|
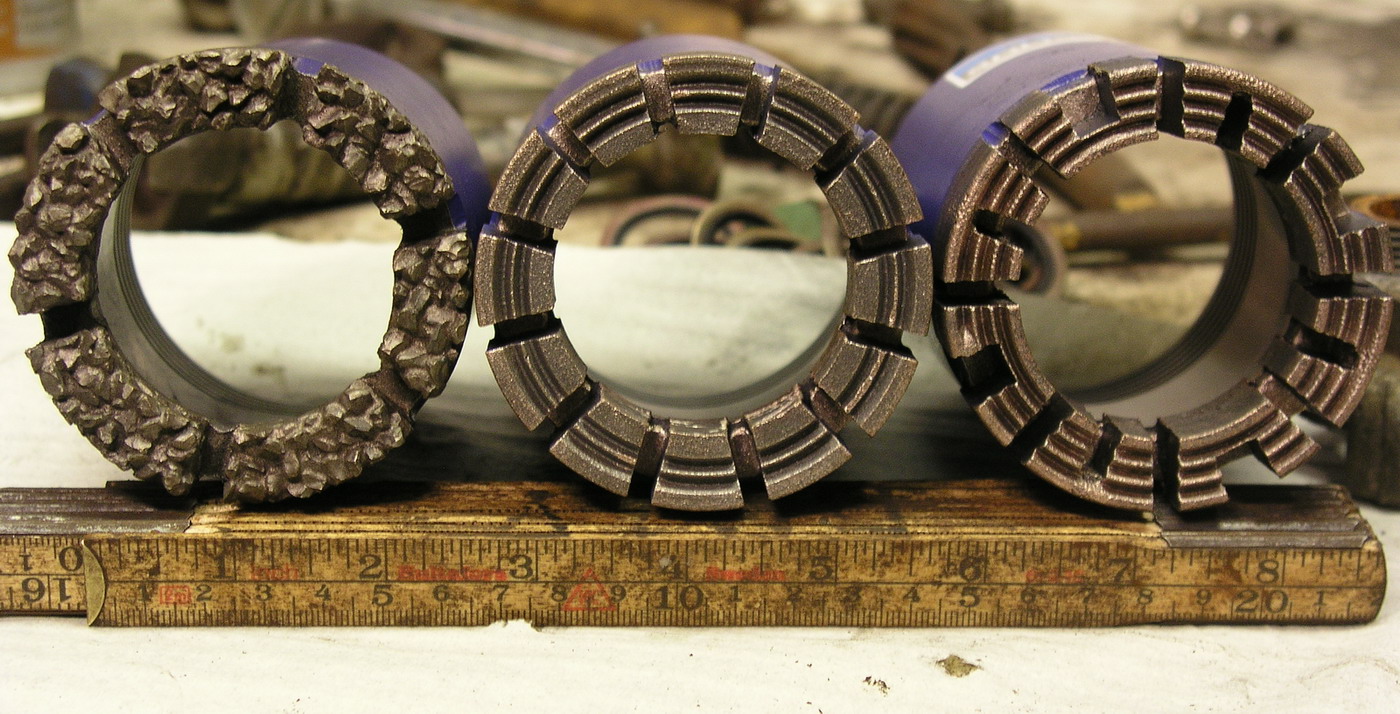
Core Drill
A modern core drill is a drill A drill is a tool used for making round holes or driving fasteners. It is fitted with a bit, either a drill or driverchuck. Hand-operated types are dramatically decreasing in popularity and cordless battery-powered ones proliferating due to ... specifically designed to remove a cylinder of material, much like a hole saw. The material left inside the drill bit is referred to as the ''core''. Core drills used in metal are called annular cutters. Core drills used for concrete and hard rock generally use industrial diamond grit as the abrasive material and may be electrical, pneumatic or hydraulic powered. Core drills are commonly water cooled, and the water also carries away the fine waste as a slurry. For drilling masonry, carbide core drills can be used, but diamond is more successful when cutting through rebar. The earliest core drills were those used by the ancient Egyptians, invented in 3000 BC. Core drills are used for many appli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Core Drill 06 2005
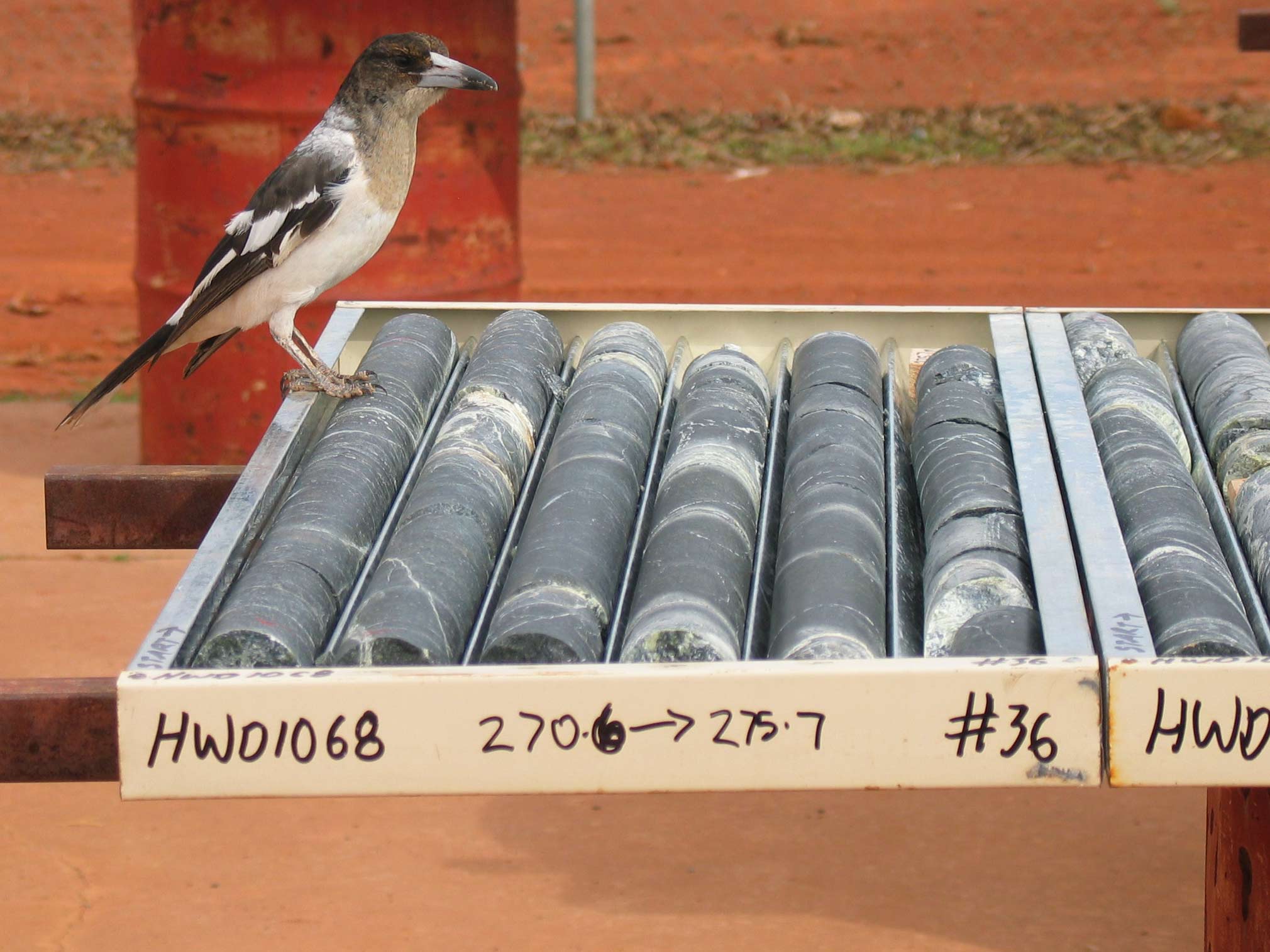
Core or cores may refer to: Science and technology * Core (anatomy), everything except the appendages * Core (manufacturing), used in casting and molding * Core (optical fiber), the signal-carrying portion of an optical fiber * Core, the central part of a fruit * Hydrophobic core, the interior zone of a protein * Nuclear reactor core, a portion containing the fuel components * Pit (nuclear weapon) or core, the fissile material in a nuclear weapon * Semiconductor intellectual property core (IP core), is a unit of design in ASIC/FPGA electronics and IC manufacturing * Atomic core, an atom with no valence electrons Geology and astrophysics * Core sample, in Earth science, a sample obtained by coring ** Ice core * Core, the central part of a galaxy; see Mass deficit * Core (anticline), the central part of an anticline or syncline * Planetary core, the center of a planet ** Earth's inner core ** Earth's outer core * Stellar core, the region of a star where nuclear fusion take ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oriented Core Goniometer Commonly Used When Logging Core
In mathematics, orientability is a property of some topological spaces such as real vector spaces, Euclidean spaces, surfaces, and more generally manifolds that allows a consistent definition of "clockwise" and "counterclockwise". A space is orientable if such a consistent definition exists. In this case, there are two possible definitions, and a choice between them is an orientation of the space. Real vector spaces, Euclidean spaces, and spheres are orientable. A space is non-orientable if "clockwise" is changed into "counterclockwise" after running through some loops in it, and coming back to the starting point. This means that a geometric shape, such as , that moves continuously along such a loop is changed into its own mirror image . A Möbius strip is an example of a non-orientable space. Various equivalent formulations of orientability can be given, depending on the desired application and level of generality. Formulations applicable to general topological manifolds of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
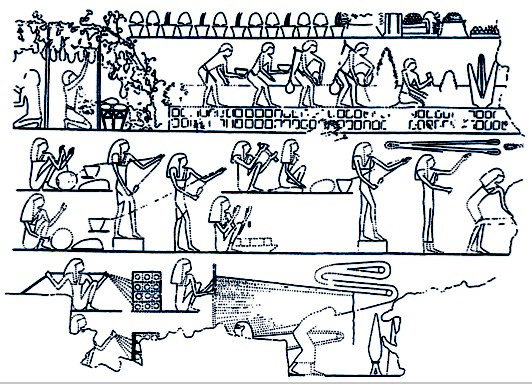
Ancient Egyptian Technology
Ancient Egyptian technology describes devices and technologies invented or used in Ancient Egypt. The Egyptians invented and used many simple machines, such as the ramp and the lever, to aid construction processes. They used rope trusses to stiffen the beam of ships. Egyptian paper, made from papyrus, and pottery were mass-produced and exported throughout the Mediterranean Basin. The wheel was used for a number of purposes, but chariots only came into use after the Second Intermediate Period. The Egyptians also played an important role in developing Mediterranean maritime technology including ships and lighthouses. Technology in Dynastic Egypt Significant advances in ancient Egypt during the dynastic period include astronomy, mathematics, and medicine. Their geometry was a necessary outgrowth of surveying to preserve the layout and ownership of fertile farmland, which was flooded annually by the Nile River. The 3,4,5 right triangle and other rules of thumb served to represe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drilling Technology
Drilling is a cutting process where a drill bit is spun to cut a hole of circular cross-section in solid materials. The drill bit is usually a rotary cutting tool, often multi-point. The bit is pressed against the work-piece and rotated at rates from hundreds to thousands of revolutions per minute. This forces the cutting edge against the work-piece, cutting off chips (swarf) from the hole as it is drilled. In rock drilling, the hole is usually not made through a circular cutting motion, though the bit is usually rotated. Instead, the hole is usually made by hammering a drill bit into the hole with quickly repeated short movements. The hammering action can be performed from outside the hole ( top-hammer drill) or within the hole ( down-the-hole drill, DTH). Drills used for horizontal drilling are called drifter drills. In rare cases, specially-shaped bits are used to cut holes of non-circular cross-section; a square cross-section is possible. Process Drilled holes are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploration Diamond Drilling
Exploration diamond drilling is used in the mining industry to probe the contents of known ore deposits and potential sites. By withdrawing a small diameter core of rock from the orebody, geologists can analyze the core by chemical assay and conduct petrologic, structural, and mineralogical studies of the rock. It is also often used in the geotechnical engineering industry for foundation testing in conjunction with soil sampling methods. History Rodolphe Leschot is often cited as being the inventor of the first core bit in 1863. Early diamond drilling opened up many new areas for mineral mining, and was related to a boom in mineral exploration in remote locations. Before the invention of the portable diamond drill, most mineral prospecting was limited to finding outcrops at the surface and hand digging. In the late 1970s, General Electric pioneered the technology of polycrystalline diamond compacts (PDCs) as a replacement for natural diamonds in drill bits. Diamond drilling Exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drilling Rig
A drilling rig is an integrated system that Drilling, drills wells, such as oil or water wells, or holes for piling and other construction purposes, into the earth's subsurface. Drilling rigs can be massive structures housing equipment used to drill water wells, oil wells, or natural gas extraction wells, or they can be small enough to be moved manually by one person and such are called auger (drill), augers. Drilling rigs can sample subsurface mineral deposits, test rock, soil and groundwater physical properties, and also can be used to install sub-surface fabrications, such as underground utilities, instrumentation, tunnels or wells. Drilling rigs can be mobile equipment mounted on trucks, tracks or trailers, or more permanent land or marine-based structures (such as oil platforms, commonly called 'offshore oil rigs' even if they don't contain a drilling rig). The term "rig" therefore generally refers to the complex equipment that is used to penetrate the surface of the Earth's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drilling Fluid
In geotechnical engineering, drilling fluid, also called drilling mud, is used to aid the drilling of boreholes into the earth. Often used while drilling oil and natural gas wells and on exploration drilling rigs, drilling fluids are also used for much simpler boreholes, such as water wells. One of the functions of drilling mud is to carry cuttings out of the hole. The three main categories of drilling fluids are: water-based muds (WBs), which can be dispersed and non-dispersed; non-aqueous muds, usually called oil-based muds (OBs); and gaseous drilling fluid, in which a wide range of gases can be used. Along with their formatives, these are used along with appropriate polymer and clay additives for drilling various oil and gas formations. The main functions of drilling fluids include providing hydrostatic pressure to prevent formation fluids from entering into the well bore, keeping the drill bit cool and clean during drilling, carrying out drill cuttings, and suspending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
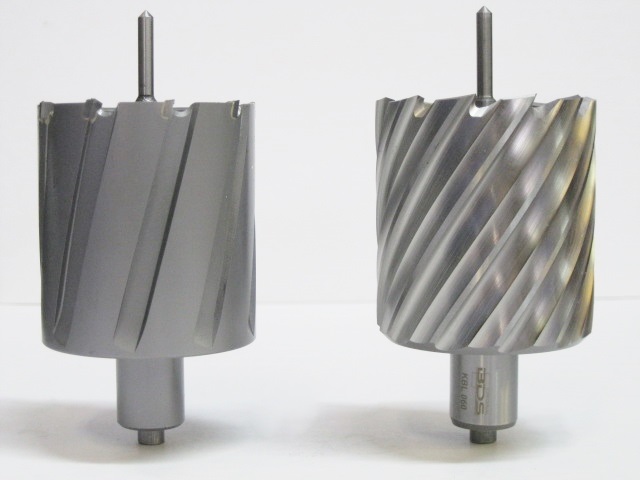
Annular Cutter
An annular cutter (also called as core drill, core cutter, broach cutter, trepanning drill, hole saw, or cup-type cutter) is form of core drill used to create holes in metal. An annular cutter, named after the annulus shape, cuts only a groove at the periphery of the hole and leaves a solid core or slug at the center. An annular cutter is a more expensive and more efficient alternative to spiral drill bits and standard hole saws. An annular cutter is similar to a hole saw but differs in geometry and material. The two most common types are high-speed steel (HSS) and tungsten carbide tipped (TCT). Like a hole saw, but unlike a spiral drill bit, an annular cutter cuts only the periphery of a hole, leaving a circular "slug" at the center. Annular cutters are available from 12 mm (1/2’’) diameter to 200 mm (7 7/8’’) and larger. Depths of 30 mm, 55 mm, 75 and 110 mm are commonly available. Annular cutters are best used with a drill press or magnetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploration Diamond Drilling
Exploration diamond drilling is used in the mining industry to probe the contents of known ore deposits and potential sites. By withdrawing a small diameter core of rock from the orebody, geologists can analyze the core by chemical assay and conduct petrologic, structural, and mineralogical studies of the rock. It is also often used in the geotechnical engineering industry for foundation testing in conjunction with soil sampling methods. History Rodolphe Leschot is often cited as being the inventor of the first core bit in 1863. Early diamond drilling opened up many new areas for mineral mining, and was related to a boom in mineral exploration in remote locations. Before the invention of the portable diamond drill, most mineral prospecting was limited to finding outcrops at the surface and hand digging. In the late 1970s, General Electric pioneered the technology of polycrystalline diamond compacts (PDCs) as a replacement for natural diamonds in drill bits. Diamond drilling Exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drill
A drill is a tool used for making round holes or driving fasteners. It is fitted with a bit, either a drill or driver chuck. Hand-operated types are dramatically decreasing in popularity and cordless battery-powered ones proliferating due to increased efficiency and ease of use. Drills are commonly used in woodworking, metalworking, construction, machine tool fabrication, construction and utility projects. Specially designed versions are made for miniature applications. History Around 35,000 BC, '' Homo sapiens'' discovered the benefits of the application of rotary tools. This would have rudimentarily consisted of a pointed rock being spun between the hands to bore a hole through another material. This led to the hand drill, a smooth stick, that was sometimes attached to flint point, and was rubbed between the palms. This was used by many ancient civilizations around the world including the Mayans. The earliest perforated artifacts, such as bone, ivory, shells, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock (geology)
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its Chemical compound, chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's outer solid layer, the Earth's crust, crust, and most of its interior, except for the liquid Earth's outer core, outer core and pockets of magma in the asthenosphere. The study of rocks involves multiple subdisciplines of geology, including petrology and mineralogy. It may be limited to rocks found on Earth, or it may include planetary geology that studies the rocks of other celestial objects. Rocks are usually grouped into three main groups: igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks are formed when magma cools in the Earth's crust, or lava cools on the ground surface or the seabed. Sedimentary rocks are formed by diagenesis and lithification of sediments, which in turn are formed by the weathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most widely used building material. Its usage worldwide, ton for ton, is twice that of steel, wood, plastics, and aluminum combined. Globally, the ready-mix concrete industry, the largest segment of the concrete market, is projected to exceed $600 billion in revenue by 2025. This widespread use results in a number of environmental impacts. Most notably, the production process for cement produces large volumes of greenhouse gas emissions, leading to net 8% of global emissions. Other environmental concerns include widespread illegal sand mining, impacts on the surrounding environment such as increased surface runoff or urban heat island effect, and potential public health implications from toxic ingredients. Significant research and developmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |