|
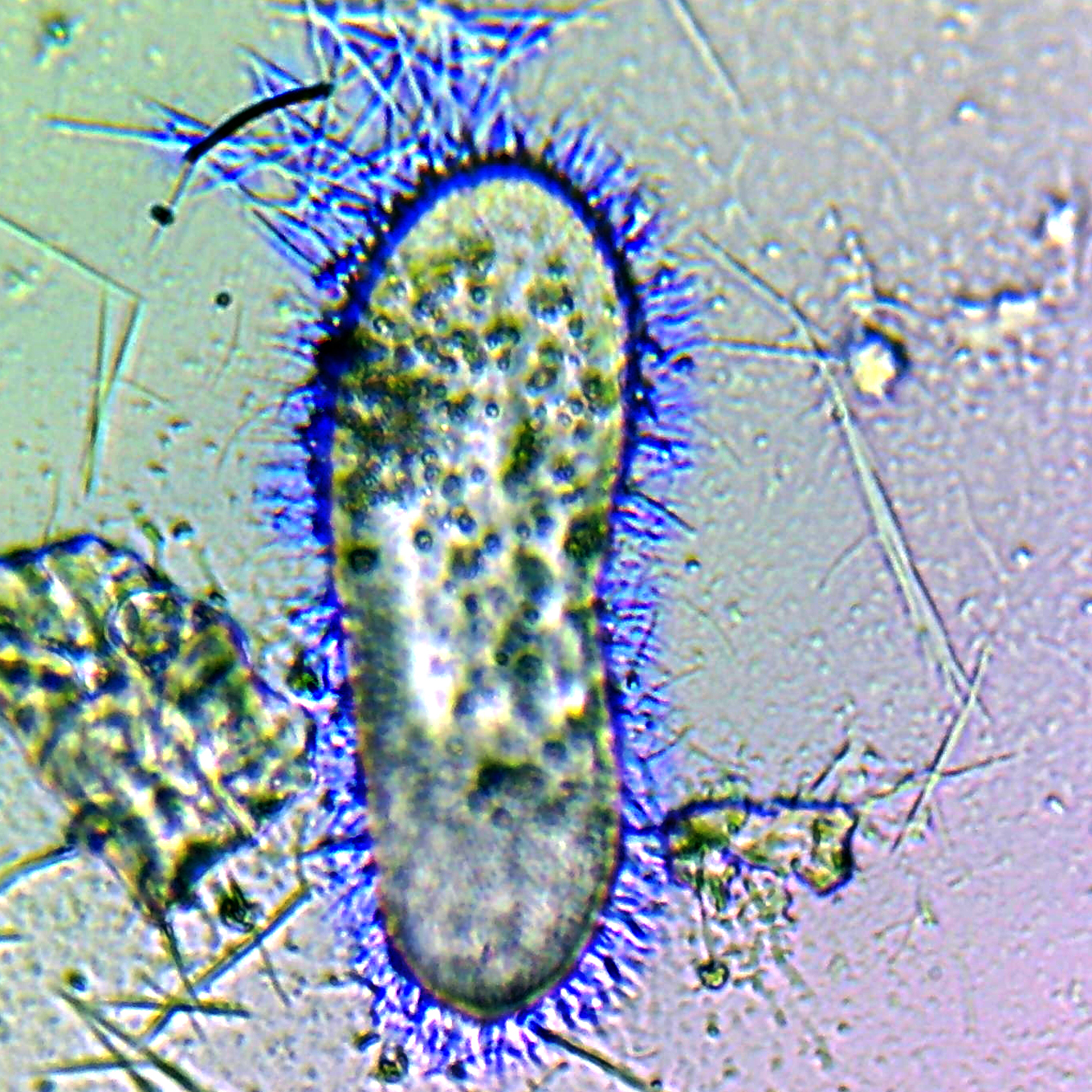
Cryptomonad
The cryptomonads (or cryptophytes) are a superclass of algae, most of which have plastids. They are traditionally considered a division of algae among phycologists, under the name of Cryptophyta. They are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 10–50 μm in size and flattened in shape, with an anterior groove or pocket. At the edge of the pocket there are typically two slightly unequal flagella. Some may exhibit mixotrophy. They are classified as superclass Cryptomonada, which is divided into two classes: heterotrophic Goniomonadea and phototrophic Cryptophyceae. The two groups are united under three shared morphological characteristics: presence of a periplast, ejectisomes with secondary scroll, and mitochondrial cristae with flat tubules. Genetic studies as early as 1994 also supported the hypothesis that ''Goniomonas'' was sister to Cryptophyceae. A study in 2018 found strong evidence that the common ancestor of Crypto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ejectisomes
The cryptomonads (or cryptophytes) are a Class (biology), superclass of algae, most of which have chloroplast, plastids. They are traditionally considered a Division (taxonomy), division of algae among phycologists, under the name of Cryptophyta. They are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 1 E-5 m, 10–50 μm in size and flattened in shape, with an anterior groove or pocket. At the edge of the pocket there are typically two slightly unequal flagellum, flagella. Some may exhibit mixotrophy. They are classified as superclass Cryptomonada, which is divided into two classes: heterotrophic Goniomonadea and phototrophic Cryptophyceae. The two groups are united under three shared morphological characteristics: presence of a periplast, ejectisomes with secondary scroll, and mitochondrial cristae with flat tubules. Genetic studies as early as 1994 also supported the hypothesis that ''Goniomonas'' was sister to Cryptophyceae. A study i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptophyceae
The cryptophyceae are a class of algae, most of which have plastids. About 230 species are known, and they are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 10–50 μm in size and flattened in shape, with an anterior groove or pocket. At the edge of the pocket there are typically two slightly unequal flagella. Some exhibit mixotrophy. Characteristics Cryptophytes are distinguished by the presence of characteristic extrusomes called ejectosomes or ejectisomes, which consist of two connected spiral ribbons held under tension. If the cells are irritated either by mechanical, chemical or light stress, they discharge, propelling the cell in a zig-zag course away from the disturbance. Large ejectosomes, visible under the light microscope, are associated with the pocket; smaller ones occur underneath the periplast, the cryptophyte-specific cell surrounding. Except for '' Chilomonas'', which has leucoplasts, cryptophytes have one or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptomonadales
Cryptomonadales is an order of Cryptophyta The cryptomonads (or cryptophytes) are a Class (biology), superclass of algae, most of which have chloroplast, plastids. They are traditionally considered a Division (taxonomy), division of algae among phycologists, under the name of Cryptophyta ... containing the families Cryptomonadaceae and Hilleaceae. References Cryptomonads Cryptista orders {{Cryptomonad-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle, organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. Chloroplasts have a high concentration of chlorophyll pigments which capture the Radiant energy, energy from sunlight and convert it to chemical energy and release oxygen. The chemical energy created is then used to make sugar and other organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process called the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in some unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like ''Arabidopsis'' and wheat. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they circulate and are moved around within cells. Their behavior is strongly influenced by environmental factors like light color and intensity. Chloroplasts cannot be made anew by the plant cell and must ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodomonas
''Rhodomonas'' is a genus of cryptomonads. It is characterized by its red colour, the square-shaped plates of its inner periplast, its short furrow ending in a gullet, and a distinctly shaped chloroplast A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle, organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. Chloroplasts have a high concentration of chlorophyll pigments which captur ... closely associated with its nucleomorph. Historically, ''Rhodomonas'' was characterized by its red chloroplast alone, but this no longer occurs as its taxonomy has become increasingly based on molecular and cellular data. Currently, there is some debate about the taxonomic validity of ''Rhodomonas'' as a genus and further research is needed to verify its taxonomic status. ''Rhodomonas'' is typically found in marine environments, although freshwater reports exist. It is commonly used as a live feed for various aquaculture species. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilomonas
''Chilomonas'' is a genus of cryptophytes, including the species '' Chilomonas paramecium''. ''Chilomonas'' is a protozoan (heterotroph). ''Chilomonas'' is golden brown and has two flagella A flagellum (; : flagella) (Latin for 'whip' or 'scourge') is a hair-like appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, from fungal spores ( zoospores), and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many pr .... References Cryptista genera {{Cryptomonad-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ejectosome
An ejectosome is a cellular organelle responsible for ejecting their contents from the cell. Two unrelated types of ejectosomes are described in the literature: # Cryptomonads have two types of characteristic extrusomes known as ejectosomes. # Intracellular pathogens, such as ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', escape from their host cells using an actin-based structure, also called an ejectosome. Cryptomonad ejectosomes contain two connected spiral ribbon-like structures, held under tension. If the cells are irritated either by mechanical, chemical or light stress, they discharge, propelling the cell in a zig-zag course away from the disturbance. Large ejectisomes, visible under the light microscope, are associated with the pocket; smaller ones occur elsewhere on the cell. Mycobacteria are ejected from host cells through the action of an actin-based ejectosome. This escape mechanism requires a cytoskeleton regulator from the host plus an intact mycobacterial ESX-1 secretion Secr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goniomonadida
''Goniomonas'' is a genus of Cryptomonads and contains five species. It is a genus of single-celled eukaryotes, including both freshwater and marine species. It lacks plastids, which is very unusual among all of the Cryptophyte genera. It may reflect one of only a small number of times that the Cryptophytes evolved into freshwater habitats. ''Goniomonas'' seems to have a number of freshwater relatives which have not yet been cultured and named. Etymology ''Goniomonas'' means angled small flagellates, combining ''goni'' and ''monas''. History of Discovery It was established by German biologist Samuel Friedrich Stein in 1878. Morphology This genus contains species that are free-swimming, flattened, biflagellate monads. They are oval in lateral view with an obliquely truncate anterior. A furrow extends along the middle of the anterior margin and for a short distance down the ventral margin and is surrounded by a single lateral row of ejectisomes. Chloroplasts, pyrenoids, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goniomonadea
Goniomonadea is a proposed class of cryptomonads which includes the orders Goniomonadida and Hemiarmida. Taxonomy * Order Goniomonadida Novarino & Lucas 1993 oniomonadales Novarino & Lucas 1993** Family Goniomonadidae Hill 1991 oniomonadaceae Hill 1991*** Genus '' Goniomonas'' von Stein 1878 * Order Hemiarmida Cavalier-Smith 2017 ** Family Hemiarmidae Cavalier-Smith 2017 *** Genus '' Hemiarma'' Shiratori & Ishida 2016 References Cryptomonads Cryptista classes {{cryptomonad-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleomorph
Nucleomorphs are small, vestigial eukaryotic nuclei found between the inner and outer pairs of membranes in certain plastids. They are thought to be vestiges of red and green algal nuclei that were engulfed by a larger eukaryote. Because the nucleomorph lies between two sets of membranes, nucleomorphs support the endosymbiotic theory and are evidence that the plastids containing them are complex plastids. Having two sets of membranes indicate that the plastid, a prokaryote, was engulfed by a eukaryote, an alga, which was then engulfed by another eukaryote, the host cell, making the plastid an example of secondary endosymbiosis. Organisms with known nucleomorphs As of 2007, only two monophyletic groups of organisms are known to contain plastids with a vestigial nucleus or nucleomorph: the cryptomonads of the supergroup Cryptista and the chlorarachniophytes of the supergroup Rhizaria, both of which have examples of sequenced nucleomorph genomes. Studies of the genomic organiza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as cyanobacteria, ''Chlorella'', and diatoms, to multicellular macroalgae such as kelp or brown algae which may grow up to in length. Most algae are aquatic organisms and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem, and phloem that are found in embryophyte, land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds. In contrast, the most complex freshwater forms are the Charophyta, a Division (taxonomy), division of green algae which includes, for example, ''Spirogyra'' and stoneworts. Algae that are carried passively by water are plankton, specifically phytoplankton. Algae constitute a Polyphyly, polyphyletic group because they do not include a common ancestor, and although Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extrusome
Extrusomes are membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells that are capable of discharging material contained within to the exterior of the cell. Due to the diversity in structure and function, it is unlikely that different types of extrusomes are homologous. Some notable extrusomes include mucocysts, which discharge a mucous mass sometimes used in cyst formation, and trichocysts, which discharge a fibrous rod. Nematocysts, the stinging structure found in Cnidarian animals, could be considered extrusomes as well, though those functions are performed by differentiated cells rather than organelles. Other extrusomes include the ancoracyst, a specialized extrusome found in the Provoran eukaryote ''Ancoracysta twista'' used to immobilize prey. Extrusomes and their functions are currently not well understood; many of their supposed functions are in doubt. Function Ciliates Within the ciliates group, numerous extrusomes–primarily trichocysts–are distributed all ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |