|
Cooperative MIMO
In radio, cooperative multiple-input multiple-output (cooperative MIMO, CO-MIMO) is a technology that can effectively exploit the spatial domain of mobile fading channels to bring significant performance improvements to wireless communication systems. It is also called network MIMO, distributed MIMO, virtual MIMO, and virtual antenna arrays. Conventional MIMO systems, known as point-to-point MIMO or collocated MIMO, require both the transmitter and receiver of a communication link to be equipped with multiple antennas. While MIMO has become an essential element of wireless communication standards, including IEEE 802.11n (Wi-Fi), IEEE 802.11ac (Wi-Fi), HSPA+ (3G), WiMAX (4G), and Long-Term Evolution (4G), many wireless devices cannot support multiple antennas due to size, cost, and/or hardware limitations. More importantly, the separation between antennas on a mobile device and even on fixed radio platforms is often insufficient to allow meaningful performance gains. Furthermore, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fading
In wireless communications, fading is variation of the attenuation of a signal with various variables. These variables include time, geographical position, and radio frequency. Fading is often modeled as a random process. A fading channel is a communication channel that experiences fading. In wireless systems, fading may either be due to multipath propagation, referred to as multipath-induced fading, weather (particularly rain), or shadowing from obstacles affecting the wave propagation, sometimes referred to as shadow fading. Key concepts The presence of reflectors in the environment surrounding a transmitter and receiver create multiple paths that a transmitted signal can traverse. As a result, the receiver sees the superposition of multiple copies of the transmitted signal, each traversing a different path. Each signal copy will experience differences in attenuation, delay and phase shift while traveling from the source to the receiver. This can result in either construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Network Coding
In computer networking, linear network coding is a program in which intermediate nodes transmit data from source nodes to sink nodes by means of linear combinations. Linear network coding may be used to improve a network's throughput, efficiency, and scalability, as well as reducing attacks and eavesdropping. The nodes of a network take ''several'' packets and combine for transmission. This process may be used to attain the maximum possible information flow in a network. It has been proven that, theoretically, linear coding is enough to achieve the upper bound in multicast problems with one source. However linear coding is not sufficient in general; even for more general versions of linearity such as convolutional coding and filter-bank coding. Finding optimal coding solutions for general network problems with arbitrary demands remains an open problem. Encoding and decoding In a linear network coding problem, a group of nodes P are involved in moving the data from S source n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaussian Elimination
In mathematics, Gaussian elimination, also known as row reduction, is an algorithm for solving systems of linear equations. It consists of a sequence of operations performed on the corresponding matrix of coefficients. This method can also be used to compute the rank of a matrix, the determinant of a square matrix, and the inverse of an invertible matrix. The method is named after Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777–1855) although some special cases of the method—albeit presented without proof—were known to Chinese mathematicians as early as circa 179 AD. To perform row reduction on a matrix, one uses a sequence of elementary row operations to modify the matrix until the lower left-hand corner of the matrix is filled with zeros, as much as possible. There are three types of elementary row operations: * Swapping two rows, * Multiplying a row by a nonzero number, * Adding a multiple of one row to another row. (subtraction can be achieved by multiplying one row with -1 and adding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimum Mean Square Error
In statistics and signal processing, a minimum mean square error (MMSE) estimator is an estimation method which minimizes the mean square error (MSE), which is a common measure of estimator quality, of the fitted values of a dependent variable. In the Bayesian setting, the term MMSE more specifically refers to estimation with quadratic loss function. In such case, the MMSE estimator is given by the posterior mean of the parameter to be estimated. Since the posterior mean is cumbersome to calculate, the form of the MMSE estimator is usually constrained to be within a certain class of functions. Linear MMSE estimators are a popular choice since they are easy to use, easy to calculate, and very versatile. It has given rise to many popular estimators such as the Wiener–Kolmogorov filter and Kalman filter. Motivation The term MMSE more specifically refers to estimation in a Bayesian setting with quadratic cost function. The basic idea behind the Bayesian approach to estimation stems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zero-forcing Precoding
Zero-forcing (or null-steering) precoding is a method of spatial signal processing by which a multiple antenna transmitter can null the multiuser interference in a multi-user MIMO wireless communication system. When the channel state information is perfectly known at the transmitter, the zero-forcing precoder is given by the pseudo-inverse of the channel matrix. Mathematical description In a multiple antenna downlink system which comprises N_t transmit antenna access points and K single receive antenna users, such that K \leq N_t, the received signal of user k is described as :y_k = \mathbf_k^T \mathbf + n_k, \quad k=1,2, \ldots, K where \mathbf = \sum_^K \sqrt s_i \mathbf_i is the N_t \times 1 vector of transmitted symbols, n_k is the noise signal, \mathbf_k is the N_t \times 1 channel vector and \mathbf_i is some N_t \times 1 linear precoding vector. Here (\cdot)^T is the matrix transpose, \sqrt is the square root of transmit power, and s_i is the message signal with zero mean an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moore's Law
Moore's law is the observation that the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empirical relationship linked to gains from experience in production. The observation is named after Gordon Moore, the co-founder of Fairchild Semiconductor and Intel (and former CEO of the latter), who in 1965 posited a doubling every year in the number of components per integrated circuit, and projected this rate of growth would continue for at least another decade. In 1975, looking forward to the next decade, he revised the forecast to doubling every two years, a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 41%. While Moore did not use empirical evidence in forecasting that the historical trend would continue, his prediction held since 1975 and has since become known as a "law". Moore's prediction has been used in the semiconductor industry to g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
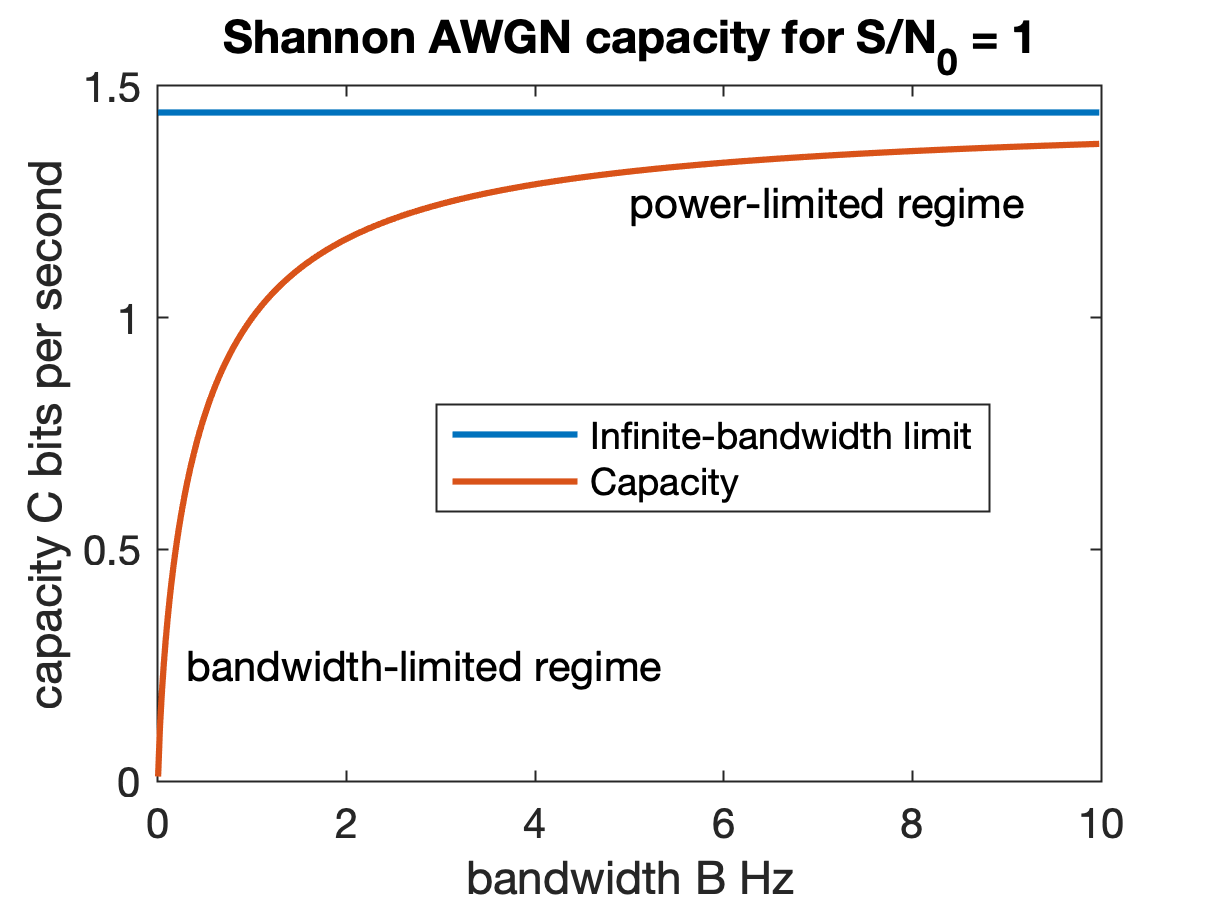
Shannon–Hartley Theorem
In information theory, the Shannon–Hartley theorem tells the maximum rate at which information can be transmitted over a communications channel of a specified bandwidth in the presence of noise. It is an application of the noisy-channel coding theorem to the archetypal case of a continuous-time analog communications channel subject to Gaussian noise. The theorem establishes Shannon's channel capacity for such a communication link, a bound on the maximum amount of error-free information per time unit that can be transmitted with a specified bandwidth in the presence of the noise interference, assuming that the signal power is bounded, and that the Gaussian noise process is characterized by a known power or power spectral density. The law is named after Claude Shannon and Ralph Hartley. Statement of the theorem The Shannon–Hartley theorem states the channel capacity C, meaning the theoretical tightest upper bound on the information rate of data that can be communicated at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Radio Head
A remote radio head (RRH), also called a remote radio unit (RRU) in wireless networks, is a remote radio transceiver that connects to an operator radio control panel via electrical or wireless interface. When used to describe aircraft radio cockpit radio systems, the control panel is often called the radio head. In wireless system technologies such as GSM, CDMA, UMTS, LTE the radio equipment is remote to the BTS/NodeB/eNodeB. The equipment is used to extend the coverage of a BTS/NodeB/eNodeB in challenging environments such as rural areas or tunnels. They are generally connected to the BTS/NodeB/eNodeB via a fiber optic cable using Common Public Radio Interface protocols. RRHs have become one of the most important subsystems of today's new distributed base stations. The RRH contains the base station's RF circuitry plus analog-to-digital/digital-to-analog converters and up/down converters. RRHs also have operation and management processing capabilities and a standardized optical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-RAN
C-RAN (Cloud-RAN), also referred to as Centralized-RAN, is an architecture for cellular networks. C-RAN is a centralized, cloud computing-based architecture for radio access networks that supports 2G, 3G, 4G and future wireless communication standards. Its name comes from the four 'C's in the main characteristics of C-RAN system, "Clean, Centralized processing, Collaborative radio, and a real-time Cloud Radio Access Network". Background Traditional cellular, or Radio Access Networks (RAN), consist of many stand-alone base stations (BTS). Each BTS covers a small area, whereas a group BTS provides coverage over a continuous area. Each BTS processes and transmits its own signal to and from the mobile terminal, and forwards the data payload to and from the mobile terminal and out to the core network via the backhaul. Each BTS has its own cooling, back haul transportation, backup battery, monitoring system, and so on. Because of limited spectral resources, network operators 'reuse' th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Computing
A distributed system is a system whose components are located on different computer network, networked computers, which communicate and coordinate their actions by message passing, passing messages to one another from any system. Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems. The components of a distributed system interact with one another in order to achieve a common goal. Three significant challenges of distributed systems are: maintaining concurrency of components, overcoming the clock synchronization, lack of a global clock, and managing the independent failure of components. When a component of one system fails, the entire system does not fail. Examples of distributed systems vary from service-oriented architecture, SOA-based systems to massively multiplayer online games to peer-to-peer, peer-to-peer applications. A computer program that runs within a distributed system is called a distributed program, and ''distributed programming' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software-defined Radio
Software-defined radio (SDR) is a radio communication system where components that have been traditionally implemented in analog hardware (e.g. mixers, filters, amplifiers, modulators/demodulators, detectors, etc.) are instead implemented by means of software on a personal computer or embedded system. While the concept of SDR is not new, the rapidly evolving capabilities of digital electronics render practical many processes which were once only theoretically possible. A basic SDR system may consist of a personal computer equipped with a sound card, or other analog-to-digital converter, preceded by some form of RF front end. Significant amounts of signal processing are handed over to the general-purpose processor, rather than being done in special-purpose hardware (electronic circuits). Such a design produces a radio which can receive and transmit widely different radio protocols (sometimes referred to as waveforms) based solely on the software used. Software radios have signif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooperative Diversity
Cooperative diversity is a cooperative multiple antenna technique for improving or maximising total network channel capacities for any given set of bandwidths which exploits user diversity by decoding the combined signal of the relayed signal and the direct signal in wireless multihop networks. A conventional single hop system uses direct transmission where a receiver decodes the information only based on the direct signal while regarding the relayed signal as interference, whereas the cooperative diversity considers the other signal as contribution. That is, cooperative diversity decodes the information from the combination of two signals. Hence, it can be seen that cooperative diversity is an antenna diversity that uses distributed antennas belonging to each node in a wireless network. Note that user cooperation is another definition of cooperative diversity. ''User cooperation'' considers an additional fact that each user relays the other user's signal while cooperative diversit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)