATP). These two processes, phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, occur four times during glycolysis. Kinases are part of the larger family of phosphotransferases. Kinases should not be confused with phosphorylases, which catalyze the addition of inorganic phosphate groups to an acceptor, nor with phosphatases, which remove phosphate groups (dephosphorylation). The phosphorylation state of a molecule, whet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filamin
Filamins are a class of proteins that hold two actin filaments at large angles. Filamin protein in mammals is made up of an actin-binding domain at its N-terminus that is followed by 24 immunoglobulin-like repeat modules of roughly 95 amino acids. There are two hinge regions; between repeats 15-16 and 23-24. Filamin gets cleaved at these hinge regions to generate smaller fragments of the protein. Filamin has two actin-binding sites with a V-linkage between them, so that it cross-links actin filaments into a network with the filaments orientated almost at right angles to one another. Filamin proteins include: * FLNA * FLNB * FLNC Over-expression of FLNA stops the regeneration of bladder carcinoma (BC) cells, by inhibiting the cell cycle and inducing apoptosis of BC cells. FLNA has also been shown to reduce the mobility Mobility may refer to: Social sciences and humanities * Economic mobility, ability of individuals or families to improve their economic status * Geographic mobi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrin
Spectrin is a cytoskeletal protein that lines the intracellular side of the plasma membrane in eukaryotic cells. Spectrin forms pentagonal or hexagonal arrangements, forming a scaffold and playing an important role in maintenance of plasma membrane integrity and cytoskeletal structure. The hexagonal arrangements are formed by tetramers of spectrin subunits associating with short actin filaments at either end of the tetramer. These short actin filaments act as junctional complexes allowing the formation of the hexagonal mesh. The protein is named spectrin since it was first isolated as a major protein component of human red blood cells which had been treated with mild detergents; the detergents lysed the cells and the hemoglobin and other cytoplasmic components were washed out. In the light microscope the basic shape of the red blood cell could still be seen as the spectrin-containing submembranous cytoskeleton preserved the shape of the cell in outline. This became known as a red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinin Alpha 1
Alpha-actinin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ACTN1'' gene. Function Alpha actinins belong to the spectrin gene superfamily which represents a diverse group of cytoskeletal proteins, including the alpha and beta spectrins and dystrophins. Alpha-actinin-1 is an F-actin cross-linking protein – a bundling protein that is thought to anchor actin to a number of intracellular structures. Alpha-actinin-1 is a non-muscle cytoskeletal isoform found along microfilament bundles and adherens-type junctions, where it is involved in binding actin to the membrane. In contrast, skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle isoforms are localized to the Z-disc and analogous dense bodies, where they help anchor the myofibrillar actin filaments. Interactions Alpha-actinin-1 has been shown to interact with: * CDK5R1, * CDK5R2, * Collagen, type XVII, alpha 1, * GIPC1, * PDLIM1, * Protein kinase N1, * SSX2IP, and * Zyxin. *PTPRT (PTPrho) See also * Actinin Actinin is a microfilamen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-terminus
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus. Chemistry Each amino acid has a carboxyl group and an amine group. Amino acids link to one another to form a chain by a dehydration reaction which joins the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next. Thus polypeptide chains have an end with an unbound carboxyl group, the C-terminus, and an end with an unbound amine group, the N-terminus. Proteins are naturally synthesized starting from the N-terminus and ending at the C-terminus. Function C-terminal retention signals While the N-terminus of a protein often c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calponin Homology Domain
Calponin homology domain (or CH domain) is a family of actin binding domains found in both cytoskeletal proteins and signal transduction proteins. The domain is about 100 amino acids in length and is composed of four alpha helices. It comprises the following groups of actin-binding domains: * Actinin-type (including spectrin, fimbrin, ABP-280) * Calponin-type A comprehensive review of proteins containing this type of actin-binding domains is given in. The CH domain is involved in actin binding in some members of the family. However, in calponins there is evidence that the CH domain is not involved in its actin binding activity. Most proteins have two copies of the CH domain, however some proteins such as calponin and the human vav proto-oncogene () have only a single copy. The structure of an example CH domain has been determined using X-ray crystallography. Examples Human genes encoding calponin homology domain-containing proteins include: * ACTN1, ACTN2, ACTN3, ACTN4, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-terminus
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amine group is bonded to the carboxylic group of another amino acid, making it a chain. That leaves a free carboxylic group at one end of the peptide, called the C-terminus, and a free amine group on the other end called the N-terminus. By convention, peptide sequences are written N-terminus to C-terminus, left to right (in LTR writing systems). This correlates the translation direction to the text direction, because when a protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, as amino acids are added to the carboxyl end of the protein. Chemistry Each amino acid has an amine group and a carboxylic group. Amino acids link to one another by peptide bonds which form through a dehydration reaction that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |