|
Comitatenses
The comitatenses and later the palatini were the units of the field armies of the late Roman Empire. They were the soldiers that replaced the legionaries, who had formed the backbone of the Roman military since the Marian reforms. Organization Units such as the Joviani and Herculiani had 5,000 soldiers and 726–800 cavalrymen. Many units' sizes would vary. There were three types of units. They were the heavy infantry, medium infantry, and light infantry. The ''comitatenses'' were the heavy infantry. The Auxiliaries, Auxilia Palatina, and the Peltasts were the medium infantry, and the psiloi were the light infantry. Comitatenses regiments consisted of 1,024 soldiers. Comitatenses legions could consist of 6,000 to 7,000 soldiers. Some of these soldiers would be lightly armed, while others would be heavily armed. During a battle the army would divide into 3-4 divisions. The army might use a double phalanx to protect its rear. Reserves would be located behind or between each di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval continuation, the Eastern Roman Empire. It is thus a term that may span approximately 2,205 years (753 BC–1453 AD), during which the Roman armed forces underwent numerous permutations in size, composition, organisation, equipment and tactics, while conserving a core of lasting traditions. Historical overview Early Roman army (c. 500 BC to c. 300 BC) The early Roman army was the armed forces of the Roman Kingdom and of the early Roman Republic. During this period, when warfare chiefly consisted of small-scale plundering raids, it has been suggested that the army followed Etruscan or Greek models of organisation and equipment. The early Roman army was based on an annual levy. The army consisted of 3,000 infantrymen and 300 cavalrymen, all of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comes
''Comes'' ( ), plural ''comites'' ( ), was a Roman title or office, and the origin Latin form of the medieval and modern title "count". Before becoming a word for various types of title or office, the word originally meant "companion", either individually or as a member of a collective denominated a "''Comitatus (classical meaning), comitatus''", especially the suite of a magnate, being in some instances sufficiently large and/or formal to justify specific denomination, e.g. a "''cohors amicorum''". "''Comes''" derives from "''com-''" ("with") and "''ire''" ("go"). Ancient Roman religion ''Comes'' was a common epithet or title that was added to the name of a hero or god in order to denote relation with another god. The coinage of Constantine I (emperor), Roman Emperor Constantine I declared him "''comes''" to Sol Invictus ("Unconquered Sun") ''qua'' god. Imperial Roman curial titles and offices styled ''Comites'' Historically more significant, "''comes''" became a secular ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Armies
A field army (or numbered army or simply army) is a military formation in many armed forces, composed of two or more corps and may be subordinate to an army group. Likewise, air armies are equivalent formation within some air forces, and within a navy the comparable notion is that of a fleet. A field army is composed of 300,000 to 600,000 troops. History Specific field armies are usually named or numbered to distinguish them from "army" in the sense of an entire national land military force. In English, the typical orthographic style for writing out the names field armies is word numbers, such as "First Army"; whereas corps are usually distinguished by Roman numerals (e.g. I Corps) and subordinate formations with ordinal numbers (e.g. 1st Division). A field army may be given a geographical name in addition to or as an alternative to a numerical name, such as the British Army of the Rhine, Army of the Potomac, Army of the Niemen or Aegean Army (also known as the Fourth Army). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limitanei
The ''līmitāneī'' (Latin, also called ''rīpēnsēs''), meaning respectively "the soldiers in frontier districts" (from the Latin phrase līmēs, meaning a military district of a frontier province) or "the soldiers on the riverbank" (from the Rhine and Danube), were an important part of the late Roman and early Byzantine army after the reorganizations of the late 3rd and early 4th centuries. The limitanei, unlike the comitātēnsēs, palātīnī, and scholæ, garrisoned fortifications along the borders of the Roman Empire and were not normally expected to fight far from their fortifications. The līmitāneī were lower-status and lower-paid than the comitātēnsēs and palātīnī,Treadgold 1995, pp. 149–157. and the distinction in role and status between scolae, palatini, comitatenses, and limitanei had largely replaced the older one between praetorians, legionaries, and auxiliaries. The limitanei and palatini both included legionary units alongside auxiliary units.Tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comes
''Comes'' ( ), plural ''comites'' ( ), was a Roman title or office, and the origin Latin form of the medieval and modern title "count". Before becoming a word for various types of title or office, the word originally meant "companion", either individually or as a member of a collective denominated a "''Comitatus (classical meaning), comitatus''", especially the suite of a magnate, being in some instances sufficiently large and/or formal to justify specific denomination, e.g. a "''cohors amicorum''". "''Comes''" derives from "''com-''" ("with") and "''ire''" ("go"). Ancient Roman religion ''Comes'' was a common epithet or title that was added to the name of a hero or god in order to denote relation with another god. The coinage of Constantine I (emperor), Roman Emperor Constantine I declared him "''comes''" to Sol Invictus ("Unconquered Sun") ''qua'' god. Imperial Roman curial titles and offices styled ''Comites'' Historically more significant, "''comes''" became a secular ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rebellion
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority. A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and then manifests itself by the refusal to submit or to obey the authority responsible for this situation. Rebellion can be individual or collective, peaceful ( civil disobedience, civil resistance, and nonviolent resistance) or violent (terrorism, sabotage and guerrilla warfare). In political terms, rebellion and revolt are often distinguished by their different aims. While rebellion generally seeks to evade and/or gain concessions from an oppressive power, a revolt seeks to overthrow and destroy that power, as well as its accompanying laws. The goal of rebellion is resistance while a revolt seeks a revolution. As power shifts relative to the external adversary, or power shifts within a mixed coalition, or positions harden or soften on ei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
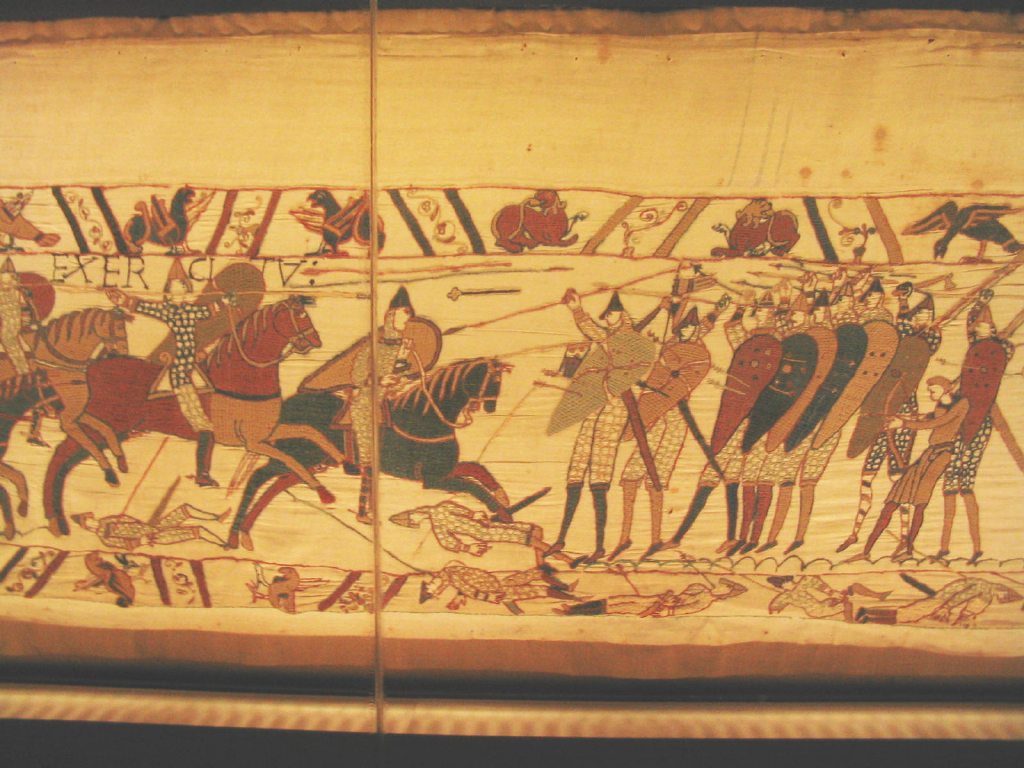
Shield Wall
A shield wall ( or in Old English, in Old Norse) is a military formation that was common in ancient and medieval warfare. There were many slight variations of this formation, but the common factor was soldiers standing shoulder to shoulder and holding their shields so that they would abut or overlap. Each soldier thus benefited from the protection of the shields of his neighbors and his own. History Ancient history The formation was known to be used by many ancient armies including the Persian Sparabara, Greek phalanx, and the early Roman army, but its origin and spread is unknown. It may have developed independently more than once. Although little is recorded about their military tactics, the Stele of the Vultures depicts Sumerian soldiers in a shield wall formation during the third millennium BC. By the seventh century BC, shield walls in ancient Greece are well-documented. The soldiers in the shield wall formations were called hoplites, so named for their equi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
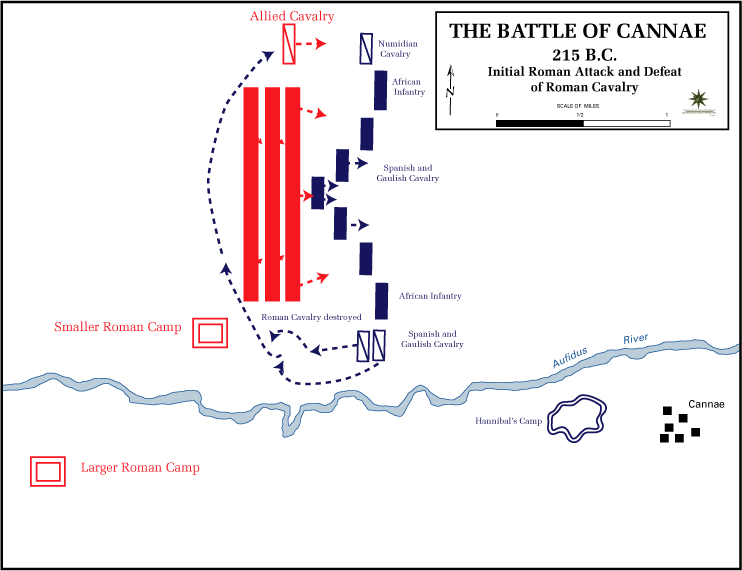
Pitched Battle
A pitched battle or set-piece battle is a battle in which opposing forces each anticipate the setting of the battle, and each chooses to commit to it. Either side may have the option to disengage before the battle starts or shortly thereafter. A pitched battle is not a chance encounter such as a meeting engagement, or where one side is forced to fight at a time not of its choosing such as happens in a siege or an ambush. Pitched battles are usually carefully planned, to maximize one's strengths against an opponent's weaknesses, and use a full range of deceptions, feints, and other manoeuvres. They are also planned to take advantage of terrain favourable to one's force. Forces strong in cavalry for example will not select swamp, forest, or mountain terrain for the planned struggle. For example, Carthaginian general Hannibal selected relatively flat ground near the village of Cannae for his great confrontation with the Romans, not the rocky terrain of the high Apennines. Likewise, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Resources
Human resources (HR) is the set of people who make up the workforce of an organization, business sector, industry, or economy. A narrower concept is human capital, the knowledge and skills which the individuals command. Similar terms include manpower, Labour (human activity), labor, personnel, associates or simply: people. The Human Resources department (HR department) of an organization performs human resource management, overseeing various aspects of employment, such as compliance with labor law and employment standards, job interview, interviewing and selection, performance management, administration of Employee benefits, organizing of employee files with the required documents for future reference, and some aspects of recruitment (also known as talent acquisition) and employee offboarding. They serve as the link between an organization's management and its employees. The duties include planning, recruitment and selection process, posting job ads, evaluating the performance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defence In Depth
Defence in depth (also known as deep defence or elastic defence) is a military strategy that seeks to delay rather than prevent the advance of an attacker, buying time and causing additional casualties by yielding space. Rather than defeating an attacker with a single, strong defensive line, defence in depth relies on the tendency of an attack to lose momentum over time or as it covers a larger area. A defender can thus yield lightly defended territory in an effort to stress an attacker's logistics or spread out a numerically superior attacking force. Once an attacker has lost momentum or is forced to spread out to pacify a large area, defensive counter-attacks can be mounted on the attacker's weak points, with the goal being to cause attrition or drive the attacker back to its original starting position. Strategy A conventional defence strategy would concentrate all military resources at a front line, which, if breached by an attacker, would leave the remaining defenders in d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)