|
Coral Nursery
Coral aquaculture, also known as coral farming or coral gardening, is the cultivation of corals for commercial purposes or coral reef restoration. Aquaculture is showing promise as a tool for restoring coral reefs, which are dying off around the world.Horoszowski-Fridman, YB, Izhaki, I & Rinkevich, B (2011"Engineering of coral reef larval supply through transplantation of nursery-farmed gravid colonies"''Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology'', 399(2): 162–166.Pomeroy, RS, Parks, JE and Balboa, CM (2006"Farming the reef: is aquaculture a solution for reducing fishing pressure on coral reefs?"''Marine Policy,'' 30(2): 111–130.Rinkevich, B (2008"Management of coral reefs: We have gone wrong when neglecting active reef restoration" ''Marine pollution bulletin,'' 56(11): 1821–1824. The process protects young corals while they are most at risk of dying. Small corals are propagated in nurseries and then replanted on the reef.Ferse, SCA 2010"Poor Performance of Corals T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commercially Supplied Coral
Commerce is the large-scale organized system of activities, functions, procedures and institutions directly and indirectly related to the exchange (buying and selling) of goods and services among two or more parties within local, regional, national or international economies. More specifically, commerce is not business, but rather the part of business which facilitates the movement and distribution of finished or unfinished but valuable goods and services from the producers to the end consumers on a large scale, as opposed to the Procurement, sourcing of raw materials and manufacturing of those goods. Commerce is subtly different from trade as well, which is the final transaction, exchange or transfer of finished goods and services between a seller and an end consumer. Commerce not only includes trade as defined above, but also a series of transactions that happen between the producer and the seller with the help of the auxiliary services and means which facilitate such trade. Thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coral Aquaculture
Coral aquaculture, also known as coral farming or coral gardening, is the cultivation of corals for commercial purposes or coral reef restoration. Aquaculture is showing promise as a tool for restoring coral reefs, which are dying off around the world.Horoszowski-Fridman, YB, Izhaki, I & Rinkevich, B (2011"Engineering of coral reef larval supply through transplantation of nursery-farmed gravid colonies"''Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology'', 399(2): 162–166.Pomeroy, RS, Parks, JE and Balboa, CM (2006"Farming the reef: is aquaculture a solution for reducing fishing pressure on coral reefs?"''Marine Policy,'' 30(2): 111–130.Rinkevich, B (2008"Management of coral reefs: We have gone wrong when neglecting active reef restoration" ''Marine pollution bulletin,'' 56(11): 1821–1824. The process protects young corals while they are most at risk of dying. Small corals are propagated in nurseries and then replanted on the reef.Ferse, SCA 2010"Poor Performance of Corals Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
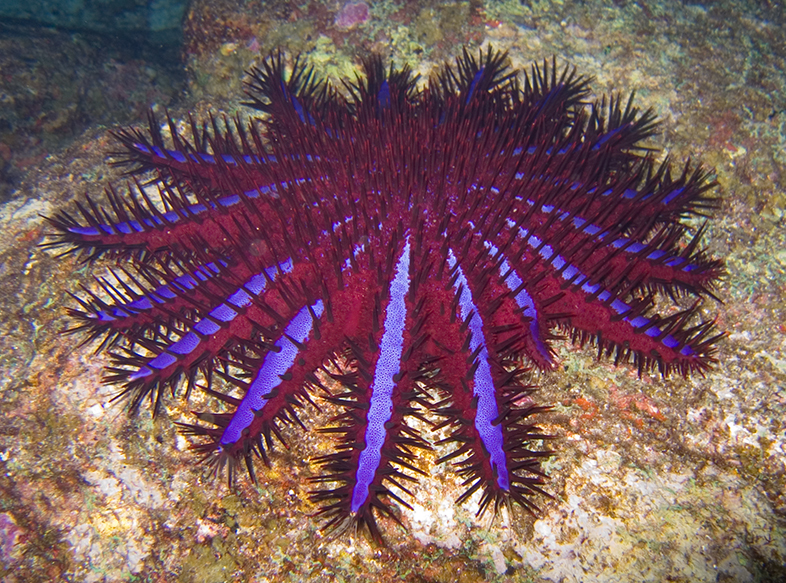
Crown Of Thorns Starfish
The crown-of-thorns starfish (frequently abbreviated to COTS), ''Acanthaster planci'', is a large starfish that preys upon hard, or stony, coral polyps (Scleractinia). The crown-of-thorns starfish receives its name from venomous thorn-like spines that cover its upper surface, resembling the biblical crown of thorns. It is one of the largest starfish in the world. ''A. planci'' has a very wide Indo-Pacific distribution. It is perhaps most common around Australia, but can occur at tropical and subtropical latitudes from the Red Sea and the East African coast across the Indian Ocean, and across the Pacific Ocean to the west coast of Central America. It occurs where coral reefs or hard coral communities occur in the region. Description The body form of the crown-of-thorns starfish is fundamentally the same as that of a typical starfish, with a central disk and radiating arms. Its special traits, however, include being disc-shaped, multiple-armed, flexible, prehensile, and heavily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an anticyclone). Cyclones are characterized by inward-spiraling winds that rotate about a zone of low pressure. The largest low-pressure systems are polar vortices and extratropical cyclones of the largest scale (the synoptic scale). Warm-core cyclones such as tropical cyclones and subtropical cyclones also lie within the synoptic scale. Mesocyclones, tornadoes, and dust devils lie within smaller mesoscale. Upper level cyclones can exist without the presence of a surface low, and can pinch off from the base of the tropical upper tropospheric trough during the summer months in the Northern Hemisphere. Cyclones have also been seen on extraterrestrial planets, such as Mars, Jupiter, and Neptune. Cyclogenesis is the process of cyclone formation and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foundation Species
In ecology, the foundation species are species that have a strong role in structuring a community. A foundation species can occupy any trophic level in a food web (i.e., they can be primary producers, herbivores or predators). The term was coined by Paul K. Dayton in 1972,Dayton, P. K. 1972Toward an understanding of community resilience and the potential effects of enrichments to the benthos at McMurdo Sound, Antarctica pp. 81–96 in Proceedings of the Colloquium on Conservation Problems Allen Press, Lawrence, Kansas. who applied it to certain members of marine invertebrate and algae communities. It was clear from studies in several locations that there were a small handful of species whose activities had a disproportionate effect on the rest of the marine community and they were therefore key to the resilience of the community. Dayton’s view was that focusing on foundation species would allow for a simplified approach to more rapidly understand how a community as a whole would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orange Cup Coral
Orange cup coral (''Tubastraea coccinea'') belongs to a group of corals known as large-polyp stony corals. This non-reef building coral extends beautiful translucent tentacles at night. ''Tubastraea coccinea'' is heterotrophic and does not contain zooxanthellae in its tissues as many tropical corals do, allowing it to grow in complete darkness as long as it can capture enough food. Habitat ''Tubastraea coccinea'' inhabits shaded vertical surfaces and caverns down to huge depths. Orange-cup-corals are also found in very cold water throughout the world. Orange-cup corals often dominate tropical habitats not occupied by other coral species, such as wrecks and cryptic reef habitats. They also colonize artificial structures, but experiments have demonstrated similar preferences for granite, cement, steel and tile. In Brazil, they are most abundant in the shallow sub-tidal zone at shallow depths between 0m and 3m.De Paula & Creed, 2004, 2005, Creed 2006 Invasive introduction and range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) that are unable to propel themselves against a Ocean current, current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalves, fish and whales. Marine plankton include bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa and drifting or floating animals that inhabit the saltwater of oceans and the brackish waters of estuaries. Freshwater plankton are similar to marine plankton, but are found in the freshwaters of lakes and rivers. Plankton are usually thought of as inhabiting water, but there are also airborne versions, the aeroplankton, that live part of their lives drifting in the atmosphere. These include plant spores, pollen and wind-scattered seeds, as well as microorganisms swept into the air from terrestrial dust storms and oceanic plankton swept into the air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbiosis
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasitic. The organisms, each termed a symbiont, must be of different species. In 1879, Heinrich Anton de Bary defined it as "the living together of unlike organisms". The term was subject to a century-long debate about whether it should specifically denote mutualism, as in lichens. Biologists have now abandoned that restriction. Symbiosis can be obligatory, which means that one or more of the symbionts depend on each other for survival, or facultative (optional), when they can generally live independently. Symbiosis is also classified by physical attachment. When symbionts form a single body it is called conjunctive symbiosis, while all other arrangements are called disjunctive symbiosis."symbiosis." Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
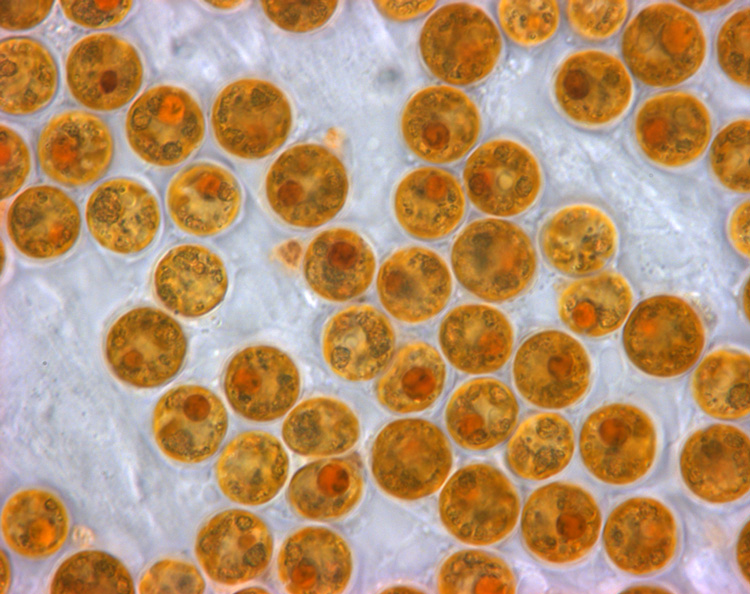
Zooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus ''Symbiodinium'', but some are known from the genus '' Amphidinium'', and other taxa, as yet unidentified, may have similar endosymbiont affinities. The true ''Zooxanthella'' K.brandt is a mutualist of the radiolarian ''Collozoum inerme'' (Joh.Müll., 1856) and systematically placed in Peridiniales. Another group of unicellular eukaryotes that partake in similar endosymbiotic relationships in both marine and freshwater habitats are green algae zoochlorellae. Zooxanthellae are photosynthetic organisms, which contain chlorophyll a and chlorophyll c, as well as the dinoflagellate pigments peridinin and diadinoxanthin. These provide the yellowish and brownish colours typical of many of the host species. During the day, they provide their host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trophic State Index
The Trophic State Index (TSI) is a classification system designed to rate water bodies based on the amount of biological productivity they sustain. Although the term "trophic index" is commonly applied to lakes, any surface water body may be indexed. The TSI of a water body is rated on a scale from zero to one hundred. Under the TSI scale, water bodies may be defined as: * oligotrophic (TSI 0–40, having the least amount of biological productivity, "good" water quality); * mesotrophic (TSI 40–60, having a moderate level of biological productivity, "fair" water quality); or * eutrophic to hypereutrophic (TSI 60–100, having the highest amount of biological productivity, "poor" water quality). The quantities of nitrogen, phosphorus, and other biologically useful nutrients are the primary determinants of a water body's TSI. Nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus tend to be limiting resources in standing water bodies, so increased concentrations tend to result in increased p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as ''Chlorella,'' ''Prototheca'' and the diatoms, to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelp, a large brown alga which may grow up to in length. Most are aquatic and autotrophic (they generate food internally) and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem and phloem that are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds, while the most complex freshwater forms are the ''Charophyta'', a division of green algae which includes, for example, ''Spirogyra'' and stoneworts. No definition of algae is generally accepted. One definition is that algae "have chlorophyll ''a'' as their primary photosynthetic pigment and lack a sterile covering of cells around thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collector Urchin
''Tripneustes gratilla'', the collector urchin, is a species of sea urchin. Collector urchins are found at depths of in the waters of the Indo-Pacific, Hawaii, the Red Sea, and The Bahamas. They can reach in size. Description Collector urchins are dark in color, usually bluish-purple with white spines. The pedicles are also white, with a dark or black base. Individuals found at Green Island had orange-tipped spines. The spines of some specimens are wholly orange, while those of others are only orange-tipped or completely white. This color disappears when the individual dies or is taken out of the ocean, and is difficult to preserve. Collector urchins reach in size. Debris tends to "collect" on these urchins, hence their name. Unlike some other sea urchins, collector urchins graze continually, day and night. They graze near the substrate, and their diet includes algae, periphyton, and seagrass. Most collector urchins feed on seagrass fronds; this has an ecological impact v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |