|
Collective Leadership In The Soviet Union
Collective leadership (russian: коллективное руководство, '), or collectivity of leadership (russian: коллективность руководства, '), was considered the ideal form of governance in the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) and other socialist states espousing communism. Its main task was to distribute powers and functions among the Politburo and the Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, as well as the Council of Ministers, to hinder any attempts to create a one-man dominance over the Soviet political system by a Soviet leader, such as that seen under Joseph Stalin's rule. On the national level, the heart of the collective leadership was officially the Central Committee of the Communist Party. Collective leadership was characterised by limiting the powers of the General Secretary and the Chairman of the Council of Ministers as related to other offices by enhancing the powers of collective bodies, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev (2 March 1931 – 30 August 2022) was a Soviet politician who served as the 8th and final leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to dissolution of the Soviet Union, the country's dissolution in 1991. He served as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1985 and additionally as head of state beginning in 1988, as Chairman of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet from 1988 to 1989, Chairman of the Supreme Soviet from 1989 to 1990 and the only President of the Soviet Union from 1990 to 1991. Ideologically, Gorbachev initially adhered to Marxism–Leninism but moved towards social democracy by the early 1990s. Gorbachev was born in Privolnoye, Stavropol Krai, Privolnoye, Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR, to a poor peasant family of Russian and Ukrainian heritage. Growing up under the rule of Joseph Stalin, in his youth he operated combine harvesters on a Collective farming, collective farm before join ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
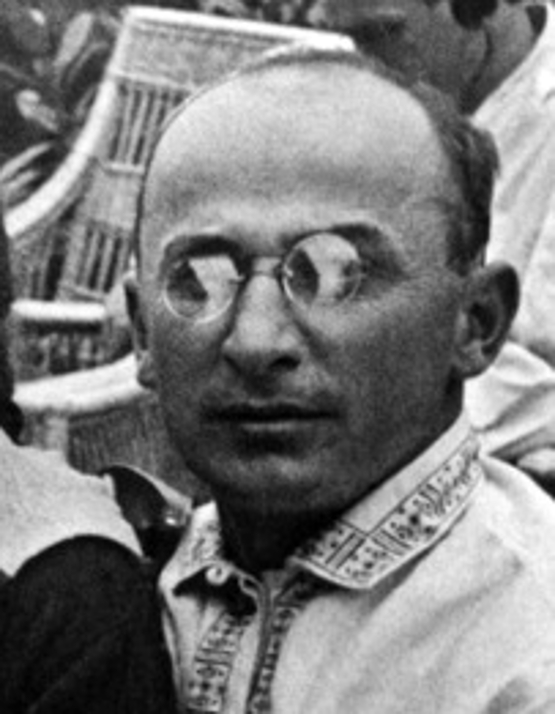
Nikolai Bulganin
Nikolai Alexandrovich Bulganin (russian: Никола́й Алекса́ндрович Булга́нин; – 24 February 1975) was a Soviet politician who served as Minister of Defense (1953–1955) and Premier of the Soviet Union (1955–1958) under Nikita Khrushchev, following service in the Red Army and as defence minister under Joseph Stalin. Early life and career Bulganin was born in 1895 in Nizhny Novgorod. The son of an office worker, he was of Russian ethnicity. He joined the Bolshevik Party in March 1917 and was recruited in 1918 into the Cheka, the Bolshevik regime's political police, where he served until 1922. During the summer of 1918, he worked with Lazar Kaganovich, the local communist leader, in imposing the Red Terror in Nizhny Novgorod. He worked with Kaganovich again in Turkestan in 1920. After the Russian Civil War (1917-1923), Bulganin became an industrial manager and worked in the electricity administration until 1927. He was the director of the Mosco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-Party Group
The Anti-Party Group ( rus, Антипартийная группа, r=Antipartiynaya gruppa) was a Stalinist group within the leadership of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union that unsuccessfully attempted to depose Nikita Khrushchev as First Secretary of the Party in June 1957. The group, given that epithet by Khrushchev, was led by former Premiers Georgy Malenkov and Vyacheslav Molotov and former First Deputy Chairman Lazar Kaganovich. The group rejected both Khrushchev's liberalization of Soviet society and his denunciation of Joseph Stalin, and promoted the full restoration and preservation of Stalinism. Motives The members of the group regarded Khrushchev's attacks on Stalin, most famously in the Secret Speech delivered at the 20th Congress of the CPSU in 1956 as wrong and hypocritical, given Khrushchev's complicity in the Great Purge and similar events as one of Stalin's favorites. They believed that Khrushchev's policy of peaceful coexistence would jeopardize strug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Centralism
Democratic centralism is a practice in which political decisions reached by voting processes are binding upon all members of the political party. It is mainly associated with Leninism, wherein the party's political vanguard of professional revolutionaries practised democratic centralism to elect leaders and officers, determine policy through free discussion, and decisively realise it through united action.Lenin, Vladimir (1906)"Report on the Unity Congress of the R.S.D.L.P." Marxists Internet Archive. Retrieved 14 February 2020. Democratic centralism has also been practised by social democratic and |
Stalin's Cult Of Personality
Joseph Stalin's cult of personality became a prominent feature of Soviet popular culture in 1929, after a lavish celebration of his purported 50th birthday. For the rest of Stalin's rule, the Soviet press presented Stalin as an all-powerful, all-knowing leader, with Stalin's name and image appearing everywhere. Historian Archie Brown sets the celebration of Stalin's 50th birthday on 21 December 1929 as the starting point for his cult of personality. Stalin's image in propaganda and the mass media The building of the cult of personality around Stalin had to proceed judiciously, as British historian Ian Kershaw explains in his history of Europe in the first half of the 20th century, ''To Hell and Back'': A Stalin cult had to be built carefully. This was not just because the man himself was so physically unprepossessing – diminutive and squat, his face dominated by a big walrus mustache and heavily pitted from smallpox – or that he was a secretive, intensely p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vyacheslav Molotov
Vyacheslav Mikhaylovich Molotov. ; (;. 9 March Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates">O._S._25_February.html" ;"title="Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Old Style and New Style dates">O. S. 25 February">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Old Style and New Style dates">O. S. 25 February1890 – 8 November 1986) was a Russian politician and diplomat, an Old Bolshevik, and a leading figure in the Soviet government from the 1920s onward. He served as Chairman of the Council of People's Commissars from 1930 to 1941 and as Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Soviet Union), Minister of Foreign Affairs from 1939 to 1949 and from 1953 to 1956. During the 1930s, he ranked second in the Soviet leadership, after Joseph Stalin, whom he supported loyally for over 30 years, and whose reputation he continued to defend after Stalin's death, having himself been deeply implicated in the worst atrocities of the Stalin years – the forced collectivisation of agriculture in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lavrentiy Beria
Lavrentiy Pavlovich Beria (; rus, Лавре́нтий Па́влович Бе́рия, Lavréntiy Pávlovich Bériya, p=ˈbʲerʲiə; ka, ლავრენტი ბერია, tr, ; – 23 December 1953) was a Georgian Bolshevik and Soviet politician, Marshal of the Soviet Union and state security administrator, chief of the Soviet security, and chief of the People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (NKVD) under Joseph Stalin during the Second World War, and promoted to deputy premier under Stalin in 1941. He officially joined the Politburo in 1946. Beria was the longest-lived and most influential of Stalin's secret police chiefs, wielding his most substantial influence during and after the war. Following the Soviet invasion of Poland in 1939, he was responsible for organizing purges such as the Katyn massacre of 22,000 Polish officers and officials. He would later also orchestrate the forced upheaval of minorities from the Caucasus as head of the NKVD, an act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
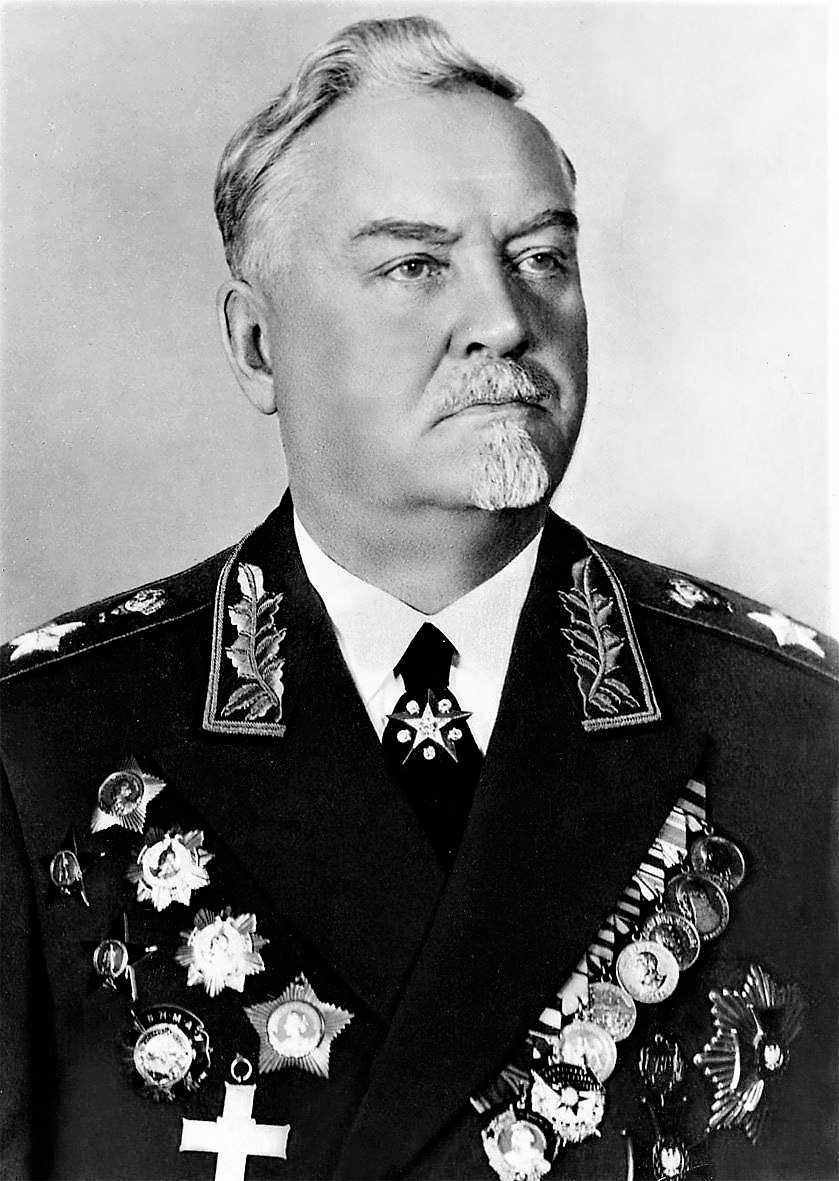
Georgy Malenkov
Georgy Maximilianovich Malenkov ( – 14 January 1988) was a Soviet politician who briefly succeeded Joseph Stalin as the leader of the Soviet Union. However, at the insistence of the rest of the Presidium, he relinquished control over the party apparatus in exchange for remaining Premier and first among equals within the Soviet collective leadership. He then became embroiled in a power struggle with Nikita Khrushchev that culminated in his removal from the premiership in 1955 as well as the Presidium in 1957. Throughout his political career, Malenkov's personal connections with Vladimir Lenin significantly facilitated his ascent within the ruling Communist Party of the Soviet Union. By 1925, he was entrusted with overseeing the party's records. This brought him into contact with Stalin who had by then successfully consolidated power as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union to become the de facto leader of the Soviet Union. As a result of this associatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Leadership
The political system of the Soviet Union took place in a Federalism, federal One-party state, single-party Soviet republic (system of government), soviet socialist republic framework which was characterized by the superior role of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU), the only party permitted by the Soviet constitution, Constitution. Background The Bolsheviks who took power during the October Revolution, the final phase of the Russian Revolution of 1917, Russian Revolution, were the first communist party to take power and attempt to apply the Leninist variant of Marxism in a practical way. Although they grew very quickly during the Revolution from 24,000 to 100,000 members and got 25% of the votes for the Russian Provisional Government, 1917, Constituent Assembly in November 1917, the Bolsheviks were a minority party when they took power by force in Petrograd and Moscow. Their advantages were discipline and a platform supporting the movement of workers, peasants, sold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Leaders Of The Soviet Union
During its 69-year history, the Soviet Union usually had a ''de facto'' leader who would not necessarily be head of state but would lead while holding an office such as premier or general secretary. Under the 1977 Constitution, the chairman of the Council of Ministers, or premier, was the head of government and the chairman of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet was the head of state. The office of the chairman of the Council of Ministers was comparable to a prime minister in the First World whereas the office of the chairman of the Presidium was comparable to a president. In the ideology of Vladimir Lenin, the head of the Soviet state was a collegiate body of the vanguard party (as described in ''What Is To Be Done?''). Following Joseph Stalin's consolidation of power in the 1920s, the post of the general secretary of the Central Committee of the Communist Party became synonymous with leader of the Soviet Union, because the post controlled both the Communist Party and the So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1924 and of the Soviet Union from 1922 to 1924. Under his administration, Russia, and later the Soviet Union, became a one-party socialist state governed by the Communist Party. Ideologically a Marxist, his developments to the ideology are called Leninism. Born to an upper-middle-class family in Simbirsk, Lenin embraced revolutionary socialist politics following his brother's 1887 execution. Expelled from Kazan Imperial University for participating in protests against the Russian Empire's Tsarist government, he devoted the following years to a law degree. He moved to Saint Petersburg in 1893 and became a senior Marxist activist. In 1897, he was arrested for sedition and exiled to Shushenskoye in Siberia for three years, where he married ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |