|
Cognitive Architecture
A cognitive architecture is both a theory about the structure of the human mind and to a computational instantiation of such a theory used in the fields of artificial intelligence (AI) and computational cognitive science. These formalized models can be used to further refine comprehensive theories of cognition and serve as the frameworks for useful artificial intelligence programs. Successful cognitive architectures include ACT-R (Adaptive Control of Thought – Rational) and SOAR. The research on cognitive architectures as software instantiation of cognitive theories was initiated by Allen Newell in 1990. A theory for a cognitive architecture is an "''hypothesis about the fixed structures that provide a mind, whether in natural or artificial systems, and how they work together — in conjunction with knowledge and skills embodied within the architecture — to yield intelligent behavior in a diversity of complex environments." History Herbert A. Simon, one of the founders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Mind
The mind is that which thinks, feels, perceives, imagines, remembers, and wills. It covers the totality of mental phenomena, including both conscious processes, through which an individual is aware of external and internal circumstances, and unconscious processes, which can influence an individual without intention or awareness. The mind plays a central role in most aspects of human life, but its exact nature is disputed. Some characterizations focus on internal aspects, saying that the mind transforms information and is not directly accessible to outside observers. Others stress its relation to outward conduct, understanding mental phenomena as dispositions to engage in observable behavior. The mind–body problem is the challenge of explaining the relation between matter and mind. Traditionally, mind and matter were often thought of as distinct substances that could exist independently from one another. The dominant philosophical position since the 20th century has b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligence (trait)
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. It can be described as the ability to perceive or infer information and to retain it as knowledge to be applied to adaptive behaviors within an environment or context. The term rose to prominence during the early 1900s. Most psychologists believe that intelligence can be divided into various domains or competencies. Intelligence has been long-studied in humans, and across numerous disciplines. It has also been observed in the cognition of non-human animals. Some researchers have suggested that plants exhibit forms of intelligence, though this remains controversial. Etymology The word '' intelligence'' derives from the Latin nouns '' intelligentia'' or '' intellēctus'', which in turn stem from the verb '' intelligere'', to comprehend or perceive. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Distributed Processing
Connectionism is an approach to the study of human mental processes and cognition that utilizes mathematical models known as connectionist networks or artificial neural networks. Connectionism has had many "waves" since its beginnings. The first wave appeared 1943 with Warren Sturgis McCulloch and Walter Pitts both focusing on comprehending neural circuitry through a formal and mathematical approach, and Frank Rosenblatt who published the 1958 paper "The Perceptron: A Probabilistic Model For Information Storage and Organization in the Brain" in ''Psychological Review'', while working at the Cornell Aeronautical Laboratory. The first wave ended with the 1969 book about the limitations of the original perceptron idea, written by Marvin Minsky and Seymour Papert, which contributed to discouraging major funding agencies in the US from investing in connectionist research. With a few noteworthy deviations, most connectionist research entered a period of inactivity until the mid-1980s. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decentralized
Decentralization or decentralisation is the process by which the activities of an organization, particularly those related to planning and decision-making, are distributed or delegated away from a central, authoritative location or group and given to smaller factions within it. Concepts of decentralization have been applied to group dynamics and management science in private businesses and organizations, political science, law and public administration, technology, economics and money. History The word "''centralisation''" came into use in France in 1794 as the post-Revolution French Directory leadership created a new government structure. The word "''décentralisation''" came into usage in the 1820s. "Centralization" entered written English in the first third of the 1800s; mentions of decentralization also first appear during those years. In the mid-1800s Tocqueville would write that the French Revolution began with "a push towards decentralization" but became, "in the en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Processor
Cryptominer, In computing and computer science, a processor or processing unit is an electrical component (circuit (computer science), digital circuit) that performs operations on an external data source, usually Memory (computing), memory or some other data stream. It typically takes the form of a microprocessor, which can be implemented on a single or a few tightly integrated metal–oxide–semiconductor integrated circuit chips. In the past, processors were constructed using multiple individual vacuum tubes, multiple individual transistors, or multiple integrated circuits. The term is frequently used to refer to the central processing unit (CPU), the main processor in a system. However, it can also refer to other coprocessors, such as a graphics processing unit (GPU). Traditional processors are typically based on silicon; however, researchers have developed experimental processors based on alternative materials such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, diamond, and alloys made of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centralized
Centralisation or centralization (American English) is the process by which the activities of an organisation, particularly those regarding planning, decision-making, and framing strategies and policies, become concentrated within a particular group within that organisation. This creates a power structure where the said group occupies the highest level of hierarchy and has significantly more authority and influence over the other groups, who are considered its subordinates. An antonym of ''centralisation'' is '' decentralisation'', where authority is shared among numerous different groups, allowing varying degree of autonomy for each. The term has a variety of meanings in several fields. In political science, centralisation refers to the concentration of a government's power—both geographically and politically—into a centralised government, which has sovereignty over all its administrative divisions. Conversely, a decentralised system of government often has significant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
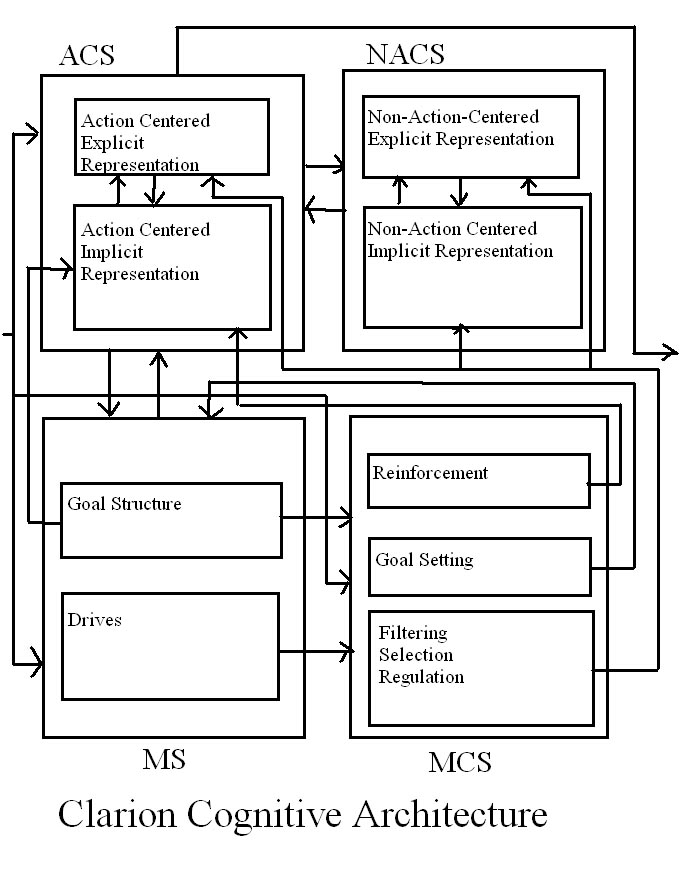
CLARION (cognitive Architecture)
Connectionist Learning with Adaptive Rule Induction On-line (CLARION) is a computational cognitive architecture that has been used to simulate many domains and tasks in cognitive psychology and social psychology, as well as implementing intelligent systems in artificial intelligence applications. An important feature of CLARION is the distinction between implicit and explicit processes and focusing on capturing the interaction between these two types of processes. The system was created by the research group led by Ron Sun. Overview CLARION is an integrative cognitive architecture. It is used to explain and simulate cognitive-psychological phenomena, which could potentially lead to an unified explanation of psychological phenomena. There are three layers to the CLARION theory. The first layer is the core theory of mind. The main theories consists of a number of distinct subsystems, which are the essential structures of CLARION, with a dual representational structure in each su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computationalism
In philosophy of mind, the computational theory of mind (CTM), also known as computationalism, is a family of views that hold that the human mind is an information processing system and that cognition and consciousness together are a form of computation. It is closely related to functionalism, a broader theory that defines mental states by what they do rather than what they are made of. Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts (1943) were the first to suggest that neural activity is computational. They argued that neural computations explain cognition. The theory was proposed in its modern form by Hilary Putnam in 1960 and 1961, and then developed by his PhD student, philosopher, and cognitive scientist Jerry Fodor in the 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s.Horst, Steven, (2005"The Computational Theory of Mind"in ''The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' It was later criticized in the 1990s by Putnam himself, John Searle, and others. The computational theory of mind holds that the human mind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Processing Language
Information Processing Language (IPL) is a programming language created by Allen Newell, Cliff Shaw, and Herbert A. Simon at RAND Corporation and the Carnegie Institute of Technology about 1956. Newell had the job of language specifier-application programmer, Shaw was the system programmer, and Simon had the job of application programmer-user. IPL included features to facilitate AI programming, specifically problem solving. such as lists, dynamic memory allocation, data types, recursion, functions as arguments, generators, and cooperative multitasking. IPL also introduced the concepts of symbol processing and list processing. Unfortunately, all of these innovations were cast in a difficult assembly-language style. Nontheless, IPL-V (the only public version of IPL) ran on many computers through the mid 1960s. Basics of IPL An IPL computer has: # A set of ''symbols''. All symbols are addresses, and name cells. Unlike symbols in later languages, symbols consist of a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitivism (psychology)
In psychology, cognitivism is a theoretical framework for understanding the mind that gained credence in the 1950s. The movement was a response to behaviorism, which cognitivists said neglected to explain cognition. Cognitive psychology derived its name from the Latin ''cognoscere'', referring to knowing and information, thus cognitive psychology is an information-processing psychology derived in part from earlier traditions of the investigation of thought and problem solving. Behaviorists acknowledged the existence of thinking but identified it as a behavior. Cognitivists argued that the way people think impacts their behavior and therefore cannot be a behavior in and of itself. Cognitivists later claimed that thinking is so essential to psychology that the study of thinking should become its own field. However, cognitivists typically presuppose a specific form of mental activity, of the kind advanced by computationalism. Cognitivism has more recently been challenged by po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid Intelligent System
Hybrid intelligent system denotes a software system which employs, in parallel, a combination of methods and techniques from artificial intelligence subfields, such as: * Neuro-symbolic systems * Neuro-fuzzy systems * Hybrid connectionist-symbolic models * Fuzzy expert systems * Connectionist expert systems * Evolutionary neural networks * Genetic fuzzy systems * Rough fuzzy hybridization * Reinforcement learning with fuzzy, neural, or evolutionary methods as well as symbolic reasoning methods. From the cognitive science perspective, every natural intelligent system is hybrid because it performs mental operations on both the symbolic and subsymbolic levels. For the past few years, there has been an increasing discussion of the importance of A.I. Systems Integration. Based on notions that there have already been created simple and specific AI systems (such as systems for computer vision, speech synthesis, etc., or software that employs some of the models mentioned above) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |