|
Contingent Valuation
Contingent valuation is a survey-based economic technique for the valuation of non- market resources, such as environmental preservation or the impact of externalities like pollution. While these resources do give people utility, certain aspects of them do not have a market price as they are not directly sold – for example, people receive benefit from a beautiful view of a mountain, but it would be tough to value using price-based models. Contingent valuation surveys are one technique which is used to measure these aspects. Contingent valuation is often referred to as a ''stated preference'' model, in contrast to a price-based ''revealed preference'' model. Both models are utility-based. Typically the survey asks how much money people would be willing to pay (or willing to accept) to maintain the existence of (or be compensated for the loss of) an environmental feature, such as biodiversity. History Contingent valuation surveys were first proposed in theory by S.V. Ciriacy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Survey
Survey methodology is "the study of survey methods". As a field of applied statistics concentrating on human-research surveys, survey methodology studies the sampling of individual units from a population and associated techniques of survey data collection, such as questionnaire construction and methods for improving the number and accuracy of responses to surveys. Survey methodology targets instruments or procedures that ask one or more questions that may or may not be answered. Researchers carry out statistical surveys with a view towards making statistical inferences about the population being studied; such inferences depend strongly on the survey questions used. Polls about public opinion, public-health surveys, market-research surveys, government surveys and censuses all exemplify quantitative research that uses survey methodology to answer questions about a population. Although censuses do not include a "sample", they do include other aspects of survey methodology, li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince William Sound
Prince William Sound (Sugpiaq: ''Suungaaciq'') is a sound of the Gulf of Alaska on the south coast of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is located on the east side of the Kenai Peninsula. Its largest port is Valdez, at the southern terminus of the Trans-Alaska Pipeline System. Other settlements on the sound, which contains numerous small islands, include Cordova and Whittier plus the Alaska native villages of Chenega and Tatitlek. History James Cook entered Prince William Sound in 1778 and initially named it Sandwich Sound, after his patron the Earl of Sandwich. Later that year, the Sound was named to honour George III's third son Prince William Henry, then aged 13 and serving as a midshipman in the Royal Navy. In 1790, the Spanish explorer Salvador Fidalgo entered the sound, naming many of its features. Some places in the sound still bear the names given by Fidalgo, as Port Valdez, Port Gravina or Cordova. The explorer landed on the actual site of Cordova and took possession of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centre For Agriculture And Bioscience International
CABI (legally CAB International, formerly Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux) is a nonprofit intergovernmental development and information organisation focusing primarily on agricultural and environmental issues in the developing world, and the creation, curation, and dissemination of scientific knowledge. Overview CABI is an international not-for-profit organisation. Their work is delivered through teams of CABI scientists and key partners working in over 40 countries across the world. CABI states its mission as "improving people’s lives worldwide by solving problems in agriculture and the environment". These problems include loss of crops caused by pests and diseases, invasive weeds and pests that damage farm production and biodiversity, and lack of global access to scientific research. Funding CABI states that only 3% of its revenue comes from core funding. Donors listed in the company's 2014 financial report include the UK's Department for International Development ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallingford, Oxfordshire
Wallingford () is a historic market town and civil parish located between Oxford and Reading on the River Thames in England. Although belonging to the historic county of Berkshire, it is within the ceremonial county of Oxfordshire for administrative purposes (since 1974) as a result of the 1972 Local Government Act. Wallingford is north of Reading, south of Oxford and north west of Henley-on-Thames. The town's population was 11,600 in the 2011 census. The town has played an important role in English history starting with the surrender of Stigand to William the Conqueror in 1066, which led to his taking the throne and the creation of Wallingford Castle. The castle and the town enjoyed royal status and flourished for much of the Middle Ages. The Treaty of Wallingford, which ended a civil war known as The Anarchy between King Stephen and Empress Matilda, was signed there. The town then entered a period of decline after the arrival of the Black Death and falling out of favou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boston, MA
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the capital city, state capital and List of municipalities in Massachusetts, most populous city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th-List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the country. The city boundaries encompass an area of about and a population of 675,647 2020 U.S. Census, as of 2020. It is the seat of Suffolk County, Massachusetts, Suffolk County (although the county government was disbanded on July 1, 1999). The city is the economic and cultural anchor of a substantially larger metropolitan area known as Greater Boston, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) home to a census-estimated 4.8 million people in 2016 and ranking as the tenth-largest MSA in the country. A broader combined statistical area (CSA), generally corresponding to the commuting area and includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northampton, MA
The city of Northampton is the county seat of Hampshire County, Massachusetts, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population of Northampton (including its outer villages, Florence and Leeds) was 29,571. Northampton is known as an academic, artistic, musical, and countercultural hub. It features a large politically liberal community along with numerous alternative health and intellectual organizations. Based on U.S. Census demographics, election returns, and other criteria, the website Epodunk rates Northampton as the most politically liberal medium-size city (population 25,000–99,000) in the United States. The city has a high proportion of residents who identify as gay and lesbian and a high number of same-sex households and is a popular destination for the LGBT community. Northampton is part of the Pioneer Valley and is one of the northernmost cities in the Knowledge Corridor—a cross-state cultural and economic partnership with other Connecticut River Valley citie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
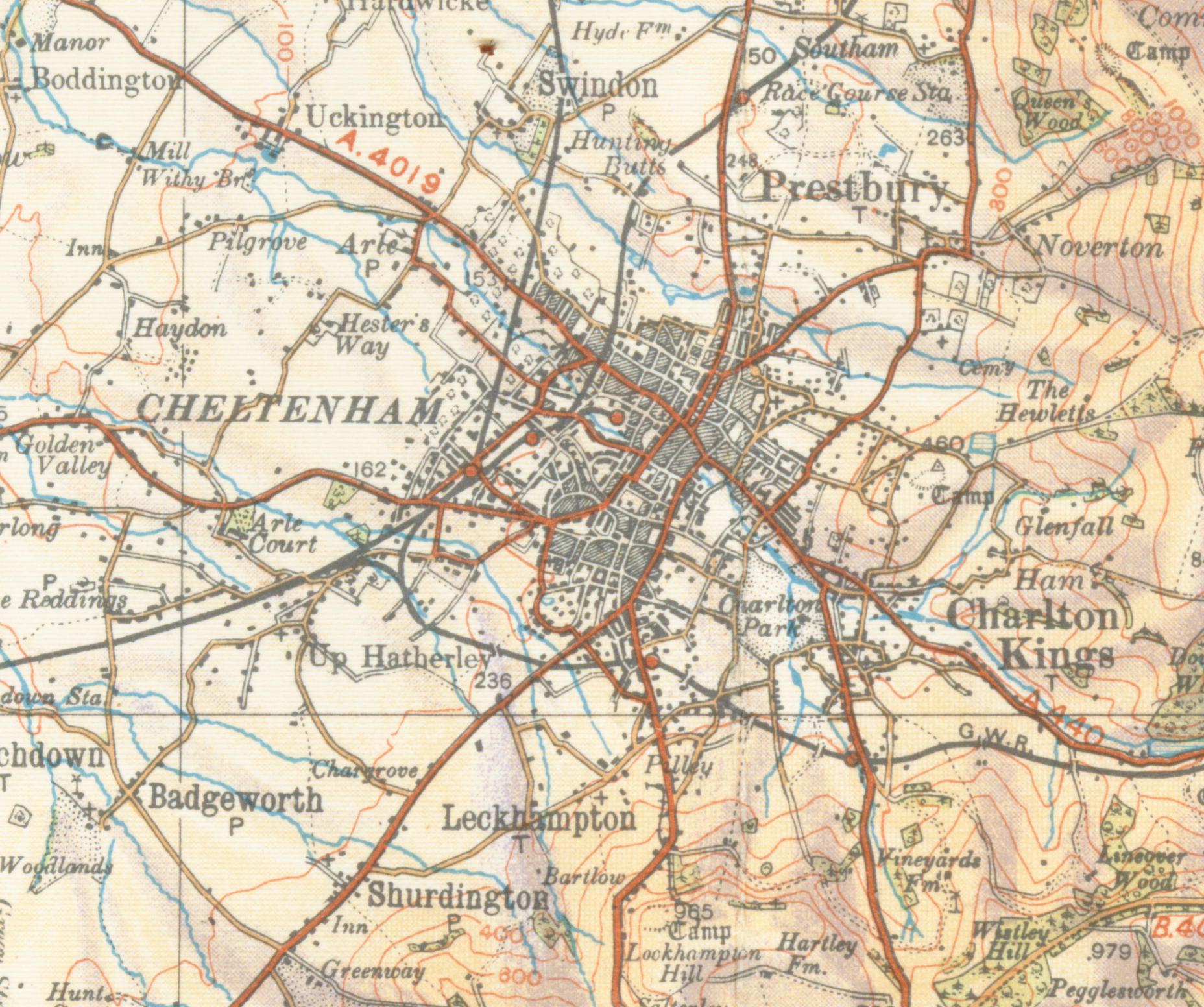
Cheltenham, UK
Cheltenham (), also known as Cheltenham Spa, is a spa town and borough on the edge of the Cotswolds in the county of Gloucestershire, England. Cheltenham became known as a health and holiday spa town resort, following the discovery of mineral springs in 1716, and claims to be the most complete Regency town in Britain. The town hosts several festivals of culture, often featuring nationally and internationally famous contributors and attendees; they include the Cheltenham Literature Festival, the Cheltenham Jazz Festival, the Cheltenham Science Festival, the Cheltenham Music Festival, the Cheltenham Cricket Festival and the Cheltenham Food & Drink Festival. In steeplechase horse racing, the Gold Cup is the main event of the Cheltenham Festival, held every March. History Cheltenham stands on the small River Chelt, which rises nearby at Dowdeswell and runs through the town on its way to the Severn. It was first recorded in 803, as ''Celtan hom''; the meaning has not been resolved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Elgar Publishing
Edward Elgar Publishing is a global publisher of academic books, journals and online resources in the social sciences and law. The company also publishes a social science and law blog with regular contributions from leading scholars. About Edward Elgar Publishing, founded in 1986, is an independent family-owned international publisher, with offices in Cheltenham and Camberley in the UK and Northampton, Massachusetts, in the USA. It specializes in the academic and professional market and publishes in the field of economics, law, management studies, public policy and social policy and the environment. The company has over 4,500 book titles in print and publishes more than 300 new titles a year. History The first Edward Elgar Publishing book titles were published in 1987 and included ''The Economics of Education and the Education of an Economist'' by Mark Blaug, ''The Economic Revival of Modern Britain'' by David Coates and John Hillard, and ''Economic Choice Under Uncertainty'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Oceanic And Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditions, charts the seas, conducts deep sea exploration, and manages fishing and protection of marine mammals and endangered species in the U.S. exclusive economic zone. Purpose and function NOAA's specific roles include: * ''Supplying Environmental Information Products''. NOAA supplies to its customers and partners information pertaining to the state of the oceans and the atmosphere, such as weather warnings and forecasts via the National Weather Service. NOAA's information services extend as well to climate, ecosystems, and commerce. * ''Providing Environmental Stewardship Services''. NOAA is a steward of U.S. coastal and marine environments. In coordination with federal, state, local, tribal and international authorities, NOAA manages the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Solow
Robert Merton Solow, GCIH (; born August 23, 1924) is an American economist whose work on the theory of economic growth culminated in the exogenous growth model named after him. He is currently Emeritus Institute Professor of Economics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, where he has been a professor since 1949. He was awarded the John Bates Clark Medal in 1961, the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1987, and the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 2014. Four of his PhD students, George Akerlof, Joseph Stiglitz, Peter Diamond and William Nordhaus later received Nobel Memorial Prizes in Economic Sciences in their own right. Biography Robert Solow was born in Brooklyn, New York, into a Jewish family on August 23, 1924, the oldest of three children. He regarded his parents as being very intelligent despite their not being able to attend college due to the necessity to work. He was well educated in the neighborhood public schools and excelled academically early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenneth Arrow
Kenneth Joseph Arrow (23 August 1921 – 21 February 2017) was an American economist, mathematician, writer, and political theorist. He was the joint winner of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences with John Hicks in 1972. In economics, he was a major figure in post-World War II neo-classical economic theory. Many of his former graduate students have gone on to win the Nobel Memorial Prize themselves. His most significant works are his contributions to social choice theory, notably "Arrow's impossibility theorem", and his work on general equilibrium analysis. He has also provided foundational work in many other areas of economics, including endogenous growth theory and the economics of information. Education and early career Arrow was born on 23 August 1921, in New York City. Arrow's mother, Lilian (Greenberg), was from Iași, Romania, and his father, Harry Arrow, was from nearby Podu Iloaiei. The Arrow family were Romanian Jews. His family was very supportive of his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfred Nobel was a Swedish chemist, engineer, and industrialist most famously known for the invention of dynamite. He died in 1896. In his will, he bequeathed all of his "remaining realisable assets" to be used to establish five prizes which became known as "Nobel Prizes." Nobel Prizes were first awarded in 1901. Nobel Prizes are awarded in the fields of Physics, Chemistry, Physiology or Medicine, Literature, and Peace (Nobel characterized the Peace Prize as "to the person who has done the most or best to advance fellowship among nations, the abolition or reduction of standing armies, and the establishment and promotion of peace congresses"). In 1968, Sveriges Riksbank (Sweden's central bank) funded the establishment of the Prize in Economi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_(NYPL_b12610608-421421).jpg)