|
Complement Receptor 2
Complement receptor type 2 (CR2), also known as complement C3d receptor, Epstein-Barr virus receptor, and CD21 (cluster of differentiation 21), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CR2 gene. CR2 is involved in the complement system. It binds to iC3b (inactive derivative of C3b), C3dg, or C3d.Frank K, Atkinson JP (2001). "Complement system." In Austen KF, Frank K, Atkinson JP, Cantor H. eds. ''Samter's Immunologic Diseases, 6th ed. Vol. 1,'' p. 281-298, Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, . B cells express CR2 receptors on their surfaces, allowing the complement system to play a role in B-cell activation and maturation. Interactions Complement receptor 2 interacts with CD19, and, on mature B cells, forms a complex with CD81 (TAPA-1). The CR2-CD19-CD81 complex is often called the B cell co-receptor complex,Abbas AK, Lichtman AH (2003). ''Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 5th ed.'' Philadelphia: Saunders, because CR2 binds to opsonized antigens through at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complement Receptor 1
Complement receptor type 1 (CR1) also known as C3b/C4b receptor or CD35 (cluster of differentiation 35) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CR1'' gene. This gene is a member of the regulators of complement activation (RCA) family and is located in the 'cluster RCA' region of chromosome 1. The gene encodes a monomeric single-pass type I membrane glycoprotein found on erythrocytes, leukocytes, glomerular podocytes, hyalocytes, and splenic follicular dendritic cells. The Knops blood group system is a system of antigens located on this protein. The protein mediates cellular binding to particles and immune complexes that have activated complement. Decreases in expression of this protein and/or mutations in its gene have been associated with gallbladder carcinomas, mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and sarcoidosis. Mutations in this gene have also been associated with a reduction in ''Plasmodium falciparum'' rosetting, conferring protecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell Lymphoma
T-cell lymphoma is a rare form of cancerous lymphoma affecting T-cells. Lymphoma arises mainly from the uncontrolled proliferation of T-cells and can become cancerous. T-cell lymphoma is categorized under Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and represents less than 15% of all Non-Hodgkin's diseases in the category. T-cell lymphomas are often categorised based on their growth patterns as either; aggressive (fast-growing) or indolent (slow-growing). Although the cause of T-cell lymphoma is not definitive, it has been associated with various risk factors and viruses such as Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) and Human T-cell leukemia virus-1 (HTLV1). The prognosis and treatment of T-cell lymphoma can vary drastically based on the specific type of lymphoma and its growth patterns. Due to their rarity and high variability between the different subtypes, the prognosis of T-cell lymphoma is significantly worse than other Non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The treatment of T-cell lymphoma is often similar to other N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
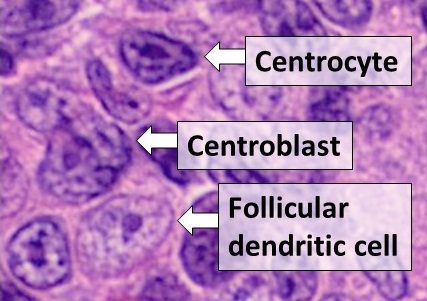
Follicular Lymphoma
Follicular lymphoma (FL) is a cancer that involves certain types of white blood cells known as lymphocytes. The cancer originates from the uncontrolled division of specific types of B-cells known as centrocytes and centroblasts. These cells normally occupy the follicles (nodular swirls of various types of lymphocytes) in the germinal centers of lymphoid tissues such as lymph nodes. The cancerous cells in FL typically form follicular or follicle-like structures (see adjacent Figure) in the tissues they invade. These structures are usually the dominant histological feature of this cancer. There are several synonymous and obsolete terms for FL such as CB/CC lymphoma (centroblastic and centrocytic lymphoma), nodular lymphoma, Brill-Symmers Disease, and the subtype designation, follicular large-cell lymphoma. In the US and Europe, this disease is the second most common form of non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, exceeded only by diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. FL accounts for 10-20% of non-Hodgki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle Cell Lymphoma
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a type of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL), comprising about 6% of NHL cases. There are only about 15,000 patients presently in the United States with mantle cell lymphoma. It is named for the mantle zone of the lymph nodes. MCL is a subtype of B-cell lymphoma, due to CD5 positive antigen-naive pregerminal center B-cell within the mantle zone that surrounds normal germinal center follicles. MCL cells generally over-express cyclin D1 due to the t(11:14) translocation, a chromosomal translocation in the DNA. Signs and symptoms At diagnosis, patients typically are in their 60s and present to their physician with advanced disease. About half have B symptoms such as fever, night sweats, or unexplained weight loss (over 10% of body weight). Enlarged lymph nodes (for example, a "bump" on the neck, armpits or groin) or enlargement of the spleen are usually present. Bone marrow, liver and gastrointestinal tract involvement occurs relatively early in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MALT Lymphoma
MALT lymphoma (MALToma) is a form of lymphoma involving the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), frequently of the stomach, but virtually any mucosal site can be affected. It is a cancer originating from B cells in the marginal zone of the MALT, and is also called extranodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma. Diagnosis and staging MALT lymphoma is an often multifocal disease in the organ of origin and is frequently macroscopically indistinguishable from other disease processes in the GI tract. Endoscopy is key to diagnosing MALT lymphoma, with multiple biopsies of the visible lesions required, as well as samples of macroscopically normal tissue, termed gastric mapping. Histologically, there is expansion of the marginal zone compartment with development of sheets of neoplastic small lymphoid cells. The morphology of the neoplastic cells is variable with small mature lymphocytes, cells resembling centrocytes (centrocyte like cells), or marginal zone/monocytoid B cells. Plasmacytoid o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoplasm
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germinal Centre
Germinal centers or germinal centres (GCs) are transiently formed structures within B cell zone (follicles) in secondary lymphoid organs – lymph nodes, ileal Peyer's patches, and the spleen – where mature B cells are activated, proliferate, differentiate, and mutate their antibody genes (through somatic hypermutation aimed at achieving higher affinity) during a normal immune response; most of the germinal center B cells (BGC) are removed by tingible body macrophages. The B cells develop dynamically after the activation of follicular B cells by T-dependent antigen. As they undergo rapid and mutative cellular division, B cells of the germinal center's dark zone are known as centroblasts. Once these B cells have stopped proliferating and moved to the light zone, they are known as centrocytes, and are subjected to selection by follicular helper T (TFH) cells in the presence of follicular dendritic cells (FDCs). Germinal centers are an important part of the B cell humoral i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frozen Section Procedure
The frozen section procedure is a pathological laboratory procedure to perform rapid microscopic analysis of a specimen. It is used most often in oncological surgery. The technical name for this procedure is cryosection. The microtome device that cold cuts thin blocks of frozen tissue is called a cryotome. The quality of the slides produced by frozen section is of lower quality than formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissue processing. While diagnosis can be rendered in many cases, fixed tissue processing is preferred in many conditions for more accurate diagnosis. The intraoperative consultation is the name given to the whole intervention by the pathologist, which includes not only frozen section but also gross evaluation of the specimen, examination of cytology preparations taken on the specimen (e.g. touch imprints), and aliquoting of the specimen for special studies (e.g. molecular pathology techniques, flow cytometry). The report given by the pathologist is often limited to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
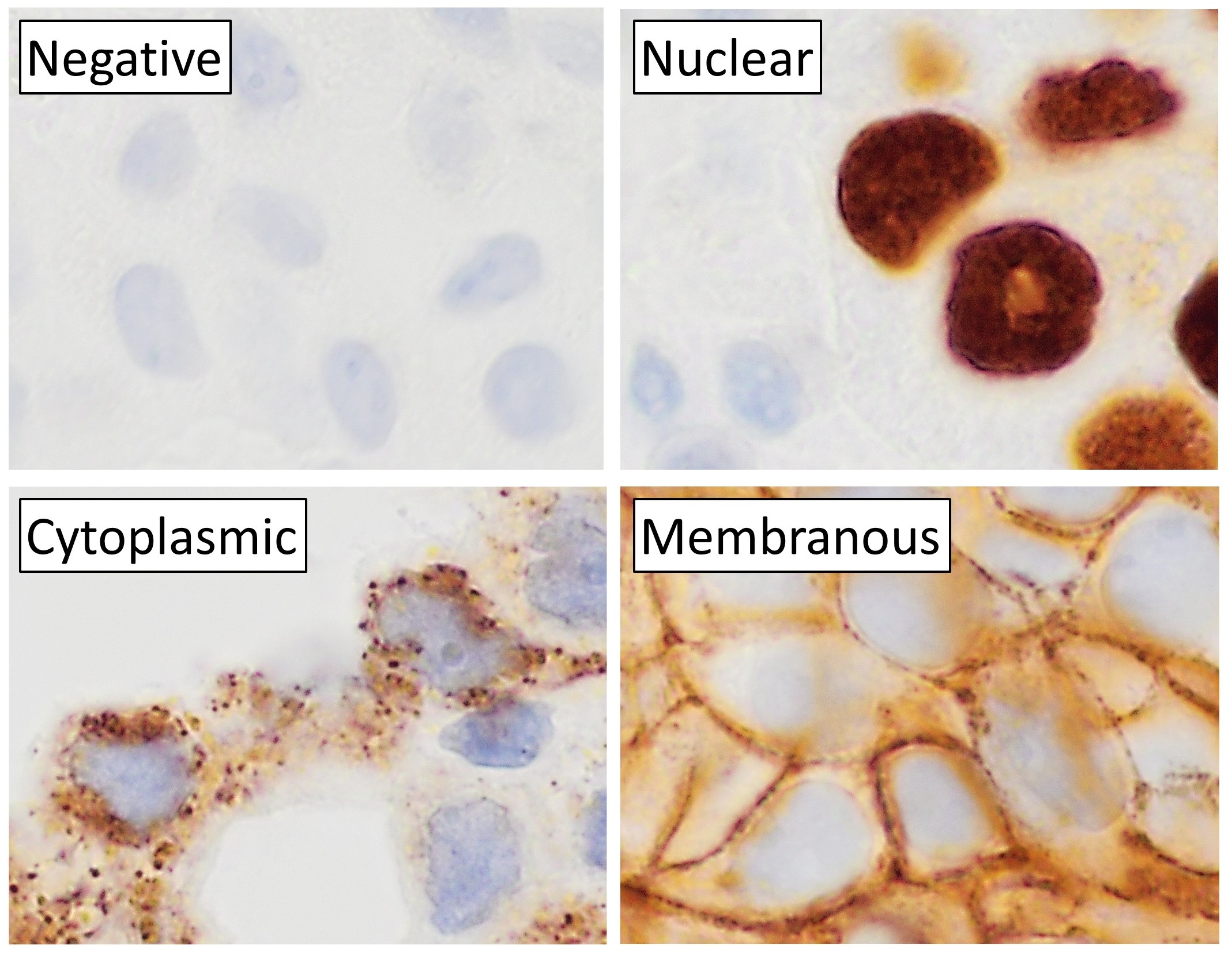
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. IHC takes its name from the roots "immuno", in reference to antibodies used in the procedure, and "histo", meaning tissue (compare to immunocytochemistry). Albert Coons conceptualized and first implemented the procedure in 1941. Visualising an antibody-antigen interaction can be accomplished in a number of ways, mainly either of the following: * ''Chromogenic immunohistochemistry'' (CIH), wherein an antibody is conjugated to an enzyme, such as peroxidase (the combination being termed immunoperoxidase), that can catalyse a colour-producing reaction. * ''Immunofluorescence'', where the antibody is tagged to a fluorophore, such as fluorescein or rhodamine. Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distribution Patterns Of CD21 Or CD23 In Follicular Lymphoma
Distribution may refer to: Mathematics *Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations *Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a variable **Cumulative distribution function, in which the probability of being no greater than a particular value is a function of that value *Frequency distribution, a list of the values recorded in a sample *Inner distribution, and outer distribution, in coding theory *Distribution (differential geometry), a subset of the tangent bundle of a manifold *Distributed parameter system, systems that have an infinite-dimensional state-space *Distribution of terms, a situation in which all members of a category are accounted for *Distributivity, a property of binary operations that generalises the distributive law from elementary algebra *Distribution (number theory) *Distribution problems, a common type of problems in combinatorics where the goal is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Follicular Dendritic Cell
Follicular dendritic cells (FDC) are cells of the immune system found in primary and secondary lymph follicles (lymph nodes) of the B cell areas of the lymphoid tissue. Unlike dendritic cells (DC), FDCs are not derived from the bone-marrow hematopoietic stem cell, but are of mesenchymal origin. Possible functions of FDC include: organizing lymphoid tissue's cells and microarchitecture, capturing antigen to support B cell, promoting debris removal from germinal centers, and protecting against autoimmunity. Disease processes that FDC may contribute include primary FDC-tumor, chronic inflammatory conditions, HIV-1 infection development, and neuroinvasive scrapie. Location and molecular markers Follicular DCs are a non-migratory population found in primary and secondary follicles of the B cell areas of lymph nodes, spleen, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). They form a stable network due to intercellular connections between FDCs processes and intimate interaction with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |