|
Contamination Control
Contamination control is the generic term for all activities aiming to control the existence, growth and proliferation of contamination in certain areas. Contamination control may refer to the atmosphere as well as to surfaces, to particulate matter as well as to microbes and to contamination prevention as well as to decontamination. Function The aim of all contamination control activities is to permanently ensure a sufficient level of cleanliness in controlled environments. This is accomplished by maintaining, reducing, or eradicating viable and non-viable contamination for either sanitary purposes or in order to maintain an efficient rate of production. Usage One of the most common environments that incorporates contamination control into its standards protocol is the cleanroom. There are many preventive procedures in place within a cleanroom environment. They include subjecting cleanroom staff to strict clothing regulations, and there is often a gowning room where the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contamination
Contamination is the presence of a constituent, impurity, or some other undesirable element that spoils, corrupts, infects, makes unfit, or makes inferior a material, physical body, natural environment, workplace, etc. Types of contamination Within the sciences, the word "contamination" can take on a variety of subtle differences in meaning, whether the contaminant is a solid or a liquid, as well as the variance of environment the contaminant is found to be in. A contaminant may even be more abstract, as in the case of an unwanted energy source that may interfere with a process. The following represent examples of different types of contamination based on these and other variances. Chemical contamination In chemistry, the term "contamination" usually describes a single constituent, but in specialized fields the term can also mean chemical mixtures, even up to the level of cellular materials. All chemicals contain some level of impurity. Contamination may be recognized or not a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biohazard
A biological hazard, or biohazard, is a biological substance that poses a threat to the health of living organisms, primarily humans. This could include a sample of a microorganism, virus or toxin that can adversely affect human health. A biohazard could also be a substance harmful to other animals. The term and Hazard symbol#Biohazard sign, its associated symbol are generally used as a warning, so that those potentially exposed to the substances will know to take precautions. The biohazard symbol was developed in 1966 by Charles Baldwin, an environmental-health engineer working for the Dow Chemical Company on the containment products. It is used in the labeling of biological materials that carry a significant health risk, including viral samples and used hypodermic needles. In Unicode, the biohazard symbol is U+2623 (☣). ANSI Z535/OSHA/ISO regulation Biohazardous safety issues are identified with specified labels, signs and paragraphs established by the American National ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrostatic Potential
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies electric charges at rest (static electricity). Since classical times, it has been known that some materials, such as amber, attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amber, (), was thus the source of the word 'electricity'. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law. Even though electrostatically induced forces seem to be rather weak, some electrostatic forces are relatively large. The force between an electron and a proton, which together make up a hydrogen atom, is about 36 orders of magnitude stronger than the gravitational force acting between them. There are many examples of electrostatic phenomena, from those as simple as the attraction of plastic wrap to one's hand after it is removed from a package, to the apparently spontaneous explosion of grain silos, the damage of electronic components during manufacturin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HEPA
HEPA (, high-efficiency particulate air) filter, also known as high-efficiency particulate absorbing filter and high-efficiency particulate arrestance filter, is an efficiency standard of air filters. Filters meeting the HEPA standard must satisfy certain levels of efficiency. Common standards require that a HEPA air filter must remove—from the air that passes through—at least 99.95% (ISO, European Standard) or 99.97% (ASME, U.S. DOE) of particles whose diameter is equal to 0.3 μm, with the filtration efficiency increasing for particle diameters both less than and greater than 0.3 μm. HEPA filters capture pollen, dirt, dust, moisture, bacteria (0.2-2.0 μm), virus (0.02-0.3 μm), and submicron liquid aerosol (0.02-0.5 μm). Some microorganisms, for example, ''Aspergillus niger'', ''Penicillium citrinum'', ''Staphylococcus epidermidis'', and ''Bacillus subtilis'' are captured by HEPA filters with photocatalytic oxidation (PCO). A HEPA filter is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical Mask
A surgical mask, also known by other names such as a medical face mask or procedure mask, is a personal protective equipment used by healthcare professionals that serves as a mechanical barrier that interferes with direct airflow in and out of respiratory orifices (i.e. human nose, nose and human mouth, mouth). This helps reduce airborne transmission of pathogens and other aerosolized contaminants between the wearer and nearby people via respiratory droplets ejected when sneezing, coughing, forceful breathing, expiration or unintentionally spitting when talking, etc. Surgical masks may be labeled as surgical, isolation, dental or medical procedure masks. Although the material of which surgical masks are made will filter out some viruses and bacteria by trapping the aerosol suspended in breathed air, they only provide partial protection from airborne diseases because of the typically loose fit between the mask edges and the wearer's face. Surgical masks are distinct from mechanical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleanroom Suit
A cleanroom suit, clean room suit, or bunny suit, is an overall garment worn in a cleanroom, an environment with a controlled level of contamination. One common type is an all-in-one coverall worn by semiconductor and nanotechnology line production workers, technicians, and process / equipment engineers. Similar garments are worn by people in similar roles creating sterile products for the medical device, biopharmaceutical and optical instrument industries. The suit covers the wearer to prevent skin and hair being shed into a clean room environment. The suit may be in one piece or consist of several separate garments worn tightly together. The suit incorporates both boots and hood designed to be breathable, lightweight while protecting wearer. Polypropylene with a polyethylene coating, or Tyvek polyethylene are standard. The materials found in cleanroom suits can also be found on personal protective equipment. More advanced designs with face covers were introduced in the 1990s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Recall
A product recall is a request from a manufacturer to return a product after the discovery of safety issues or product defects that might endanger the consumer or put the maker/seller at risk of legal action. The recall is an effort to limit ruination of the corporate image and limit liability for corporate negligence, which can cause significant legal costs. It can be difficult, if not impossible, to determine how costly can be releasing to the consumer a product that could endanger someone's life and the economic loss resulting from unwanted publicity. Recalls are costly. Costs include having to handle the recalled product, replacing it and possibly being held financially responsible for the consequences of the recalled product. A country's consumer protection laws will have specific requirements in regard to product recalls. Such regulations may include how much of the cost the maker will have to bear, situations in which a recall is compulsory (usually because the risk is b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particulates
Particulates – also known as atmospheric aerosol particles, atmospheric particulate matter, particulate matter (PM) or suspended particulate matter (SPM) – are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspended in the air. The term '' aerosol'' commonly refers to the particulate/air mixture, as opposed to the particulate matter alone. Sources of particulate matter can be natural or anthropogenic. They have impacts on climate and precipitation that adversely affect human health, in ways additional to direct inhalation. Types of atmospheric particles include suspended particulate matter; thoracic and respirable particles; inhalable coarse particles, designated PM, which are coarse particles with a diameter of 10 micrometers (μm) or less; fine particles, designated PM, with a diameter of 2.5 μm or less; ultrafine particles, with a diameter of 100 nm or less; and soot. The IARC and WHO designate airborne particulates as a Group 1 carcinogen. Particula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmonella Enteritidis
''Salmonella enterica'' subsp. ''enterica'' is a subspecies of ''Salmonella enterica'', the rod-shaped, flagellated, aerobic, Gram-negative bacterium. Many of the pathogenic serovars of the ''S. enterica'' species are in this subspecies, including that responsible for typhoid. Serovars ''S. enterica'' subsp. ''enterica'' contains a large number of serovars which can infect a broad range of vertebrate hosts. The individual members range from being highly host-adapted (only able to infect a narrow range of species) to displaying a broad host range. A number of techniques are currently used to differentiate between serotypes. These include looking for the presence or absence of antigens, phage typing, molecular fingerprinting and biotyping, where serovars are differentiated by which nutrients they are able to ferment. A possible factor in determining the host range of particular serovars is phage-mediated acquisition of a small number of genetic elements that enable infection of a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
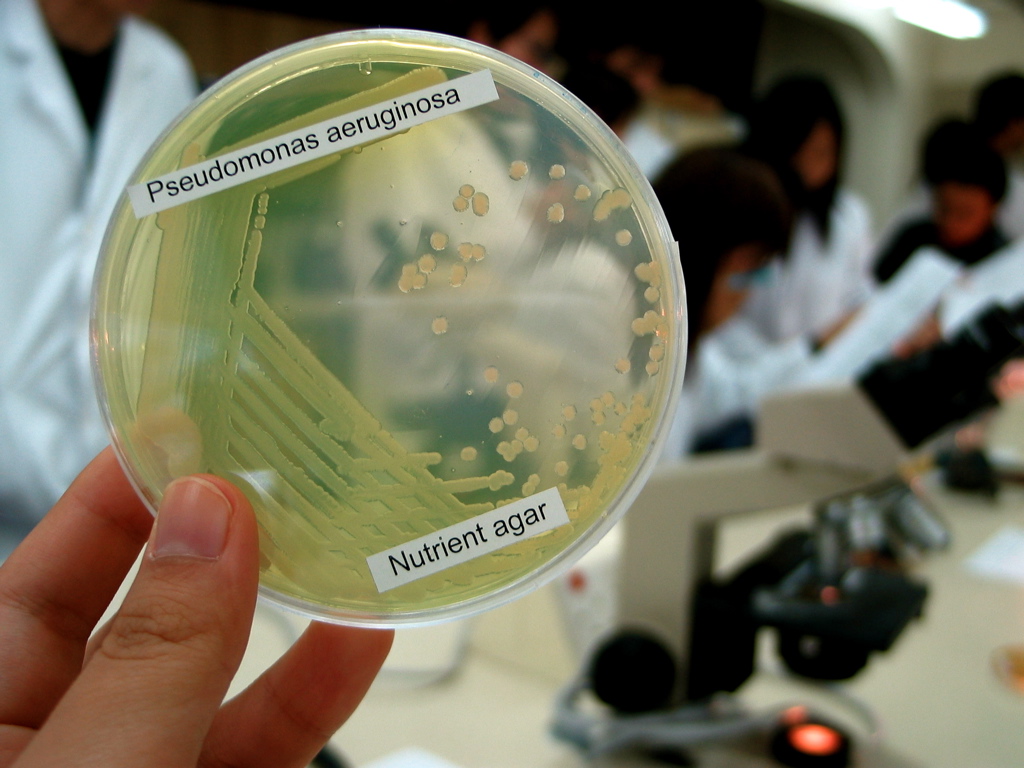
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic–facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aeruginosa'' is a multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes. The organism is considered opportunistic insofar as serious infection often occurs during existing diseases or conditions – most notably cystic fibrosis and traumatic burns. It generally affects the immunocompromised but can also infect the immunocompetent as in hot tub folliculitis. Treatment of ''P. aeruginosa'' infections can be difficult due to its natural resistance to antibiotics. When more advanced antibiotic drug regimens are needed adverse effects may re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
Methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) is a group of Gram-positive bacteria that are genetically distinct from other strains of ''Staphylococcus aureus''. MRSA is responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans. It caused more than 100,000 deaths attributable to antimicrobial resistance in 2019. MRSA is any strain of ''S. aureus'' that has developed (through natural selection) or acquired (through horizontal gene transfer) a multiple drug resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. Beta-lactam (β-lactam) antibiotics are a broad-spectrum group that include some penams (penicillin derivatives such as methicillin and oxacillin) and cephems such as the cephalosporins. Strains unable to resist these antibiotics are classified as methicillin-susceptible ''S. aureus'', or MSSA. MRSA is common in hospitals, prisons, and nursing homes, where people with open wounds, invasive devices such as catheters, and weakened immune systems are at greater risk of healt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are harmless, but some serotypes ( EPEC, ETEC etc.) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains do not cause disease in humans and are part of the normal microbiota of the gut; such strains are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |