|
Contour Plot
A contour line (also isoline, isopleth, or isarithm) of a function of two variables is a curve along which the function has a constant value, so that the curve joins points of equal value. It is a plane section of the three-dimensional graph of the function f(x,y) parallel to the (x,y)-plane. More generally, a contour line for a function of two variables is a curve connecting points where the function has the same particular value. In cartography, a contour line (often just called a "contour") joins points of equal elevation (height) above a given level, such as mean sea level. A contour map is a map illustrated with contour lines, for example a topographic map, which thus shows valleys and hills, and the steepness or gentleness of slopes. The contour interval of a contour map is the difference in elevation between successive contour lines. The gradient of the function is always perpendicular to the contour lines. When the lines are close together the magnitude of the gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halley Compass Variations 1702
Halley may refer to: Science * Halley's Comet, officially designated 1P/Halley, a comet that becomes visible from Earth every 75-76 years * Halley (lunar crater), a lunar crater named after Edmond Halley * Halley (Martian crater), a Martian crater named after Edmond Halley * Halley Research Station, a British research facility on the Brunt Ice Shelf floating on the Weddell Sea in Antarctica Entertainment * Halley (nightclub), a defunct Argentine nightclub * "Halley" (song), the Turkish entrant to the Eurovision Song Contest 1986 * "Halley" (film), a 2012 Mexican horror movie People * Halley (surname), multiple people ** Edmond Halley (1656–1742), English astronomer * Halley (given name), multiple people See also * Haley (other) * Halle (other) * Hailey (other) *Hayley (other) Hayley may refer to: ;People * Hayley (list of people with this given name) * Hayley (surname) (list of people with this surname) ;Places * Hayley Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
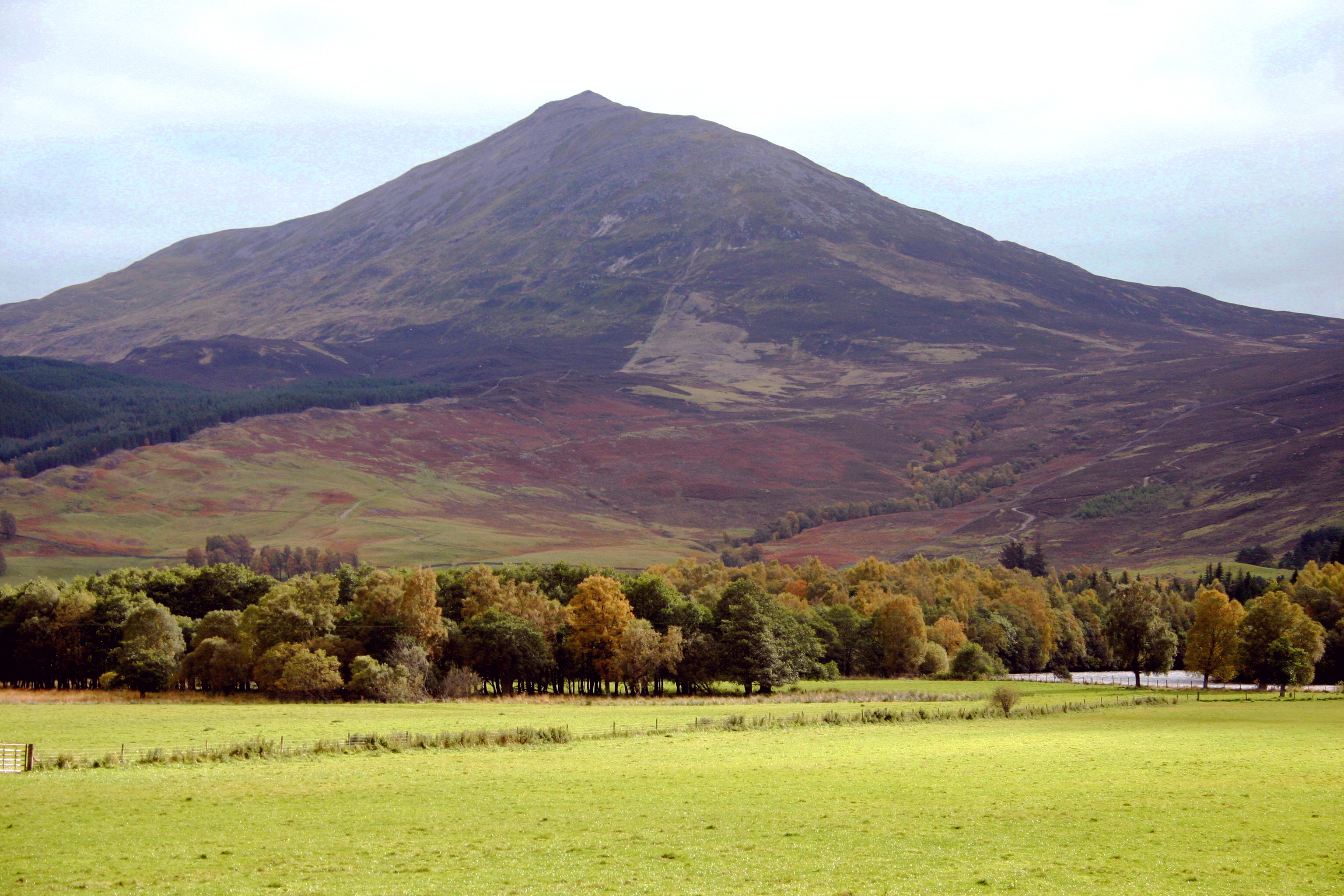
Schiehallion Experiment
The Schiehallion experiment was an 18th-century experiment to determine the mean density of the Earth. Funded by a grant from the Royal Society, it was conducted in the summer of 1774 around the Scottish mountain of Schiehallion, Perthshire. The experiment involved measuring the tiny deflection of the vertical due to the gravitational attraction of a nearby mountain. Schiehallion was considered the ideal location after a search for candidate mountains, thanks to its isolation and almost symmetrical shape. The experiment had previously been considered, but rejected, by Isaac Newton as a practical demonstration of his theory of gravitation; however, a team of scientists, notably Nevil Maskelyne, the Astronomer Royal, was convinced that the effect would be detectable and undertook to conduct the experiment. The deflection angle depended on the relative densities and volumes of the Earth and the mountain: if the density and volume of Schiehallion could be ascertained, then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Hutton
Charles Hutton FRS FRSE LLD (14 August 1737 – 27 January 1823) was a British mathematician and surveyor. He was professor of mathematics at the Royal Military Academy, Woolwich from 1773 to 1807. He is remembered for his calculation of the density of the earth from Nevil Maskelyne's measurements collected during the Schiehallion experiment. Life Hutton was born on Percy Street in Newcastle upon Tyne in the north of England, the son of a superintendent of mines, who died when he was still very young. He was educated at a school at Jesmond, kept by Mr Ivison, an Anglican clergyman. There is reason to believe, on the evidence of two pay-bills, that for a short time in 1755 and 1756 Hutton worked in the colliery at Old Long Benton. Following Ivison's promotion to a living, Hutton took over the Jesmond school, which, in consequence of his increasing number of pupils, he relocated to nearby Stotes Hall. While he taught during the day at Stotes Hall, which overlooked Jesmon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Modena And Reggio
The Duchy of Modena and Reggio ( Emilian: ''Duchêt ed Mòdna e Rèz'', it, Ducato di Modena e Reggio, la, Ducatus Mutinae et Regii) was an Italian state created in 1452 located in Northwestern Italy, in the present day region of Emilia-Romagna. It was ruled since its establishment by the noble House of Este, and since 1814 by the Austria-Este branch of the family. The Este dynasty was a great sponsor of the arts, making the Duchy a cultural reference during the Renaissance and Baroque periods. House of Este In 1452 Emperor Frederick III offered the duchy to Borso d'Este, whose family had ruled the city of Modena and nearby Reggio Emilia for centuries. Borso in 1450 had also succeeded his brother as margrave in the adjacent Papal Duchy of Ferrara, where he received the ducal title in 1471. The Este lands on the southern border of the Holy Roman Empire with the Papal States formed a stabilizing buffer state in the interest of both. The first Este dukes ruled well and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" ( Cotentinais) or (Jèrriais), ( Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kanaal, "The Channel"; german: Ärmelkanal, "Sleeve Channel" (French: ''la Manche;'' also called the British Channel or simply the Channel) is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates Southern England from northern France. It links to the southern part of the North Sea by the Strait of Dover at its northeastern end. It is the busiest shipping area in the world. It is about long and varies in width from at its widest to at its narrowest in the Strait of Dover."English Channel". ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 2004. It is the smallest of the shallow seas around the continental shelf of Europe, covering an area of some . The Channel was a key factor in Britain becoming a naval superpower and has been utilised by Britain as a natural d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippe Buache
Philippe Buache (born La Neuville-au-Pont, 7 February 1700; died Paris, 24 January 1773) was a French geographer, known for inventing a new system of geography and popularizing this field. Life and work Buache was trained under the geographer Guillaume Delisle, whose daughter he married, and whom he succeeded in the Académie des sciences in 1730. Buache was nominated first geographer of the king in 1729. He established the division of the world by seas and river systems. He believed in a southern continent, an hypothesis which was confirmed by later discoveries. In 1754, he published an "Atlas physique." He also wrote several pamphlets. His nephew, Jean Nicolas Buache (born La Neuville-au-Pont, 15 February 1741; died Paris Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fathom
A fathom is a unit of length in the imperial and the U.S. customary systems equal to , used especially for measuring the depth of water. The fathom is neither an International Standard (SI) unit, nor an internationally-accepted non-SI unit. Historically, however, it is the most frequently employed maritime measure of depth in the English-speaking world. There are two yards (6 feet) in an imperial fathom. Originally the span of a man's outstretched arms, the size of a fathom has varied slightly depending on whether it was defined as a thousandth of an (Admiralty) nautical mile or as a multiple of the imperial yard. Formerly, the term was used for any of several units of length varying around . Name The name (pronounced ) derives from the Old English word ''fæðm'', cognate to the Danish (via the Vikings) word "favn" meaning embracing arms or a pair of outstretched arms. Cognate maybe also via the Old High German word "fadum" of the same meaning.''Oxford English Dictio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
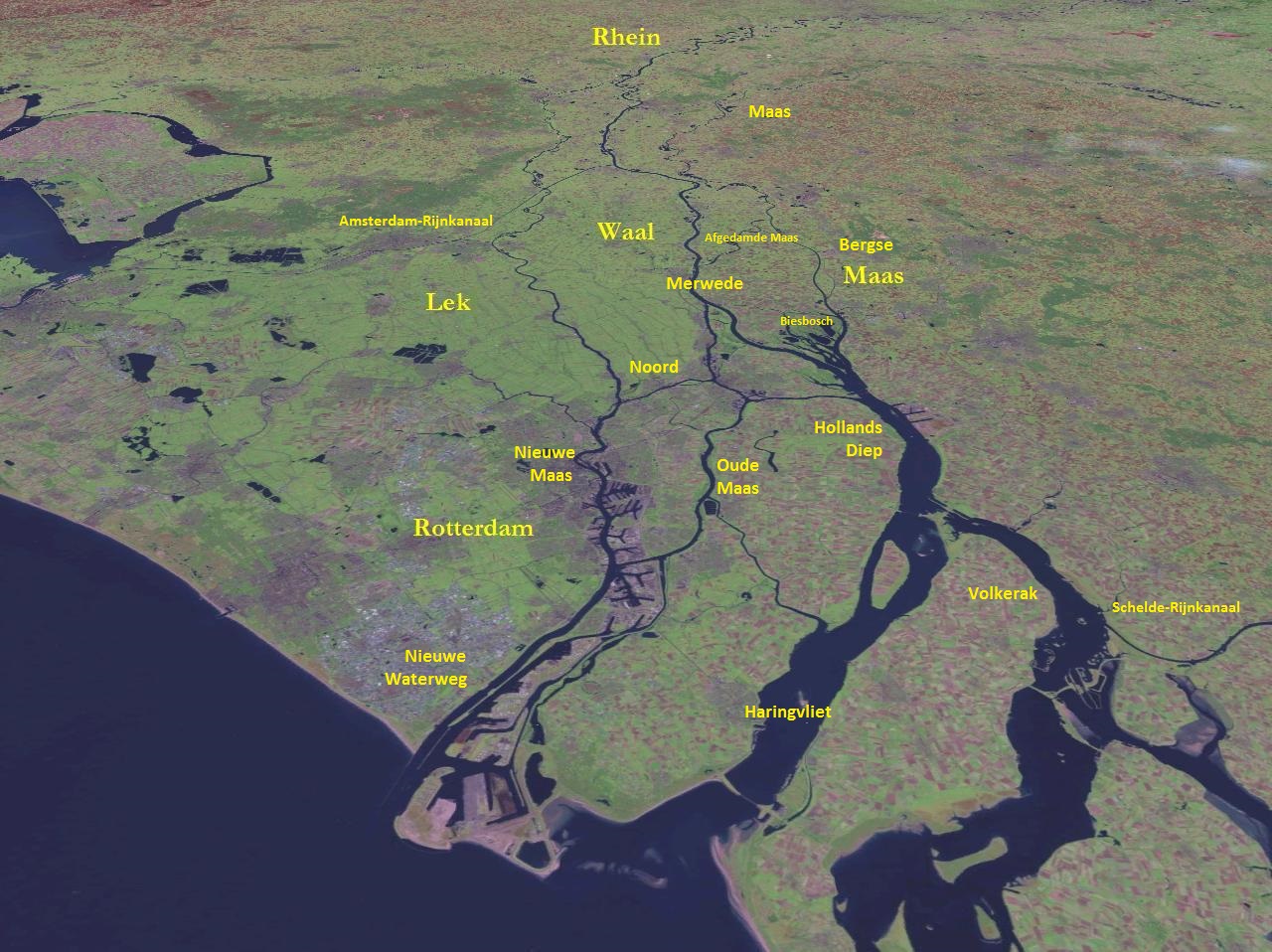
Merwede
The Merwede () etymology uncertain, possibly derived from the ancient Dutch ''Merwe'' or ''Merowe'', a word meaning "wide water") is the name of several connected stretches of river in the Netherlands, between the cities of Woudrichem, Dordrecht and Papendrecht. The river is part of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and is mostly fed by the river Rhine. At first, a disconnected branch of the Meuse joins the Waal at Woudrichem to form the Boven Merwede (Upper Merwede). A few kilometers downstream it splits into the Beneden Merwede (Lower Merwede) on the right and the Nieuwe Merwede (New Merwede) on the left. All these rivers are tidal. The Nieuwe Merwede joins the Bergse Maas near Lage Zwaluwe to form the Hollands Diep estuary, and separates the Island of Dordrecht from the Biesbosch National Park. The Beneden Merwede splits into the Noord River and Oude Maas near Papendrecht. History In medieval times the name Merwede (or "Merwe" in Middle Dutch) was the name of a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolaas Kruik
Nicolaas Samuelszoon Kruik ( la, Nicolaus Samuelis Cruquius; 2 December 1678, West-Vlieland – 5 February 1754, Spaarndam), also known as Klaas Kruik and Nicolaes Krukius, was a Dutch land surveyor, cartographer, astronomer and weatherman. He is commemorated by the Museum De Cruquius. He was a perfectionist who liked to measure things and he calculated temperature measurements in Fahrenheit from 1706 to 1734. His historical calculations are still used today by the KNMI, the Dutch meteorological institute. He not only measured weather changes in wind speed, rainfall, air pressure, temperature, and humidity, but also measured sea level. His method of visualising planes of water level to illustrate contours of depth ( isobaths) in his map of the Merwede (1728) was the first of its kind. He was an advocate of pumping out the Haarlemmermeer (Haarlem lake), which was done a century after his death. Biography He became a surveyor at the age of 19 and began to draw maps, a lucrativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmond Halley
Edmond (or Edmund) Halley (; – ) was an English astronomer, mathematician and physicist. He was the second Astronomer Royal in Britain, succeeding John Flamsteed in 1720. From an observatory he constructed on Saint Helena in 1676–77, Halley catalogued the southern celestial hemisphere and recorded a transit of Mercury across the Sun. He realised that a similar transit of Venus could be used to determine the distances between Earth, Venus, and the Sun. Upon his return to England, he was made a fellow of the Royal Society, and with the help of King Charles II of England, Charles II, was granted a master's degree from University of Oxford, Oxford. Halley encouraged and helped fund the publication of Isaac Newton's influential ''Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica'' (1687). From observations Halley made in September 1682, he used Newton's laws of motion to compute the periodicity of Halley's Comet in his 1705 ''Synopsis of the Astronomy of Comets''. It was named afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch (ethnic Group)
The Dutch ( Dutch: ) are an ethnic group and nation native to the Netherlands. They share a common history and culture and speak the Dutch language. Dutch people and their descendants are found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in Aruba, Suriname, Guyana, Curaçao, Argentina, Brazil, Canada,Based on Statistics Canada, Canada 2001 Censusbr>Linkto Canadian statistics. Australia, South Africa, New Zealand and the United States.According tFactfinder.census.gov The Low Countries were situated around the border of France and the Holy Roman Empire, forming a part of their respective peripheries and the various territories of which they consisted had become virtually autonomous by the 13th century. Under the Habsburgs, the Netherlands were organised into a single administrative unit, and in the 16th and 17th centuries the Northern Netherlands gained independence from Spain as the Dutch Republic. The high degree of urbanization characteristic of Dutch society was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |