|
Cot–caught Merger
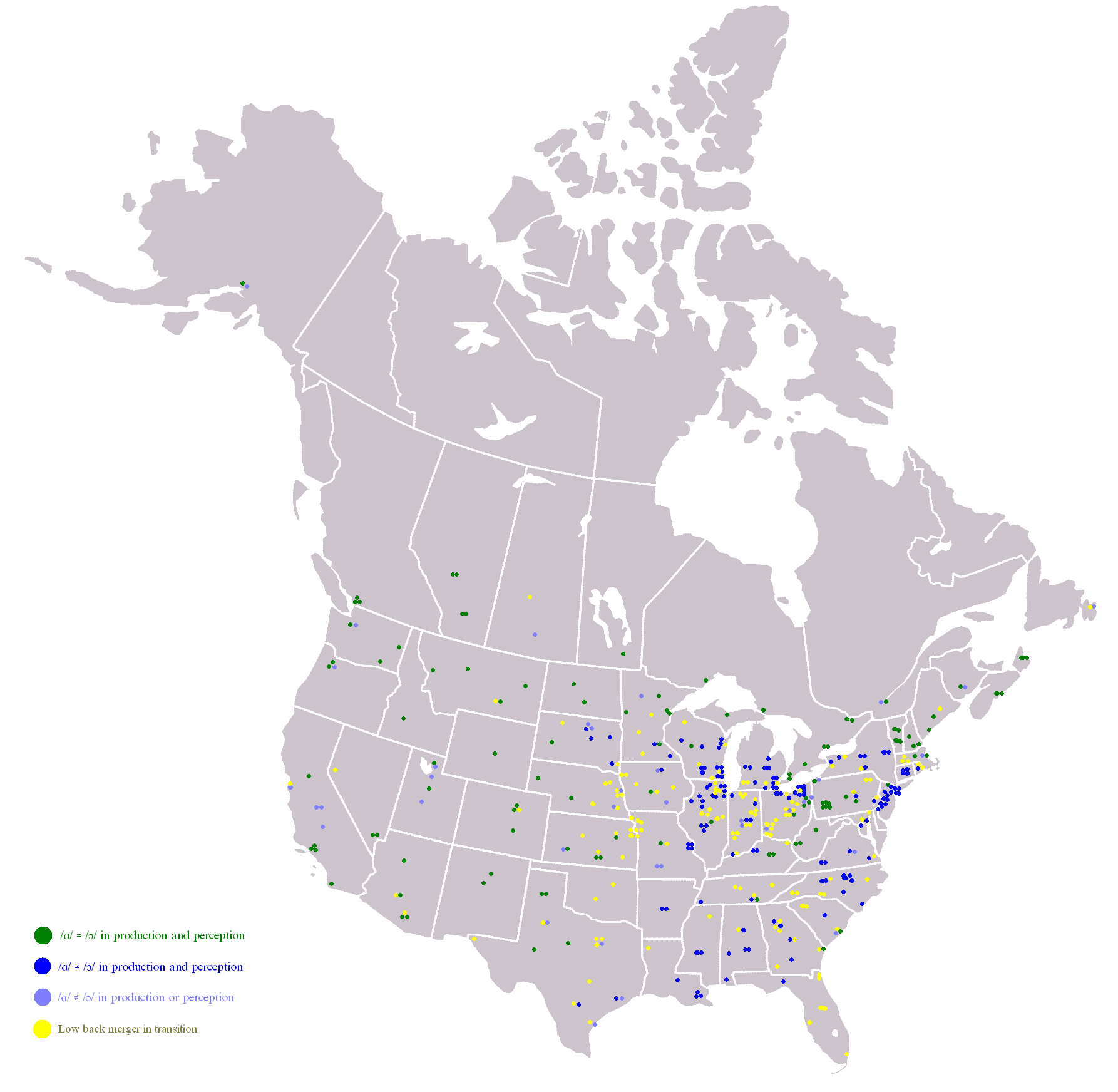
The ''cot''–''caught'' merger or merger, formally known in linguistics as the low back merger, is a sound change present in some dialects of English where speakers do not distinguish the vowel phonemes in "cot" and "caught". "Cot" and "caught" (along with "bot" and "bought", "pond" and "pawned", etc.) is an example of a minimal pair that is lost as a result of this sound change. The phonemes involved in the cot–caught merger, the low back vowels, are typically represented in the International Phonetic Alphabet as and , respectively (in the U.S., co-occurring with the father–bother merger, as and ). The merger is typical of most Canadian and Scottish English dialects as well as some Irish and U.S. English dialects. An additional vowel merger, the father–bother merger, which spread through North America in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, has resulted today in a three-way merger in which most Canadian and some U.S. accents have no vowel difference in words like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Change
A sound change, in historical linguistics, is a change in the pronunciation of a language. A sound change can involve the replacement of one speech sound (or, more generally, one phonetic feature value) by a different one (called phonetic change) or a more general change to the speech sounds that exist (phonological change), such as the merger of two sounds or the creation of a new sound. A sound change can eliminate the affected sound, or a new sound can be added. Sound changes can be environmentally conditioned if the change occurs in only some sound environments, and not others. The term "sound change" refers to diachronic changes, which occur in a language's sound system. On the other hand, " alternation" refers to changes that happen synchronically (within the language of an individual speaker, depending on the neighbouring sounds) and do not change the language's underlying system (for example, the ''-s'' in the English plural can be pronounced differently depending on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broad And General Accents
The distinction between broad and general accents is a socio-economic-linguistic contrast made between different accents of the same language, typically spoken in a single geographical location and perceived by the language users themselves: *A broad accent (sometimes equated with a local or vernacular accent) is popularly perceived as very "strong" or "thick", highly recognizable to a particular population (typically within a particular region), and often linguistically conservative; almost always, it is the accent associated with the traditional speech of the local people or the working class (whether rural or urban) of a given region. *A general accent (sometimes equated with a standard accent) is perceived as geographically more widespread, not particularized to a certain population or location, sounding more "neutral" or "weak", and historico-linguistically innovative; it is typically associated with the middle class of a given region, a growing process of standardization o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Maritime English
Atlantic Canadian English is a class of Canadian English dialects spoken in the Atlantic provinces of Canada and notably distinct from Standard Canadian English. It is composed of Maritime English (or Maritimer English) and Newfoundland English. It was mostly influenced by British and Irish English, Irish and Scottish Gaelic, and some Acadian French. Atlantic Canada is the easternmost region of Canada, comprising four provinces located on the Atlantic coast: Newfoundland and Labrador, plus the three Maritime provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Prince Edward Island. Regions such as Miramichi and Cape Breton have a wide variety of phrases and words not spoken outside of their respective regions. History Canadian English owes its very existence to important historical events, especially the Treaty of Paris of 1763. English was first spoken in Canada in the 17th century, in seasonal fishing communities along the Atlantic coast, including the island of Newfoundland, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Canadian English
Standard Canadian English is the largely homogeneous variety of Canadian English that is spoken particularly across Ontario and Western Canada, as well as throughout Canada among urban middle-class speakers from English-speaking families, excluding the regional dialects of Atlantic Canadian English. Canadian English has a mostly uniform phonology and much less dialectal diversity than neighbouring American English. In particular, Standard Canadian English is defined by the cot–caught merger to and an accompanying chain shift of vowel sounds, which is called the Canadian Shift. A subset of the dialect geographically at its central core, excluding British Columbia to the west and everything east of Montréal, has been called ''Inland Canadian English''. It is further defined by both of the phenomena that are known as Canadian raising (which is found also in British Columbia and Ontario): the production of and with back starting points in the mouth and the production of wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midland American English
Midland American English is a regional dialect or super-dialect of American English, geographically lying between the traditionally-defined Northern United States, Northern and Southern United States. The boundaries of Midland American English are not entirely clear, being revised and reduced by linguists due to definitional changes and several Midland sub-regions undergoing rapid and diverging pronunciation shifts since the early-middle 20th century onwards. It is seen as a linguistic "middle region" of American English. Today, these general characteristics of the Midland regional accent are firmly established: fronting (phonetics), fronting of the , , and vowels occurs towards the center or even the front of the mouth; the cot–caught merger is neither fully completed nor fully absent; and æ tensing, short-''a'' tensing evidently occurs strongest before nasal consonants. The currently-documented core of the Midland dialect region spans from central Ohio at its eastern extre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicano English
Chicano English, or Mexican-American English, is a dialect of American English spoken primarily by Mexican Americans (sometimes known as Chicanos), particularly in the Southwestern United States ranging from Texas to California,Newman, Michael.The New York Latino English Project Page" Queens College. Accessed 2015. "Almost all recent research on Latino English in the US has been done in the Southwest, particularly California. NYLE New_York_Latino_English">nowiki/>New_York_Latino_English.html" ;"title="New_York_Latino_English.html" ;"title="nowiki/>New York Latino English">nowiki/>New York Latino English">New_York_Latino_English.html" ;"title="nowiki/>New York Latino English">nowiki/>New York Latino Englishdiffers in two respects from these forms." as well as in Chicago. Chicano English is sometimes mistakenly conflated with Spanglish, which is a mixing of Spanish language, Spanish and English language, English; however, Chicano English is a fully formed and native dialect of Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North-Central American English
North-Central American English (in the United States, also known as the Upper Midwestern or North-Central dialect and stereotypically recognized as a Minnesota accent or Wisconsin accent) is an American English dialect native to the Upper Midwestern United States, an area that somewhat overlaps with speakers of the separate Inland North dialect situated more in the eastern Great Lakes region. The North-Central dialect is considered to have developed in a residual dialect region from the neighboring distinct dialect regions of the Western United States, Inland North, and Canada. If a strict ''cot–caught'' merger is used to define the North-Central regional dialect, it covers the Upper Peninsula of Michigan, the northern border of Wisconsin, the whole northern half of Minnesota, some of northern South Dakota, and most of North Dakota; otherwise, the dialect may be considered to extend to all of Minnesota, North Dakota, most of South Dakota, northern Iowa, and all of Wisconsin ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cajun English
Cajun English, or Cajun Vernacular English, is the dialect of English spoken by Cajuns living in Southern Louisiana. Cajun English is significantly influenced by Louisiana French, the historical language of the Cajun people, a subset of Louisiana Creoles—although many today prefer not to identify as such—who descend largely from the Acadian people expelled from the Maritime provinces during '' Le Grand Dérangement'' (among many others). It is derived from Louisiana French and is on the list of dialects of the English language for North America. Louisiana French differs, sometimes markedly, from Metropolitan French in terms of pronunciation and vocabulary, partially due to unique features in the original settlers' dialects and partially because of the long isolation of Louisiana Creoles (including Cajuns) from the greater francophone world. English is now spoken by the vast majority of the Cajun population, but French influence remains strong in terms of inflection and vocabu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western American English
Western American English (also known as Western U.S. English) is a variety of American English American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the Languages of the United States, most widely spoken lan ... that largely unites the entire Western United States as a single dialect region, including the states of California, Nevada, Arizona, Utah, New Mexico, Colorado, and Wyoming. It also generally encompasses Washington (state), Washington, Oregon, Idaho, and Montana, some of whose speakers are classified additionally under Pacific Northwest English. The Western United States, West was the last area in the United States to be reached during the gradual westward expansion of settlement by English speakers and its history shows considerable mixing and dialect levelling, leveling of the linguistic patterns of other regions. Therefore, since th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boston Accent
A Boston accent is a local accent of Eastern New England English, native specifically to the city of Boston and its suburbs. Northeastern New England English is classified as traditionally including New Hampshire, Maine, and all of eastern Massachusetts, though some uniquely local vocabulary appears only around Boston. A 2006 study co-authored by William Labov claims that the accent remains relatively stable,Labov, William (2010). The Politics of Language Change: Dialect Divergence in America'. The University of Virginia Press. Pre-publication draft. p. 53. though a 2018 study suggests the accent's traditional features may be retreating, particularly among the city's younger residents, and becoming increasingly confined to the historically Irish-American neighborhood of South Boston. Phonological characteristics Boston accents typically have the cot-caught merger but not the father-bother merger. This means that instead of merging the historical "short ''o''" sound (as in ) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New England English
New England English is, collectively, the various distinct dialects and varieties of American English originating in the New England area. Most of eastern and central New England once spoke the " Yankee dialect", some of whose accent features still remain in eastern New England today, such as "R-dropping" (though this feature is now receding among younger speakers). Accordingly, one linguistic division of New England is into Eastern versus Western New England English, as defined in the 1939 ''Linguistic Atlas of New England'' and the 2006 '' Atlas of North American English'' (ANAE). The ANAE further argues for a division between Northern versus Southern New England English, especially on the basis of the cot–caught merger and fronting (applying twice, for example, in the phrase ''Park the car''). The ANAE also categorizes the strongest differentiated New England accents into four combinations of the above dichotomies, simply defined as follows: * Northeastern New England Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pittsburgh English
Western Pennsylvania English, known more narrowly as Pittsburgh English or popularly as Pittsburghese, is a dialect of American English native primarily to the western half of Pennsylvania, centered on the city of Pittsburgh, but potentially appearing in some speakers as far north as Erie County, as far west as Youngstown, Ohio, and as far south as Clarksburg, West Virginia. Commonly associated with the white working class of Pittsburgh, users of the dialect are colloquially known as "Yinzers". Overview Scots-Irish, Pennsylvania Dutch, Polish, Ukrainian and Croatian immigrants to the area all provided certain loanwords to the dialect (see "Vocabulary" below). Many of the sounds and words found in the dialect are popularly thought to be unique to Pittsburgh, but that is a misconception since the dialect resides throughout the greater part of western Pennsylvania and the surrounding areas. Central Pennsylvania, currently an intersection of several dialect regions, was identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)