|
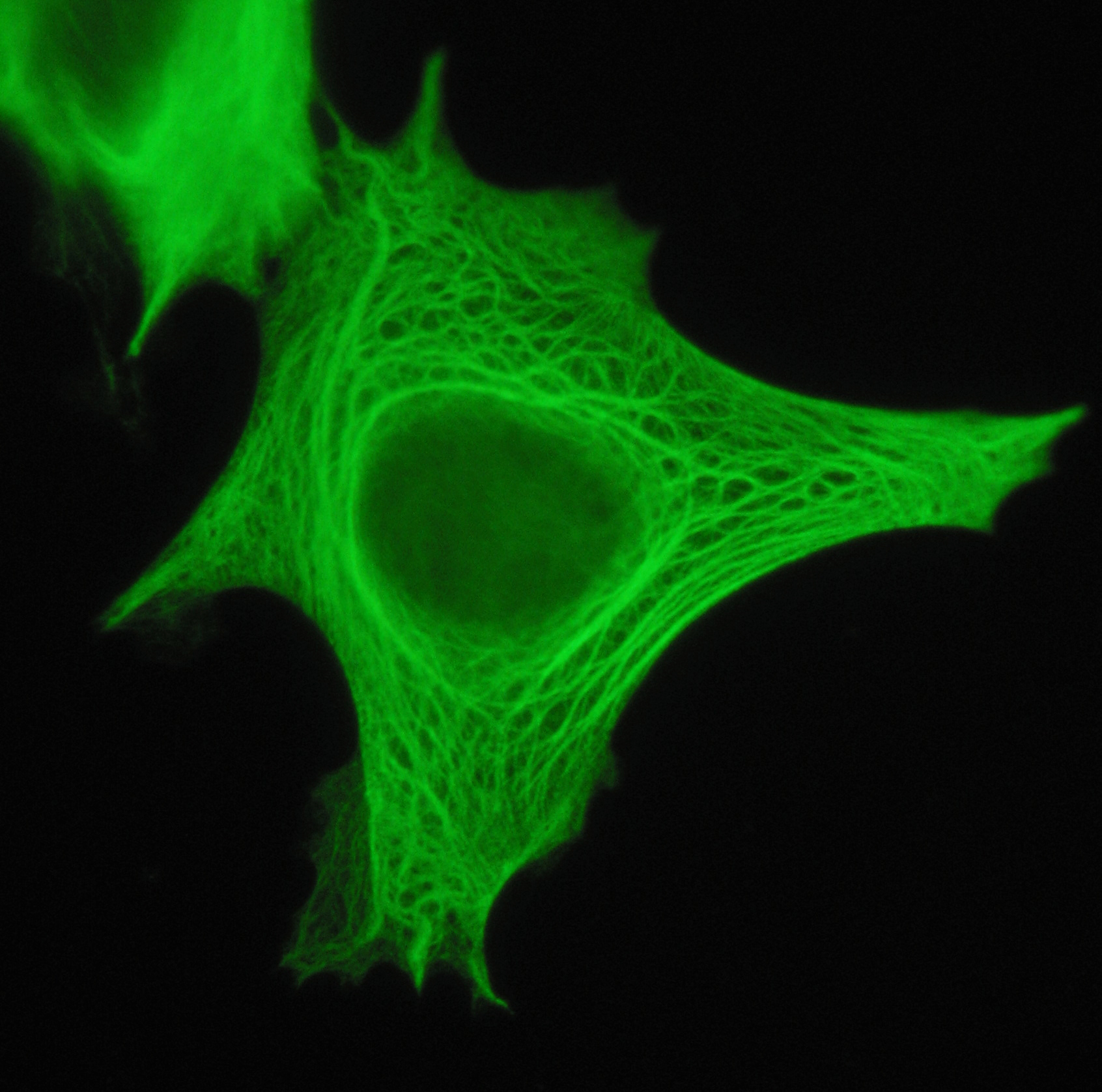
Cytokeratin 5 6 Antibodies
Cytokeratins are keratin proteins found in the intracytoplasmic cytoskeleton of epithelial tissue. They are an important component of intermediate filaments, which help cells resist mechanical stress. Expression of these cytokeratins within epithelial cells is largely specific to particular organs or tissues. Thus they are used clinically to identify the cell of origin of various human tumors. Naming The term ''cytokeratin'' began to be used in the late 1970s, when the protein subunits of keratin intermediate filaments inside cells were first being identified and characterized. In 2006 a new systematic nomenclature for mammalian keratins was created, and the proteins previously called ''cytokeratins'' are simply called ''keratins'' (human epithelial category). For example, cytokeratin-4 (CK-4) has been renamed keratin-4 (K4). However, they are still commonly referred to as cytokeratins in clinical practice. Types There are two categories of cytokeratins: the acidic type I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin 2
Keratin 2A also known as keratin 2E or keratin 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT2A'' gene. Keratin 2A is a type II cytokeratin. It is found largely in the upper spinous layer of epidermal keratinocytes and mutations in the gene encoding this protein have been associated with ichthyosis bullosa of Siemens Ichthyosis bullosa of Siemens is a type of familial, autosomal dominant ichthyosis, a rare skin disorder.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. . It is also known as bullous congenital .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * Keratins {{gene-12-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin 7
Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 7 also known as cytokeratin-7 (CK-7) or keratin-7 (K7) or sarcolectin (SCL) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT7'' gene. Keratin 7 is a type II keratin. It is specifically expressed in the simple epithelia lining the cavities of the internal organs and in the gland ducts and blood vessels. Function Keratin-7 is a member of the keratin gene family. The type II cytokeratins consist of basic or neutral proteins which are arranged in pairs of heterotypic keratin chains coexpressed during differentiation of simple and stratified epithelial tissues. This type II cytokeratin is specifically expressed in the simple epithelia lining the cavities of the internal organs and in the gland ducts and blood vessels. The genes encoding the type II cytokeratins are clustered in a region of chromosome 12q12-q13. Alternative splicing may result in several transcript variants; however, not all variants have been fully described. Keratin-7 is found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin 17
Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT17'' gene. Keratin 17 is a type I cytokeratin. It is found in nail beds, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and other epidermal appendages. Mutations in the gene encoding this protein lead to PC-K17 (previously known as Jackson-Lawler) type pachyonychia congenita and steatocystoma multiplex. Interactions Keratin 17 has been shown to interact with CCDC85B Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 85B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CCDC85B'' gene. Function Hepatitis delta virus (HDV) is a pathogenic human virus whose RNA genome and replication cycle resemble those of plant viroids. .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Pachyonychia Congenita Keratins {{gene-17-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin 16
Keratin 16 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT16'' gene. Keratin 16 is a type I cytokeratin. It is paired with keratin 6 in a number of epithelial tissues, including nail bed, esophagus, tongue, and hair follicles. Mutations in the gene encoding this protein are associated with the genetic skin disorders including pachyonychia congenita, non-epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma and unilateral palmoplantar verrucous nevus A Unilateral palmoplantar verrucous nevus is a cutaneous condition that has features of pachyonychia congenita. See also * Unilateral nevoid telangiectasia * List of cutaneous conditions Many skin conditions affect the human integumenta .... References External links GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Pachyonychia Congenita Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Keratins {{Gene-17-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin 15
Keratin 15 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT15'' gene. It has also been referred to as cytokeratin 15, K1CO and KRTB. Keratin 15 is a type I cytokeratin Type I keratins (or Type I cytokeratins) are cytokeratins that constitute the Type I intermediate filaments (IFs) of the intracytoplasmatic cytoskeleton, which is present in all mammalian epithelial cells. Most of the type I keratins consist of aci .... It is well-expressed in the basal layer of complex epithelia. However, acral keratinocytes express little to no keratin 15. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Keratins {{Gene-17-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin 14
Keratin 14 is a member of the type I keratin family of intermediate filament proteins. Keratin 14 was the first type I keratin sequence determined. Keratin 14 is also known as cytokeratin-14 (CK-14) or keratin-14 (KRT14). In humans it is encoded by the ''KRT14'' gene. Keratin 14 is usually found as a heterodimer with type II keratin 5 and form the cytoskeleton of epithelial cells. Pathology Mutations in the genes for these keratins are associated with epidermolysis bullosa simplex and dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis, both of which are autosomal dominant mutations. See also *34βE12 34βE12, often written as 34betaE12 and also known as CK34βE12 and keratin 903 (CK903), is an antibody specific for high molecular weight cytokeratins 1, 5, 10 and 14. It is sometimes, less precisely, referred to as high-molecular weight kerat ... (keratin 903) References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links GeneReviews/NCBI/UW/NIH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin 13
Keratin 13 (or cytokeratin 13) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT13'' gene. Keratin 13 is a type I cytokeratin, it is paired with keratin 4 and found in the suprabasal layers of non-cornified stratified epithelia. Mutations in the gene encoding this protein and keratin 4 have been associated with the autosomal dominant disorder White Sponge Nevus White sponge nevus (WSN) is an autosomal dominant condition of the oral mucosa (the mucous membrane lining of the mouth). It is caused by a mutations in certain genes coding for keratin, which causes a defect in the normal process of keratinizati .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Keratins {{Gene-17-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin 12
Keratin 12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT12 gene. Keratin 12 is keratin Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ... found expressed in corneal epithelia. Mutations in the gene encoding this protein lead to Meesmann corneal dystrophy. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * Keratins {{Gene-17-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin 10
Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 10 also known as cytokeratin-10 (CK-10) or keratin-10 (K10) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT10'' gene. Keratin 10 is a type I keratin. Function Keratin-10 is a member of the type I (acidic) cytokeratin family, which belongs to the superfamily of intermediate filament (IF) proteins. Keratins are heteropolymeric structural proteins which form the intermediate filament. These filaments, along with actin microfilaments and microtubules, compose the cytoskeleton of epithelial cells. Mutations in this gene are associated with epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. This gene is located within a cluster of keratin family members on chromosome 17q21. Interactions Keratin 10 has been shown to interact with AKT1. See also *34βE12 34βE12, often written as 34betaE12 and also known as CK34βE12 and keratin 903 (CK903), is an antibody specific for high molecular weight cytokeratins 1, 5, 10 and 14. It is sometimes, less precisely, referred to as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin 9
Keratin 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT9'' gene. Keratin 9 is a type I cytokeratin. It is found only in the terminally differentiated epidermis of palms and soles. Mutations in the gene encoding this protein cause epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma Epidermolytic ichthyosis (EI), also known as bullous epidermis ichthyosis (BEI), epidermolytic hyperkeratosis (EHK), bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma (BCIE), bullous ichthyosiform erythrodermaFreedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick' .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Keratins {{Gene-17-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin 6
Keratin 6A is one of the 27 different type II keratins expressed in humans. Keratin 6A was the first type II keratin sequence determined. Analysis of the sequence of this keratin together with that of the first type I keratin led to the discovery of the four helical domains in the central rod of keratins. In humans Keratin 6A is encoded by the ''KRT6A'' gene. Keratins Keratins are the intermediate filament proteins that form a dense meshwork of filaments throughout the cytoplasm of epithelial cells. Keratins form heteropolymers consisting of a type I and a type II keratin. Keratins are generally expressed in particular pairs of type I and type II keratin proteins in a tissue-specific and cellular differentiation-specific manner. The keratin proteins of epithelial tissues are commonly known as "keratins" or are sometimes referred to as "epithelial keratins" or "cytokeratins". The specialized keratins of hair and nail are known as "hard keratins" or " trichocyte keratins". Tric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |