|
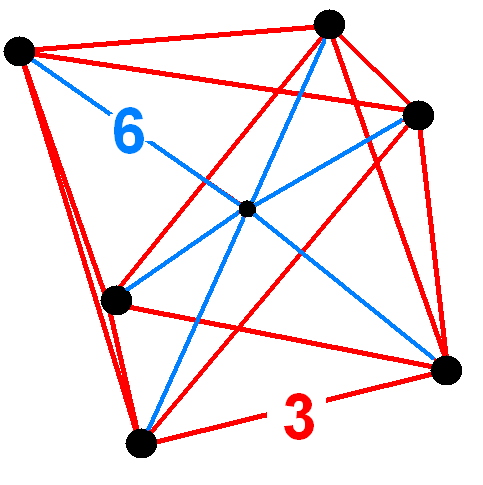
Cubic Pyramid
In 4-dimensional geometry, the cubic pyramid is bounded by one cube on the base and 6 square pyramid cells which meet at the apex. Since a cube has a circumradius divided by edge length less than one, the square pyramids can be made with regular faces by computing the appropriate height. Images Related polytopes and honeycombs Exactly 8 regular cubic pyramids will fit together around a vertex in four-dimensional space (the apex of each pyramid). This construction yields a tesseract with 8 cubical bounding cells, surrounding a central vertex with 16 edge-length long radii. The tesseract tessellates 4-dimensional space as the tesseractic honeycomb. The 4-dimensional content of a unit-edge-length tesseract is 1, so the content of the regular cubic pyramid is 1/8. The regular 24-cell has ''cubic pyramids'' around every vertex. Placing 8 cubic pyramids on the cubic bounding cells of a tesseract is Gosset's construction of the 24-cell. Thus the 24-cell is constructed from exactly 16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Pyramid
In 4-dimensional geometry, the cubic pyramid is bounded by one cube on the base and 6 square pyramid cells which meet at the apex. Since a cube has a circumradius divided by edge length less than one, the square pyramids can be made with regular faces by computing the appropriate height. Images Related polytopes and honeycombs Exactly 8 regular cubic pyramids will fit together around a vertex in four-dimensional space (the apex of each pyramid). This construction yields a tesseract with 8 cubical bounding cells, surrounding a central vertex with 16 edge-length long radii. The tesseract tessellates 4-dimensional space as the tesseractic honeycomb. The 4-dimensional content of a unit-edge-length tesseract is 1, so the content of the regular cubic pyramid is 1/8. The regular 24-cell has ''cubic pyramids'' around every vertex. Placing 8 cubic pyramids on the cubic bounding cells of a tesseract is Gosset's construction of the 24-cell. Thus the 24-cell is constructed from exactly 16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (mathematics)
In solid geometry, a face is a flat surface (a planar region) that forms part of the boundary of a solid object; a three-dimensional solid bounded exclusively by faces is a ''polyhedron''. In more technical treatments of the geometry of polyhedra and higher-dimensional polytopes, the term is also used to mean an element of any dimension of a more general polytope (in any number of dimensions).. Polygonal face In elementary geometry, a face is a polygon on the boundary of a polyhedron. Other names for a polygonal face include polyhedron side and Euclidean plane ''tile''. For example, any of the six squares that bound a cube is a face of the cube. Sometimes "face" is also used to refer to the 2-dimensional features of a 4-polytope. With this meaning, the 4-dimensional tesseract has 24 square faces, each sharing two of 8 cubic cells. Number of polygonal faces of a polyhedron Any convex polyhedron's surface has Euler characteristic :V - E + F = 2, where ''V'' is the number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truncated Cubic Honeycomb
The cubic honeycomb or cubic cellulation is the only proper regular space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb) in Euclidean 3-space made up of cubic cells. It has 4 cubes around every edge, and 8 cubes around each vertex. Its vertex figure is a regular octahedron. It is a self-dual tessellation with Schläfli symbol . John Horton Conway called this honeycomb a cubille. Related honeycombs It is part of a multidimensional family of hypercube honeycombs, with Schläfli symbols of the form , starting with the square tiling, in the plane. It is one of 28 uniform honeycombs using convex uniform polyhedral cells. Isometries of simple cubic lattices Simple cubic lattices can be distorted into lower symmetries, represented by lower crystal systems: Uniform colorings There is a large number of uniform colorings, derived from different symmetries. These include: Projections The ''cubic honeycomb'' can be orthogonally projected into the euclidean plane with various symmetr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polyhedra and the only one that has fewer than 5 faces. The tetrahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a Euclidean simplex, and may thus also be called a 3-simplex. The tetrahedron is one kind of pyramid, which is a polyhedron with a flat polygon base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. In the case of a tetrahedron the base is a triangle (any of the four faces can be considered the base), so a tetrahedron is also known as a "triangular pyramid". Like all convex polyhedra, a tetrahedron can be folded from a single sheet of paper. It has two such nets. For any tetrahedron there exists a sphere (called the circumsphere) on which all four vertices lie, and another sphere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octahedron
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex. A regular octahedron is the dual polyhedron of a cube. It is a rectified tetrahedron. It is a square bipyramid in any of three orthogonal orientations. It is also a triangular antiprism in any of four orientations. An octahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a cross polytope. A regular octahedron is a 3-ball in the Manhattan () metric. Regular octahedron Dimensions If the edge length of a regular octahedron is ''a'', the radius of a circumscribed sphere (one that touches the octahedron at all vertices) is :r_u = \frac a \approx 0.707 \cdot a and the radius of an inscribed sphere (tangent to each of the octahedron's faces) is :r_i = \frac a \approx 0.408\cdot a while the midradius, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octahedral Pyramid
In 4-dimensional geometry, the octahedral pyramid is bounded by one octahedron on the base and 8 triangular pyramid cells which meet at the apex. Since an octahedron has a circumradius divided by edge length less than one, the triangular pyramids can be made with regular faces (as regular tetrahedrons) by computing the appropriate height. Having all regular cells, it is a Blind polytope. Two copies can be augmented to make an octahedral bipyramid which is also a Blind polytope. Occurrences of the octahedral pyramid The regular 16-cell has ''octahedral pyramids'' around every vertex, with the octahedron passing through the center of the 16-cell. Therefore placing two regular octahedral pyramids base to base constructs a 16-cell. The 16-cell tessellates 4-dimensional space as the 16-cell honeycomb. Exactly 24 regular octahedral pyramids will fit together around a vertex in four-dimensional space (the apex of each pyramid). This construction yields a 24-cell with octahedral bound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
24-cell Honeycomb
In Four-dimensional space, four-dimensional Euclidean geometry, the 24-cell honeycomb, or icositetrachoric honeycomb is a regular polytope, regular space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb (geometry), honeycomb) of 4-dimensional Euclidean space by regular 24-cells. It can be represented by Schläfli symbol . The dual polytope, dual tessellation by regular 16-cell honeycomb has Schläfli symbol . Together with the tesseractic honeycomb (or 4-cubic honeycomb) these are the only regular tessellations of Euclidean 4-space. Coordinates The 24-cell honeycomb can be constructed as the Voronoi tessellation of the D4 or F4 lattice, F4 root lattice. Each 24-cell is then centered at a D4 lattice point, i.e. one of :\left\. These points can also be described as Hurwitz quaternions with even square norm. The vertices of the honeycomb lie at the deep holes of the D4 lattice. These are the Hurwitz quaternions with odd square norm. It can be constructed as a #Symmetry constructions, birecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
24-cell
In geometry, the 24-cell is the convex regular 4-polytope (four-dimensional analogue of a Platonic solid) with Schläfli symbol . It is also called C24, or the icositetrachoron, octaplex (short for "octahedral complex"), icosatetrahedroid, octacube, hyper-diamond or polyoctahedron, being constructed of octahedral cells. The boundary of the 24-cell is composed of 24 octahedral cells with six meeting at each vertex, and three at each edge. Together they have 96 triangular faces, 96 edges, and 24 vertices. The vertex figure is a cube. The 24-cell is self-dual. It and the tesseract are the only convex regular 4-polytopes in which the edge length equals the radius. The 24-cell does not have a regular analogue in 3 dimensions. It is the only one of the six convex regular 4-polytopes which is not the four-dimensional analogue of one of the five regular Platonic solids. However, it can be seen as the analogue of a pair of irregular solids: the cuboctahedron and its dual the rhombic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tesseractic Honeycomb
In four-dimensional euclidean geometry, the tesseractic honeycomb is one of the three regular space-filling tessellations (or honeycombs), represented by Schläfli symbol , and constructed by a 4-dimensional packing of tesseract facets. Its vertex figure is a 16-cell. Two tesseracts meet at each cubic cell, four meet at each square face, eight meet on each edge, and sixteen meet at each vertex. It is an analog of the square tiling, , of the plane and the cubic honeycomb, , of 3-space. These are all part of the hypercubic honeycomb family of tessellations of the form . Tessellations in this family are Self-dual. Coordinates Vertices of this honeycomb can be positioned in 4-space in all integer coordinates (i,j,k,l). Sphere packing Like all regular hypercubic honeycombs, the tesseractic honeycomb corresponds to a sphere packing of edge-length-diameter spheres centered on each vertex, or (dually) inscribed in each cell instead. In the hypercubic honeycomb of 4 dimensions, verte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tesseract
In geometry, a tesseract is the four-dimensional analogue of the cube; the tesseract is to the cube as the cube is to the square. Just as the surface of the cube consists of six square faces, the hypersurface of the tesseract consists of eight cubical cells. The tesseract is one of the six convex regular 4-polytopes. The tesseract is also called an 8-cell, C8, (regular) octachoron, octahedroid, cubic prism, and tetracube. It is the four-dimensional hypercube, or 4-cube as a member of the dimensional family of hypercubes or measure polytopes. Coxeter labels it the \gamma_4 polytope. The term ''hypercube'' without a dimension reference is frequently treated as a synonym for this specific polytope. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the word ''tesseract'' to Charles Howard Hinton's 1888 book ''A New Era of Thought''. The term derives from the Greek ( 'four') and from ( 'ray'), referring to the four edges from each vertex to other vertices. Hinton originally spell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Pyramid
In 4-dimensional geometry, the cubic pyramid is bounded by one cube on the base and 6 square pyramid cells which meet at the apex. Since a cube has a circumradius divided by edge length less than one, the square pyramids can be made with regular faces by computing the appropriate height. Images Related polytopes and honeycombs Exactly 8 regular cubic pyramids will fit together around a vertex in four-dimensional space (the apex of each pyramid). This construction yields a tesseract with 8 cubical bounding cells, surrounding a central vertex with 16 edge-length long radii. The tesseract tessellates 4-dimensional space as the tesseractic honeycomb. The 4-dimensional content of a unit-edge-length tesseract is 1, so the content of the regular cubic pyramid is 1/8. The regular 24-cell has ''cubic pyramids'' around every vertex. Placing 8 cubic pyramids on the cubic bounding cells of a tesseract is Gosset's construction of the 24-cell. Thus the 24-cell is constructed from exactly 16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a ''geometer''. Until the 19th century, geometry was almost exclusively devoted to Euclidean geometry, which includes the notions of point, line, plane, distance, angle, surface, and curve, as fundamental concepts. During the 19th century several discoveries enlarged dramatically the scope of geometry. One of the oldest such discoveries is Carl Friedrich Gauss' ("remarkable theorem") that asserts roughly that the Gaussian curvature of a surface is independent from any specific embedding in a Euclidean space. This implies that surfaces can be studied ''intrinsically'', that is, as stand-alone spaces, and has been expanded into the theory of manifolds and Riemannian geometry. Later in the 19th century, it appeared that geometries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)