|
Cost Analysis
In production, research, retail, and accounting, a cost is the value of money that has been used up to produce something or deliver a service, and hence is not available for use anymore. In business, the cost may be one of acquisition, in which case the amount of money expended to acquire it is counted as cost. In this case, money is the input that is gone in order to acquire the thing. This acquisition cost may be the sum of the cost of production as incurred by the original producer, and further costs of transaction as incurred by the acquirer over and above the price paid to the producer. Usually, the price also includes a mark-up for profit over the cost of production. More generalized in the field of economics, cost is a metric that is totaling up as a result of a process or as a differential for the result of a decision. Hence cost is the metric used in the standard modeling paradigm applied to economic processes. Costs (pl.) are often further described based on thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
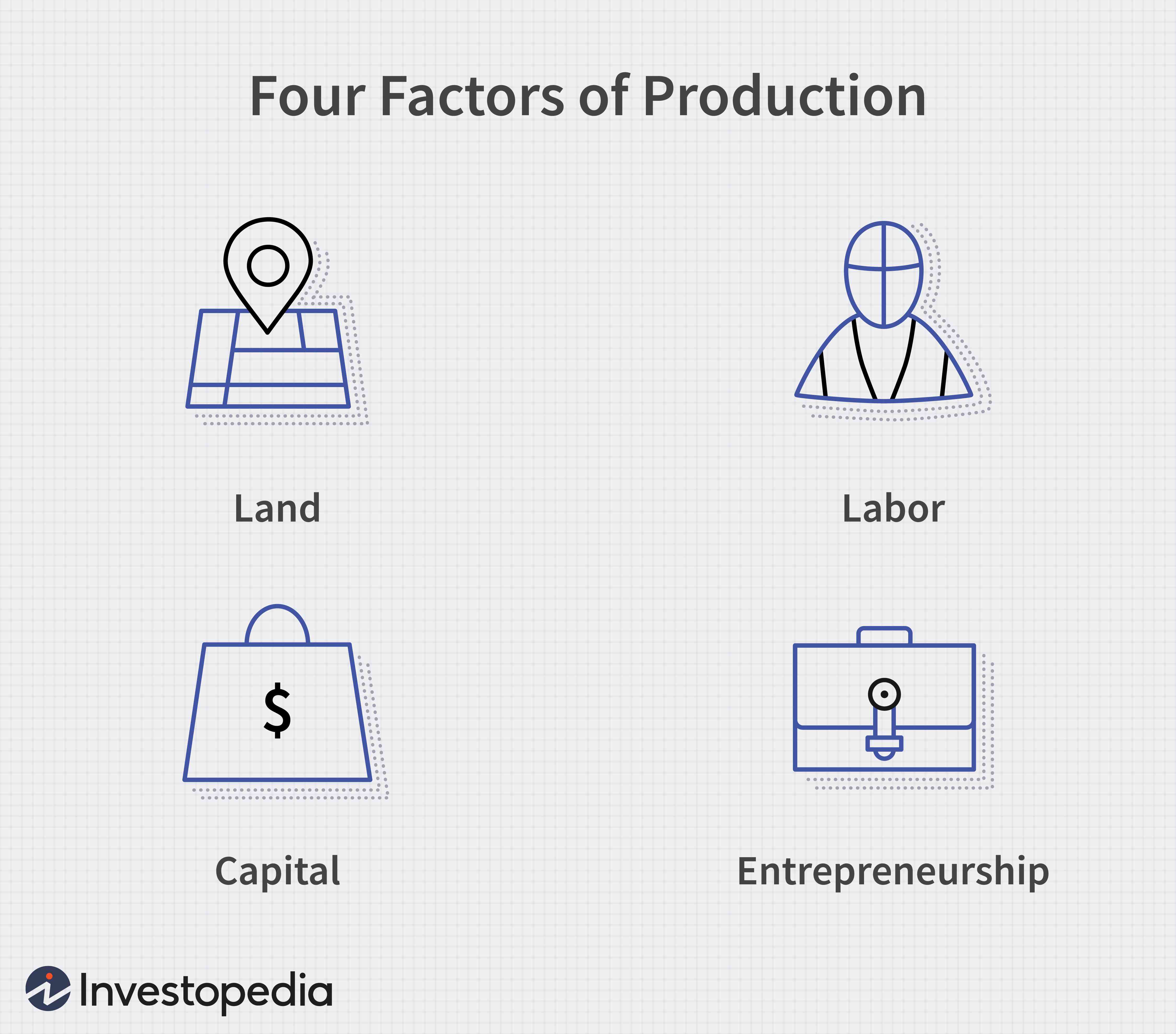
Production (economics)
Production is the process of combining various inputs, both material (such as metal, wood, glass, or plastics) and immaterial (such as plans, or knowledge) in order to create output. Ideally this output will be a good or service which has value and contributes to the utility of individuals. The area of economics that focuses on production is called production theory, and it is closely related to the consumption (or consumer) theory of economics. The production process and output directly result from productively utilising the original inputs (or factors of production). Known as primary producer goods or services, land, labour, and capital are deemed the three fundamental production factors. These primary inputs are not significantly altered in the output process, nor do they become a whole component in the product. Under classical economics, materials and energy are categorised as secondary factors as they are byproducts of land, labour and capital. Delving further, primary fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Production Function
In economics, a production function gives the technological relation between quantities of physical inputs and quantities of output of goods. The production function is one of the key concepts of mainstream neoclassical theories, used to define marginal product and to distinguish allocative efficiency, a key focus of economics. One important purpose of the production function is to address allocative efficiency in the use of factor inputs in production and the resulting distribution of income to those factors, while abstracting away from the technological problems of achieving technical efficiency, as an engineer or professional manager might understand it. For modelling the case of many outputs and many inputs, researchers often use the so-called Shephard's distance functions or, alternatively, directional distance functions, which are generalizations of the simple production function in economics. In macroeconomics, aggregate production functions are estimated to create a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manufacturing Overhead Cost
Manufacturing overhead costs (MOH cost) are all manufacturing costs that are related to the cost object (work in process and then finished goods) but cannot be traced to that cost object in an economically feasible way. Examples include supplies, indirect materials such as lubricants, indirect manufacturing labor such as plant maintenance and cleaning labor, plant rent, plant insurance, property tax A property tax or millage rate is an ad valorem tax on the value of a property.In the OECD classification scheme, tax on property includes "taxes on immovable property or net wealth, taxes on the change of ownership of property through inher ...es on the plant, plant depreciation, and the compensation of plant managers. This cost category is also referred to as Factory overhead cost (FO cost). Items of the overhead Manufacturing overhead includes other costs in manufacturing that are neither direct materials costs nor direct labor costs. It might also be referred as the fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Labor Cost
Direct labor cost is a part of wage-bill or payroll that can be specifically and consistently assigned to or associated with the manufacture of a product, a particular work order, or provision of a service. Also, we can say it is the cost of the work done by those workers who actually make the product on the production line. Determination of the direct labor cost *Planning the work to be performed. *Describing the job content of the work, by indicating the skill, knowledge, etc. *Matching the jobs with the employees. Usage The direct labor cost is part of the manufacturing cost. Calculation of direct labor cost In the direct labor cost we need to have the job time and wage we will pay it to the worker to calculate the direct labor cost as in this formulation:- \text = \text \times \text Depending on the context, there are various methods to calculate personnel costs, such as on an hourly or daily basis. Wage The wage is the payment rendered to the worker per hour as a compensa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Materials Cost
Direct materials cost the cost of direct materials which can be easily identified with the unit of production. For example, the cost of glass is a direct materials cost in light bulb manufacturing. The manufacture of products or goods required material as the prime element. In general, these materials are divided into two categories. These categories are direct materials and indirect materials. Direct materials are also called productive materials, raw materials, raw stock, stores and only materials without any descriptive title. Direct materials cost estimation Steps to estimate the direct material costs:Phillip W. Gillet, Jr., J.D. notes, Chapter three #Find the total amount to be produced. This is usually noted as the order size. #Calculate the total amount of raw materials required to produce the order size. #Multiply that amount by the cost associated with the raw materials. #If there is a waste or scrap, its cost should be added to the costs in step 3. #If the waste or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raw Materials
A raw material, also known as a feedstock, unprocessed material, or primary commodity, is a basic material that is used to produce goods, finished goods, energy, or intermediate materials that are feedstock for future finished products. As feedstock, the term connotes these materials are bottleneck assets and are required to produce other products. The term ''raw material'' denotes materials in unprocessed or minimally processed states; e.g., raw latex, crude oil, cotton, coal, raw biomass, iron ore, air, lumber, logs, water, or "any product of agriculture, forestry, fishing or mineral in its natural form or which has undergone the transformation required to prepare it for international marketing in substantial volumes". The term ''secondary raw material'' denotes waste material which has been recycled and injected back into use as productive material. Ceramic While pottery originated in many different points around the world, it is certain that it was brought to light mostly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high-tech, but it is most commonly applied to industrial design, in which raw materials from the primary sector of the economy, primary sector are transformed into finished goods on a large scale. Such goods may be sold to other manufacturers for the production of other more complex products (such as aircraft, Major appliance, household appliances, furniture, sports equipment or automobiles), or distributed via the tertiary industry to end users and consumers (usually through wholesalers, who in turn sell to retailers, who then sell them to individual customers). Manufacturing engineering is the field of engineering that designs and optimizes the manufacturing process, or the steps through whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manufacturing Cost
Manufacturing cost is the sum of costs of all resources consumed in the process of making a product. The manufacturing cost is classified into three categories: direct materials cost, direct labor cost and manufacturing overhead. It is a factor in total delivery cost. Direct materials cost Direct materials are the raw materials that become a part of the finished product. Manufacturing adds value to raw materials by applying a chain of operations to maintain a deliverable product. There are many operations that can be applied to raw materials such as welding, cutting and painting. It is important to differentiate between direct materials and indirect materials. Direct labour cost The direct labour cost is the cost of workers who can be easily identified with the unit of production. Types of labour who are considered to be part of the direct labour cost are the assembly workers on an assembly line. Manufacturing overhead Manufacturing overhead is any manufacturing cost t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cost Overrun
A cost overrun, also known as a cost increase or budget overrun, involves unexpected incurred costs. When these costs are in excess of budgeted amounts due to a value engineering underestimation of the actual cost during budgeting, they are known by these terms. Cost overruns are common in infrastructure, building, and technology projects. For IT projects, a 2004 industry study by the Standish Group found an average cost overrun of 43 percent; 71 percent of projects came in over budget, exceeded time estimates, and had estimated too narrow a scope; and total waste was estimated at $55 billion per year in the US alone. Many major construction projects have incurred cost overruns; cost estimates used to decide whether important transportation infrastructure should be built can mislead grossly and systematically. Cost overrun is distinguished from cost escalation, which is an ''anticipated'' growth in a budgeted cost due to factors such as inflation. Causes Recent works by Ah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
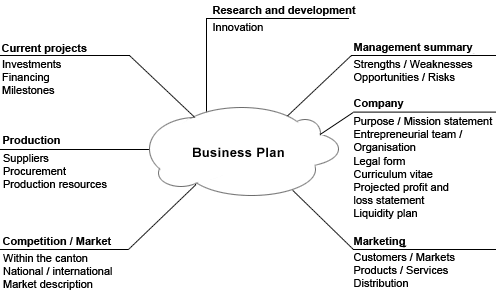
Business Plan
A business plan is a formal written document containing the goals of a business, the methods for attaining those goals, and the time-frame for the achievement of the goals. It also describes the nature of the business, background information on the organization, the organization's financial projections, and the strategies it intends to implement to achieve the stated targets. In its entirety, this document serves as a road-map (a plan) that provides direction to the business. Written business plans are often required to obtain a bank loan or other kind of financing. Templates and guides, such as the ones offered in the United States by the Small Business Administration can be used to facilitate producing a business plan. Audience Business plans may be internally or externally focused. Externally-focused plans draft goals that are important to outside stakeholders, particularly financial stakeholders. These plans typically have detailed information about the organization or t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Degradation
Environmental degradation is the deterioration of the environment through depletion of resources such as quality of air, water and soil; the destruction of ecosystems; habitat destruction; the extinction of wildlife; and pollution. It is defined as any change or disturbance to the environment perceived to be deleterious or undesirable. Environmental concerns can be defined as the negative effects of any human activity on the environment. The biological as well as the physical features of the environment are included. Some of the primary environmental challenges that are causing great worry are air pollution, water pollution, natural environment pollution, rubbish pollution, and so o Environmental degradation is one of the ten threats officially cautioned by the High-level Panel on Threats, Challenges and Change, high-level PaneI on Threats, Challenges and Change of the United Nations. The United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction defines environmental d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)