|
Counts Of Dillingen
The Counts of Dillingen were a Swabian comital family of the Hupaldinger (Hucpaldinger) dynasty during AD 955–1286. History The family originate in Wittislingen, with archaeological evidence of grave goods suggesting the presence of Alamannic nobility from at least the 7th century. They acquired substantial territory west of the Danube, between Gundelfingen and Donauwörth, by the second half of the 8th century. The founder of the dynasty was Hucpald I who died in 910 and was succeeded by his son Dietpald I. Dietpald's brother Ulrich of Augsburg was appointed Prince-Bishopric of Augsburg in 923. Hucpald's daughter Heylwig married Herman I, Count Palatine of Lotharingia. In 953, rebellion broke out led by King Otto's son, Liudolf, Duke of Swabia. The duchies of Bavaria, Swabia, and Franconia were in open civil war against the King, and even in his native Duchy of Saxony revolts began to spread. The Dillingens supported the king. In 954 Arnulf II, Count Palatine of Bavaria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schloss Dillingen A
''Schloss'' (; pl. ''Schlösser''), formerly written ''Schloß'', is the German term for a building similar to a château, palace, or manor house. Related terms appear in several Germanic languages. In the Scandinavian languages, the cognate word ''slot''/''slott'' is normally used for what in English could be either a palace or a castle (instead of words in rarer use such as ''palats''/''palæ'', ''kastell'', or ''borg''). In Dutch, the word ''slot'' is considered to be more archaic. Nowadays, one commonly uses ''paleis'' or ''kasteel''. But in English, the term does not appear, for instance, in the United Kingdom, this type of structure would be known as a stately home or country house. Most ''Schlösser'' were built after the Middle Ages as residences for the nobility, not as true fortresses, although originally, they often were fortified. The usual German term for a true castle is ''burg'', that for a fortress is ''festung'', and — the slightly more archaic term — ''v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Heinrich Wüest Burg Kyburg
Johann, typically a male given name, is the German form of ''Iohannes'', which is the Latin form of the Greek name ''Iōánnēs'' (), itself derived from Hebrew name ''Yochanan'' () in turn from its extended form (), meaning "Yahweh is Gracious" or "Yahweh is Merciful". Its English language equivalent is John. It is uncommon as a surname. People People with the name Johann include: Mononym *Johann, Count of Cleves (died 1368), nobleman of the Holy Roman Empire *Johann, Count of Leiningen-Dagsburg-Falkenburg (1662–1698), German nobleman *Johann, Prince of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen (1578–1638), German nobleman A–K * Johann Adam Hiller (1728–1804), German composer * Johann Adam Reincken (1643–1722), Dutch/German organist * Johann Adam Remele (died 1740), German court painter * Johann Adolf I, Duke of Saxe-Weissenfels (1649–1697) * Johann Adolph Hasse (1699-1783), German Composer * Johann Altfuldisch (1911—1947), German Nazi SS concentration camp officer executed for wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diessenhofen
Diessenhofen is a village and a municipality in Frauenfeld District in the canton of Thurgau in Switzerland. The village is situated on the south shore of the High Rhine just opposite the German town of Gailingen am Hochrhein. History Diessenhofen is first mentioned in 757 as ''Deozincova''. In 2000, the village of Willisdorf was incorporated into the municipality. The earliest traces of a settlement are Stone and Bronze Age scattered objects found in the shallow valleys of the district and on the banks of the Rhine. A hoard of coins from the Roman era (251-270), and the remains of three towers of the Danube-Iller-Rhein limes (4th century) show Roman settlements in the area. The reference in a deed of the Abbey of St. Gall from 757 mention an Alamanni village, which was probably on the plateau south of the church. In 1178 Count Hartmann III of Kyburg, raised the village to town and probably appointed a Ministerialis (unfree knights in the service of a feudal overlord) family as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
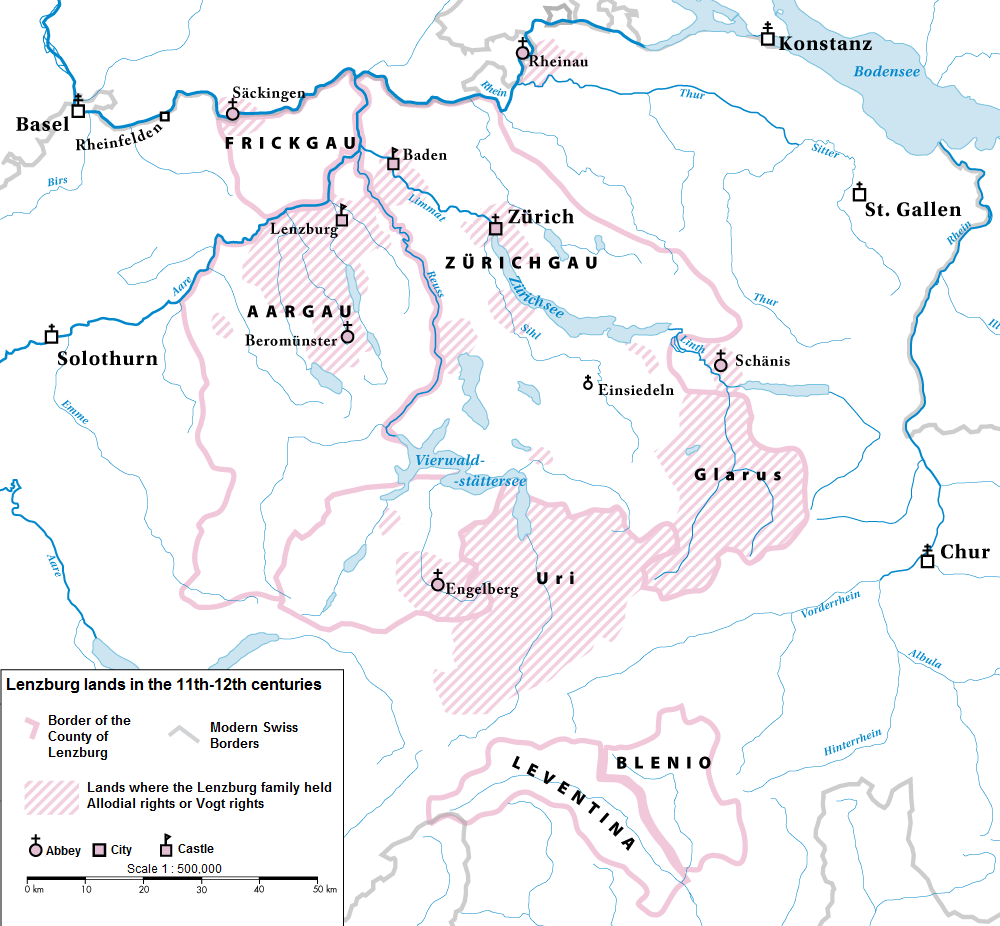
Counts Of Lenzburg
The Counts of Lenzburg (also Counts of Baden by the early 12th century) were a comital family in the Duchy of Swabia in the 11th and 12th centuries, controlling substantial portions of the '' pagi'' of Aargau and Zürichgau. After the extinction of their male line in 1173, their lands were distributed between the houses of Kyburg, Zähringen and Hohenstaufen. Subsequent Habsburg expansion into former Lenzburg territories were one of several factors that led to the formation of the Old Swiss Confederacy in the late 13th century. History The Lenzburg family was first mentioned in 1077 in connection with Lenzburg Castle, though they were probably descended from the Carolingian Count Hunfrid of Rhaetia through a female line to the Lords of Schänis, the religious vogt over Schänis Abbey. Through this line, Ulrich (died 972) is usually considered the first member of the Lenzburg family. The Lenzburgs were related to several other noble houses including the Counts of Habsb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count Of Kyburg
The Kyburg family (; ; also Kiburg) was a noble family of ''grafen'' (counts) in the Duchy of Swabia, a cadet line of the counts of Dillingen, who in the late 12th and early 13th centuries ruled the County of Kyburg, corresponding to much of what is now Northeastern Switzerland. The family was one of the four most powerful noble families in the Swiss plateau (beside the House of Habsburg, the House of Zähringen and the House of Savoy) during the 12th century. With the extinction of the Kyburg family's male line in 1264, Rudolph of Habsburg laid claim to the Kyburg lands and annexed them to the Habsburg holdings, establishing the line of "Neu-Kyburg", which was in turn extinct in 1417. History Early history The first line of counts of Kyburg were influential in local politics during the 1020s, but the male line died out in 1078. Kyburg castle, southeast of Winterthur (in the modern canton of Zürich), passed on to the Swabian counts of Dillingen. Through the marriage of Hartmann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staufer
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynasty's most prominent rulers – Frederick I (1155), Henry VI (1191) and Frederick II (1220) – ascended the imperial throne and also reigned over Italy and Burgundy. The non-contemporary name of 'Hohenstaufen' is derived from the family's Hohenstaufen Castle on the Hohenstaufen mountain at the northern fringes of the Swabian Jura, near the town of Göppingen. Under Hohenstaufen rule, the Holy Roman Empire reached its greatest territorial extent from 1155 to 1268. Name The name Hohenstaufen was first used in the 14th century to distinguish the 'high' (''hohen'') conical hill named Staufen in the Swabian Jura (in the district of Göppingen) from the village of the same name in the valley below. The new name was only applied to the hill ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welfs
The House of Welf (also Guelf or Guelph) is a European dynasty that has included many German and British monarchs from the 11th to 20th century and Emperor Ivan VI of Russia in the 18th century. The originally Franconian family from the Meuse-Moselle area was closely related to the imperial family of the Carolingians. Origins The (Younger) House of Welf is the older branch of the House of Este, a dynasty whose earliest known members lived in Veneto and Lombardy in the late 9th/early 10th century, sometimes called Welf-Este. The first member was Welf I, Duke of Bavaria, also known as Welf IV. He inherited the property of the Elder House of Welf when his maternal uncle Welf III, Duke of Carinthia and Verona, the last male Welf of the Elder House, died in 1055. Welf IV was the son of Welf III's sister Kunigunde of Altdorf and her husband Albert Azzo II, Margrave of Milan. In 1070, Welf IV became Duke of Bavaria. Welf II, Duke of Bavaria married Countess Matilda of Tuscany, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turgowe
The Thurgau (''Turgowe, Turgovia'') was a pagus of the Duchy of Alamannia in the early medieval period. A County of Thurgau ('' Landgrafschaft Thurgau'') existed from the 13th century until 1798. Parts of Thurgau were acquired by the Old Swiss Confederacy during the early 15th century, and the entire county passed to the Confederacy as a condominium in 1460. The county became the Canton of Thurgau within the Helvetic Republic in 1798, and with the Act of Mediation of 1803 a canton of the restored Confederacy. Alamannic pagus The ''Turgowe'' pagus within Alamannia was named for the Thur, and it included the entire Alamannic territory between Upper Rhine and Reuss. With the Alamannic settlement of Central Switzerland in the 6th to 8th centuries, Turgowe included most of what is now Northeastern and Central Switzerland. Odilo, son of duke Gotfrid, was count of Turgowe between 709 and 736 (when he acceded as duke of Bavaria). After the Council of Cannstatt, a Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Constance
The Prince-Bishopric of Constance, (german: Hochstift Konstanz, Fürstbistum Konstanz, Bistum Konstanz) was a small ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire from the mid-12th century until its secularisation in 1802–1803. In his dual capacity as prince and as bishop, the prince-bishop also governed the Diocese of Konstanz, which existed from about 585 until its dissolution in 1821, and whose territory extended over an area much larger than the principality."Diocese of Konstanz " ''''. David M. Cheney. Retrieved February 29, 2016 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godfrey Of Bouillon
Godfrey of Bouillon (, , , ; 18 September 1060 – 18 July 1100) was a French nobleman and pre-eminent leader of the First Crusade. First ruler of the Kingdom of Jerusalem from 1099 to 1100, he avoided the title of king, preferring that of prince (''princeps'') and ''Advocatus Sancti Sepulchri'', or Advocate of the Holy Sepulchre. Second son of Eustace II, Count of Boulogne, Godfrey became Lord of Bouillon in 1076 and in 1087 Emperor Henry IV confirmed him as Duke of Lower Lorraine, a reward for his support during the Great Saxon Revolt. Along with his brothers Eustace III and Baldwin of Boulogne, Godfrey joined the First Crusade in 1096. He took part in actions at Nicaea, Dorylaeum and Antioch, before playing a key role during the capture of Jerusalem in 1099. When Raymond IV of Toulouse declined the offer to become ruler of the new kingdom, Godfrey accepted the role and secured his kingdom by defeating the Fatimids at Ascalon a month later, bringing the First Crusade to an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic rule. While Jerusalem had been under Muslim rule for hundreds of years, by the 11th century the Seljuk takeover of the region threatened local Christian populations, pilgrimages from the West, and the Byzantine Empire itself. The earliest initiative for the First Crusade began in 1095 when Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos requested military support from the Council of Piacenza in the empire's conflict with the Seljuk-led Turks. This was followed later in the year by the Council of Clermont, during which Pope Urban II supported the Byzantine request for military assistance and also urged faithful Christians to undertake an armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem. This call was met with an enthusiastic popular response across all social classes in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neresheim Abbey
Neresheim Abbey or the Abbey of Saints Ulrich and Afra, Neresheim (german: Abtei Neresheim or ) is located above the town of Neresheim in Baden-Württemberg, southern Germany. It is now a Benedictine monastery and is part of the Beuronese Congregation. First foundation Neresheim was founded in 1095 as a house of (secular) Augustinian Canons, and converted to a Benedictine monastery in 1106. From 1140 until 1164, Ortlieb of Zwiefalten served as abbot. In the 13th century, the abbey owned seven villages and it had an income from a further 71 places in the area. Ten parish churches were incorporated. The present abbey was erected between 1747 and 1792 from plans by Balthasar Neumann. After his death in 1753 his disciples and followers continued his work. It is a masterpiece of European baroque. During wars and conflicts the monastery was destroyed several times for example during the Thirty Years' War and during Napoleonic Wars of the beginning of the 19th century Second founda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |