|
Cobalt(II) Bromide
Cobalt(II) bromide (CoBr2) is an inorganic compound. In its anhydrous form, it is a green solid that is soluble in water, used primarily as a catalyst in some processes. Properties When anhydrous, cobalt(II) bromide appears as green crystals. It is hygroscopic and forms the hexahydrate in air, which appears as red-purple crystals. The hexahydrate loses four water of crystallization molecules at 100 °C forming the dihydrate: :CoBr2·6H2O → CoBr2·2H2O + 4 H2O Further heating to 130 °C produces the anhydrous form: :CoBr2·2H2O → CoBr2 + 2 H2O The anhydrous form melts at 678 °C. At higher temperatures, cobalt(II) bromide reacts with oxygen, forming cobalt(II,III) oxide and bromine vapor. Preparation Cobalt(II) bromide can be prepared as a hydrate by the reaction of cobalt hydroxide with hydrobromic acid: :Co(OH)2(s) + 2HBr(aq) → CoBr2·6H2O(aq) Reactions and uses The classical coordination compound bromopentaamminecobalt(III) bromide is prep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the ordered arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystal, crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from the intrinsic nature of the constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of Three-dimensional space (mathematics), three-dimensional space in matter. The smallest group of particles in the material that constitutes this repeating pattern is the unit cell of the structure. The unit cell completely reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal, which is built up by repetitive Translation (geometry), translation of the unit cell along its principal axes. The translation vectors define the nodes of the Bravais lattice. The lengths of the principal axes, or edges, of the unit cell and the angles between them are the lattice constants, also called ''lattice parameters'' or ''cell parameters''. The symmetry properties of the crystal are described by the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hygroscopy
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption or adsorption from the surrounding environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water molecules become suspended among the substance's molecules, adsorbing substances can become physically changed, e.g., changing in volume, boiling point, viscosity or some other physical characteristic or property of the substance. For example, a finely dispersed hygroscopic powder, such as a salt, may become clumpy over time due to collection of moisture from the surrounding environment. ''Deliquescent'' materials are sufficiently hygroscopic that they absorb so much water that they become liquid and form an aqueous solution. Etymology and pronunciation The word ''hygroscopy'' () uses combining forms of '' hygro-'' and '' -scopy''. Unlike any other ''-scopy'' word, it no longer refers to a viewing or imaging mode. It did begin that way, with the word ''hygroscope'' referring in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobalt(II) Compounds
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal. Cobalt-based blue pigments (cobalt blue) have been used since ancient times for jewelry and paints, and to impart a distinctive blue tint to glass, but the color was for a long time thought to be due to the known metal bismuth. Miners had long used the name ''kobold ore'' (German for ''goblin ore'') for some of the blue-pigment-producing minerals; they were so named because they were poor in known metals, and gave poisonous arsenic-containing fumes when smelted. In 1735, such ores were found to be reducible to a new metal (the first discovered since ancient times), and this was ultimately named for the ''kobold''. Today, some cobalt is produced specifically from one of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobalt Poisoning
Cobalt poisoning is intoxication caused by excessive levels of cobalt in the body. Cobalt is an essential element for health in animals in minute amounts as a component of Vitamin B. A deficiency of cobalt, which is very rare, is also potentially lethal, leading to pernicious anemia. Exposure to cobalt metal dust is most common in the fabrication of tungsten carbide. Another source is from wear and tear of certain metal-on-metal hip prostheses. Per the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), cobalt metal with tungsten carbide is "''probably carcinogenic to humans''" ( IARC Group 2A Agent), whereas cobalt metal without tungsten carbide is "''possibly carcinogenic to humans''" ( IARC Group 2B Agent). Cobalt salts The value for soluble cobalt salts has been estimated to be between 150 and 500 mg/kg. Thus, for a 100 kg person the LD50 would be about 20 grams. Soluble cobalt(II) salts are "''possibly carcinogenic to humans''" ( IARC Group 2B Agents). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
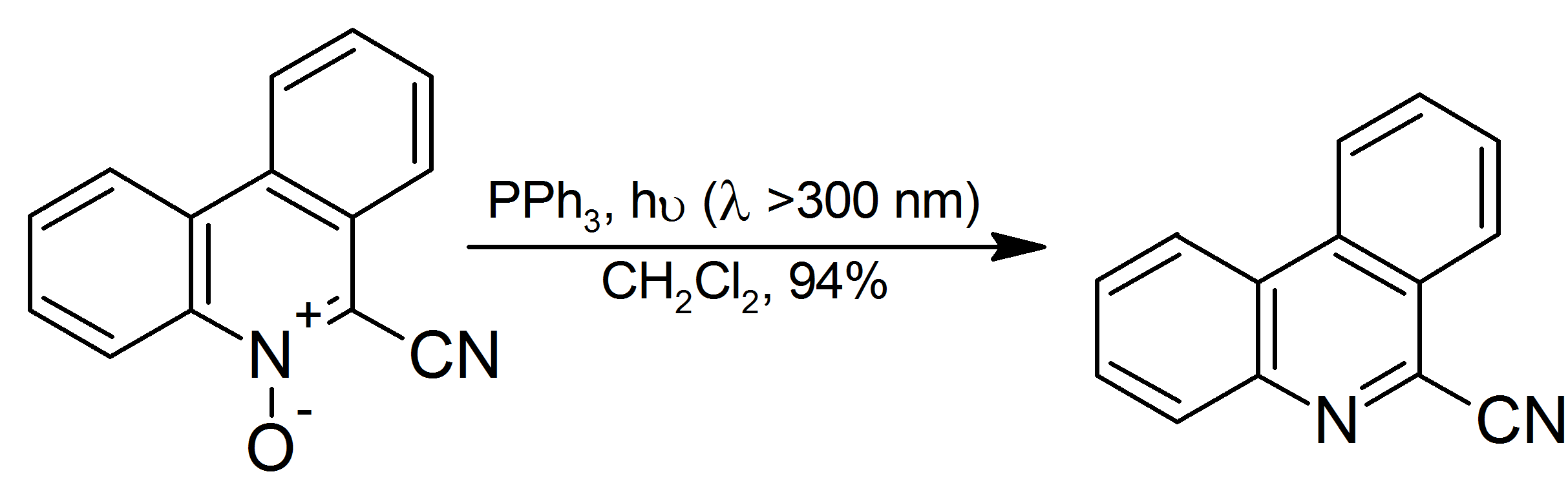
Triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to P Ph3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether. Preparation and structure Triphenylphosphine can be prepared in the laboratory by treatment of phosphorus trichloride with phenylmagnesium bromide or phenyllithium. The industrial synthesis involves the reaction between phosphorus trichloride, chlorobenzene, and sodium: :PCl3 + 3 PhCl + 6 Na → PPh3 + 6 NaCl Triphenylphosphine crystallizes in triclinic and monoclinic modification. In both cases, the molecule adopts a pyramidal structure with propeller-like arrangement of the three phenyl groups. Principal reactions with chalcogens, halogens, and acids Oxidation Triphenylphosphine undergoes slow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromopentaamminecobalt(III) Bromide
Bromopentaamminecobalt(III) bromide is the dibromide salt of the cobalt coordination compound with the formula o(NH3)5Brsup>2+. It is a purple, water-soluble solid. The analogous chloropentaamminecobalt(III) chloride is also well known. Synthesis and reactions The title compound is prepared by oxidation of a solution of cobalt(II) salts in aqueous ammonia. :2 CoBr2 + 8 NH3 + 2 NH4Br + H2O2 → 2 o(NH3)5Brr2 + 2 H2O It was first reported in the 1870s, before the structure or even formulae were understood for such complexes. This early work showed that only two thirds of the bromide groups were exchangeable with other anions such as nitrate and dithionate The dithionate (or metabisulfate) anion, , is a sulfur oxoanion derived from dithionic acid, H2S2O6. Its chemical formula is sometimes written in a semistructural format, as 3SSO3sup>2−. It is the first member of the polythionates. The sul .... The complex undergoes aquation, meaning that bromide is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Compound
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom are common. These compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrobromic Acid
Hydrobromic acid is a strong acid formed by dissolving the diatomic molecule hydrogen bromide (HBr) in water. "Constant boiling" hydrobromic acid is an aqueous solution that distills at and contains 47.6% HBr by mass, which is 8.77 mol/L. Hydrobromic acid has a p''K''a of −9, making it a stronger acid than hydrochloric acid, but not as strong as hydroiodic acid. Hydrobromic acid is one of the strongest mineral acids known. Uses Hydrobromic acid is mainly used for the production of inorganic bromides, especially the bromides of zinc, calcium, and sodium. It is a useful reagent for generating organobromine compounds. Certain ethers are cleaved with HBr. It also catalyzes alkylation reactions and the extraction of certain ores. Industrially significant organic compounds prepared from hydrobromic acid include allyl bromide, tetrabromobis(phenol), and bromoacetic acid. HBr almost uniquely participates in anti-Markovnikov hydrohalogenation of alkenes. The resulting 1-bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobalt Hydroxide
Cobalt(II) hydroxide or cobaltous hydroxide is the inorganic compound with the formula , consisting of divalent cobalt cations and hydroxide anions . The pure compound, often called the "beta form" (β-) is a pink solid insoluble in water. The name is also applied to a related compound, often called "alpha" or "blue" form (α-), which incorporates other anions in its molecular structure. This compound is blue and rather unstable.Xiaohe Liu, Ran Yi, Ning Zhang, Rongrong Shi, Xingguo Li, and Guanzhou Qiu (2008): "Cobalt hydroxide nanosheets and their thermal decomposition to cobalt oxide nanorings". ''Chemistry: An Asian Journal'', volume 3, issue 4, pages 732-738. Cobalt(II) hydroxide is most used as a drying agent for paints, varnishes, and inks, in the preparation of other cobalt compounds, as a catalyst and in the manufacture of battery electrodes. Preparation Cobalt(II) hydroxide precipitates as a solid when an alkali metal hydroxide is added to an aqueous solution of Co2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table (halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between those of chlorine and iodine. Isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig (in 1825) and Antoine Jérôme Balard (in 1826), its name was derived from the Ancient Greek (bromos) meaning "stench", referring to its sharp and pungent smell. Elemental bromine is very reactive and thus does not occur as a native element in nature but it occurs in colourless soluble crystalline mineral halide salts, analogous to table salt. In fact, bromine and all the halogens are so reactive that they form bonds in pairs—never in single atoms. While it is rather rare in the Earth's crust, the high solubility of the bromide ion (Br) has caused its accumulation in the oceans. Commercial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobalt(II,III) Oxide
Cobalt(II,III) oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula Co3O4. It is one of two well characterized cobalt oxides. It is a black antiferromagnetic solid. As a mixed valence compound, its formula is sometimes written as CoIICoIII2O4 and sometimes as CoO•Co2O3. Structure Co3O4 adopts the normal spinel structure, with Co2+ ions in tetrahedral interstices and Co3+ ions in the octahedral interstices of the cubic close-packed lattice of oxide anions. Synthesis Cobalt(II) oxide, CoO, converts to Co3O4 upon heating at around 600–700 °C in air. Above 900 °C, CoO is stable. These reaction are described by the following equilibrium: :2 Co3O4 6 CoO + O2 Applications Cobalt(II,III) oxide is used as a blue coloring agent for pottery enamel and glass, as an alternative to cobalt(II) oxide.Frank Hamer, Janet Hamer (2004)''The Potter's Dictionary of Materials and Techniques'' University of Pennsylvania Press; 437 pp. Cobalt(II,III) oxide is used as an elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen is Earth's most abundant element, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bind to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the formula . Diatomic oxygen gas currently constitutes 20.95% of the Earth's atmosphere, though this has changed considerably over long periods of time. Oxygen makes up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of oxides.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. Many major classes of organic molecules in living organisms contain oxygen atoms, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and fats, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






-oxide-xtal-2006-Co(II)-coord-CM-3D-balls.png)
