|
Communicate
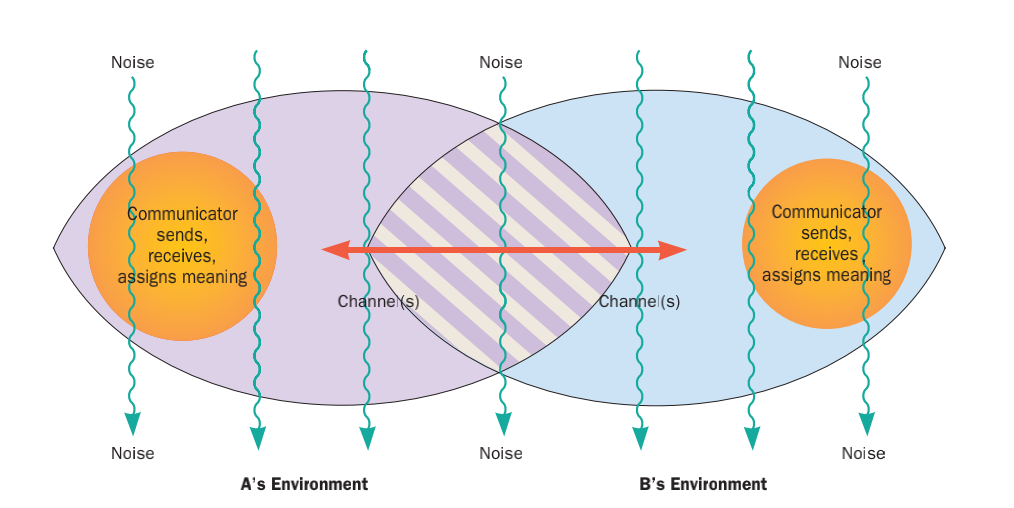
Communication is commonly defined as the transmission of information. Its precise definition is disputed and there are disagreements about whether unintentional or failed transmissions are included and whether communication not only transmits meaning but also creates it. Models of communication are simplified overviews of its main components and their interactions. Many models include the idea that a source uses a coding system to express information in the form of a message. The message is sent through a channel to a receiver who has to decode it to understand it. The main field of inquiry investigating communication is called communication studies. A common way to classify communication is by whether information is exchanged between humans, members of other species, or non-living entities such as computers. For human communication, a central contrast is between verbal and non-verbal communication. Verbal communication involves the exchange of messages in linguistic form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-verbal Communication
Nonverbal communication is the transmission of messages or signals through a nonverbal platform such as eye contact (oculesics), body language (kinesics), social distance (proxemics), touch (Haptic communication, haptics), voice (prosody (linguistics), prosody and paralanguage), physical environments/appearance, and use of objects. When communicating, nonverbal channels are utilized as means to convey different messages or signals, whereas others interpret these messages. The study of nonverbal communication started in 1872 with the publication of ''The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals'' by Charles Darwin. Darwin began to study nonverbal communication as he noticed the interactions between animals such as lions, tigers, dogs etc. and realized they also communicated by gestures and expressions. For the first time, nonverbal communication was studied and its relevance noted. Today, scholars argue that nonverbal communication can convey more meaning than verbal communica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Communication
Human communication, or anthroposemiotics, is a field of study dedicated to understanding how humans Communication, communicate. Humans' ability to communicate with one another would not be possible without an understanding of what we are referencing or thinking about. Because humans are unable to fully understand one another's perspective, there needs to be a creation of commonality through a shared mindset or viewpoint. The field of communication is very diverse, as there are multiple layers of what communication is and how we use its different features as human beings. Humans have communicatory abilities other animals do not. For example, humans are able to communicate about time and place as though they are solid objects. Humans communicate to request help, inform others, and share attitudes for bonding. Communication is a joint activity largely dependent on the ability to maintain common attention. We share relevant background knowledge and joint experience in order to commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpersonal Communication
Interpersonal communication is an exchange of information between two or more people. It is also an area of research that seeks to understand how humans use verbal and nonverbal cues to accomplish several personal and relational goals. Communication includes utilizing communication skills within one's surroundings, including physical and psychological spaces. It is essential to see the visual/nonverbal and verbal cues regarding the physical spaces. In the psychological spaces, self-awareness and awareness of the emotions, cultures, and things that are not seen are also significant when communicating. Interpersonal communication research addresses at least six categories of inquiry: 1) how humans adjust and adapt their verbal communication and nonverbal communication during Face-to-face interaction, face-to-face communication; 2) how messages are produced; 3) how uncertainty influences behavior and information-management strategies; 4) Interpersonal deception theory, deceptive com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Communication
Animal communication is the transfer of information from one or a group of animals (sender or senders) to one or more other animals (receiver or receivers) that affects the current or future behavior of the receivers. Information may be sent intentionally, as in a courtship display, or unintentionally, as in the transfer of scent from the predator to prey with kairomones. Information may be transferred to an "audience" of several receivers. Animal communication is a rapidly growing area of study in disciplines including Ethology, animal behavior, sociology, neurology, and animal cognition. Many aspects of animal behavior, such as symbolic name use, emotional expression, learning, and Animal sexual behavior, sexual behavior, are being understood in new ways. When the information from the sender changes the behavior of a receiver, the information is referred to as a "signal". Signalling theory predicts that for a signal to be maintained in the population, both the sender and receiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sign Language
Sign languages (also known as signed languages) are languages that use the visual-manual modality to convey meaning, instead of spoken words. Sign languages are expressed through manual articulation in combination with #Non-manual elements, non-manual markers. Sign languages are full-fledged natural languages with their own grammar and lexicon. Sign languages are not universal and are usually not mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible, although there are similarities among different sign languages. Linguists consider both spoken and signed communication to be types of natural language, meaning that both emerged through an abstract, protracted aging process and evolved over time without meticulous planning. This is supported by the fact that there is substantial overlap between the neural substrates of sign and spoken language processing, despite the obvious differences in modality. Sign language should not be confused with body language, a type of non verbal communicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Language
Body language is a type of nonverbal communication in which physical behaviors, as opposed to words, are used to express or convey information. Such behavior includes facial expressions, body posture, gestures, eye movement, touch and the use of space. Although body language is an important part of communication, most of it happens without conscious awareness. In social communication, body language often complements verbal communication. Nonverbal communication has a significant impact on doctor-patient relationships, as it affects how open patients are with their doctor. As an unstructured, ungrammatical, and broadly-interpreted form of communication, body language is not a form of language. It differs from sign language, sign languages, which are true languages with complex grammar systems and exhibiting the fundamental properties considered to exist in all languages. Some researchers conclude that nonverbal communication accounts for the majority of information transmitted d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Communication
Plants are exposed to many stress factors such as disease, temperature changes, herbivory, injury and more. Therefore, in order to respond or be ready for any kind of physiological state, they need to develop some sort of system for their survival in the moment and/or for the future. Plant communication encompasses communication using volatile organic compounds, electrical signaling, and common mycorrhizal networks between plants and a host of other organisms such as soil microbes, other plants (of the same or other species), animals, insects, and fungi. Plants communicate through a host of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can be separated into four broad categories, each the product of distinct chemical pathways: fatty acid derivatives, phenylpropanoids/benzenoids, amino acid derivatives, and terpenoids. Due to the physical/chemical constraints most VOCs are of low molecular mass (< 300 Da), are hydrophobic, and have high vapor pressures. The responses of organisms to plant e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication Technology
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of transmission may be divided into communication channels for multiplexing, allowing for a single medium to transmit several concurrent communication sessions. Long-distance technologies invented during the 20th and 21st centuries generally use electric power, and include the telegraph, telephone, television, and radio. Early telecommunication networks used metal wires as the medium for transmitting signals. These networks were used for telegraphy and telephony for many decades. In the first decade of the 20th century, a revolution in wireless communication began with breakthroughs including those made in radio communications by Guglielmo Marconi, who won the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics. Other early pioneers in electrical and electronic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantics
Semantics is the study of linguistic Meaning (philosophy), meaning. It examines what meaning is, how words get their meaning, and how the meaning of a complex expression depends on its parts. Part of this process involves the distinction between sense and reference. Sense is given by the ideas and concepts associated with an expression while reference is the object to which an expression points. Semantics contrasts with syntax, which studies the rules that dictate how to create grammatically correct sentences, and pragmatics, which investigates how people use language in communication. Lexical semantics is the branch of semantics that studies word meaning. It examines whether words have one or several meanings and in what lexical relations they stand to one another. Phrasal semantics studies the meaning of sentences by exploring the phenomenon of compositionality or how new meanings can be created by arranging words. Formal semantics (natural language), Formal semantics relies o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed language, signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing system, writing. Human language is characterized by its cultural and historical diversity, with significant variations observed between cultures and across time. Human languages possess the properties of Productivity (linguistics), productivity and Displacement (linguistics), displacement, which enable the creation of an infinite number of sentences, and the ability to refer to objects, events, and ideas that are not immediately present in the discourse. The use of human language relies on social convention and is acquired through learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication Studies
Communication studies (or communication science) is an academic discipline that deals with processes of human communication and behavior, patterns of communication in interpersonal relationships, social interactions and communication in different cultures. Communication is commonly defined as giving, receiving or exchanging ideas, information, signals or messages through appropriate media, enabling individuals or groups to persuade, to seek information, to give information or to express emotions effectively. Communication studies is a social science that uses various methods of empirical investigation and critical analysis to develop a body of knowledge that encompasses a range of topics, from face-to-face conversation at a level of individual agency and interaction to social and cultural communication systems at a macro level. Scholarly communication theorists focus primarily on refining the theoretical understanding of communication, examining statistics in order to help ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Communication
The history of communication technologies (media and appropriate inscription tools) have evolved in tandem with shifts in political and economic systems, and by extension, systems of power. Communication can range from very subtle processes of exchange to full conversations and mass communication. The history of communication itself can be traced back since the origin of speech circa 100,000 Common Era, BCE. The use of technology in communication may be considered since the first use of symbols about 30,000 years BCE. Among the symbols used, there are cave paintings, petroglyphs, pictograms and ideograms. History of writing, Writing was a major innovation, as well as History of printing, printing technology and, more recently, History of telecommunication, telecommunications and the History of the Internet, Internet. Primitive times Human communication was initiated with the origin of speech approximately 100,000 BCE. Symbols were developed about 30,000 years ago. The imperfection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |