|
Co-clustering
Biclustering, block clustering, Co-clustering or two-mode clustering is a data mining technique which allows simultaneous clustering of the rows and columns of a matrix. The term was first introduced by Boris Mirkin to name a technique introduced many years earlier, in 1972, by J. A. Hartigan. Given a set of m samples represented by an n-dimensional feature vector, the entire dataset can be represented as m rows in n columns (i.e., an m \times n matrix). The Biclustering algorithm generates Biclusters, a subset of rows which exhibit similar behavior across a subset of columns, or vice versa. Development Biclustering was originally introduced by J. A. Hartigan in 1972. The term "Biclustering" was then later used and refined by Mirkin. This algorithm was not generalized until 2000, when Y. Cheng and G. M. Church proposed a Biclustering algorithm based on variance and applied it to biological gene expression data. In 2001 and 2003, I.S. Dhillon published two algorithms applyin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicluster
Biclustering, block clustering, Co-clustering or two-mode clustering is a data mining technique which allows simultaneous clustering of the rows and columns of a matrix. The term was first introduced by Boris Mirkin to name a technique introduced many years earlier, in 1972, by J. A. Hartigan. Given a set of m samples represented by an n-dimensional feature vector, the entire dataset can be represented as m rows in n columns (i.e., an m \times n matrix). The Biclustering algorithm generates Biclusters, a subset of rows which exhibit similar behavior across a subset of columns, or vice versa. Development Biclustering was originally introduced by J. A. Hartigan in 1972. The term "Biclustering" was then later used and refined by Mirkin. This algorithm was not generalized until 2000, when Y. Cheng and G. M. Church proposed a Biclustering algorithm based on variance and applied it to biological gene expression data. In 2001 and 2003, I.S. Dhillon published two algorithms applying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time-series Data
In mathematics, a time series is a series of data points indexed (or listed or graphed) in time order. Most commonly, a time series is a sequence taken at successive equally spaced points in time. Thus it is a sequence of discrete-time data. Examples of time series are heights of ocean tides, counts of sunspots, and the daily closing value of the Dow Jones Industrial Average. A time series is very frequently plotted via a run chart (which is a temporal line chart). Time series are used in statistics, signal processing, pattern recognition, econometrics, mathematical finance, weather forecasting, earthquake prediction, electroencephalography, control engineering, astronomy, communications engineering, and largely in any domain of applied science and engineering which involves temporal measurements. Time series ''analysis'' comprises methods for analyzing time series data in order to extract meaningful statistics and other characteristics of the data. Time series ''forecasting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Super-majority
A supermajority, supra-majority, qualified majority, or special majority is a requirement for a proposal to gain a specified level of support which is greater than the threshold of more than one-half used for a simple majority. Supermajority rules in a democracy can help to prevent a majority from eroding fundamental rights of a minority, but they can also hamper efforts to respond to problems and encourage corrupt compromises in the times action is taken. Changes to constitutions, especially those with entrenched clauses, commonly require supermajority support in a legislature. Parliamentary procedure requires that any action of a deliberative assembly that may alter the rights of a minority have a supermajority requirement, such as a two-thirds vote. Related concepts regarding alternatives to the majority vote requirement include a majority of the entire membership and a majority of the fixed membership. A supermajority can also be specified based on the entire membership or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold Standard (test)
In medicine and statistics, a gold standard test is usually the diagnostic test or benchmark that is the best available under reasonable conditions. In other words, a gold standard is the most accurate test possible without restrictions. Both meanings are different because for example, in medicine, dealing with conditions that would require an autopsy to have a perfect diagnosis, the gold standard test would be the best one that keeps the patient alive instead of the autopsy. In medicine "Gold standard" can refer to the criteria by which scientific evidence is evaluated. For example, in resuscitation research, the "gold standard" test of a medication or procedure is whether or not it leads to an increase in the number of neurologically intact survivors that walk out of the hospital.''ACLS: Principles and Practice''. p. 62. Dallas: American Heart Association, 2003. . Other types of medical research might regard a significant decrease in 30-day mortality as the gold standard. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
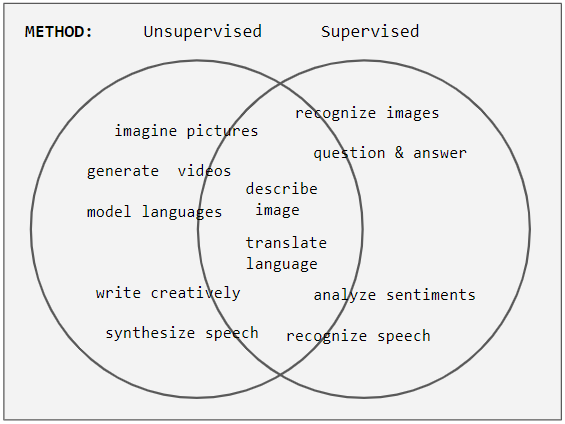
Unsupervised Classification
Unsupervised learning is a type of algorithm that learns patterns from untagged data. The hope is that through mimicry, which is an important mode of learning in people, the machine is forced to build a concise representation of its world and then generate imaginative content from it. In contrast to supervised learning where data is tagged by an expert, e.g. tagged as a "ball" or "fish", unsupervised methods exhibit self-organization that captures patterns as probability densities or a combination of neural feature preferences encoded in the machine's weights and activations. The other levels in the supervision spectrum are reinforcement learning where the machine is given only a numerical performance score as guidance, and semi-supervised learning where a small portion of the data is tagged. Neural networks Tasks vs. methods Neural network tasks are often categorized as discriminative (recognition) or generative (imagination). Often but not always, discriminative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minima
In mathematical analysis, the maxima and minima (the respective plurals of maximum and minimum) of a function, known collectively as extrema (the plural of extremum), are the largest and smallest value of the function, either within a given range (the ''local'' or ''relative'' extrema), or on the entire domain (the ''global'' or ''absolute'' extrema). Pierre de Fermat was one of the first mathematicians to propose a general technique, adequality, for finding the maxima and minima of functions. As defined in set theory, the maximum and minimum of a set are the greatest and least elements in the set, respectively. Unbounded infinite sets, such as the set of real numbers, have no minimum or maximum. Definition A real-valued function ''f'' defined on a domain ''X'' has a global (or absolute) maximum point at ''x''∗, if for all ''x'' in ''X''. Similarly, the function has a global (or absolute) minimum point at ''x''∗, if for all ''x'' in ''X''. The value of the fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Datatype
In computer science and computer programming, a data type (or simply type) is a set of possible values and a set of allowed operations on it. A data type tells the compiler or interpreter how the programmer intends to use the data. Most programming languages support basic data types of integer numbers (of varying sizes), floating-point numbers (which approximate real numbers), characters and Booleans. A data type constrains the possible values that an expression, such as a variable or a function, might take. This data type defines the operations that can be done on the data, the meaning of the data, and the way values of that type can be stored. Concept A data type is a collection or grouping of data values. Such a grouping may be defined for many reasons: similarity, convenience, or to focus the attention. It is frequently a matter of good organization that aids the understanding of complex definitions. Almost all programming languages explicitly include the notion of da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffix Tree
In computer science, a suffix tree (also called PAT tree or, in an earlier form, position tree) is a compressed trie containing all the suffixes of the given text as their keys and positions in the text as their values. Suffix trees allow particularly fast implementations of many important string operations. The construction of such a tree for the string S takes time and space linear in the length of S. Once constructed, several operations can be performed quickly, for instance locating a substring in S, locating a substring if a certain number of mistakes are allowed, locating matches for a regular expression pattern etc. Suffix trees also provide one of the first linear-time solutions for the longest common substring problem. These speedups come at a cost: storing a string's suffix tree typically requires significantly more space than storing the string itself. History The concept was first introduced by . Rather than the suffix S ..n/math>, Weiner stored in his trie the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String Processing
String functions are used in computer programming languages to manipulate a string or query information about a string (some do both). Most programming languages that have a string datatype will have some string functions although there may be other low-level ways within each language to handle strings directly. In object-oriented languages, string functions are often implemented as properties and methods of string objects. In functional and list-based languages a string is represented as a list (of character codes), therefore all list-manipulation procedures could be considered string functions. However such languages may implement a subset of explicit string-specific functions as well. For function that manipulate strings, modern object-oriented languages, like C# and Java have immutable strings and return a copy (in newly allocated dynamic memory), while others, like C manipulate the original string unless the programmer copies data to a new string. See for example Concate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression consisting of indeterminates (also called variables) and coefficients, that involves only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and positive-integer powers of variables. An example of a polynomial of a single indeterminate is . An example with three indeterminates is . Polynomials appear in many areas of mathematics and science. For example, they are used to form polynomial equations, which encode a wide range of problems, from elementary word problems to complicated scientific problems; they are used to define polynomial functions, which appear in settings ranging from basic chemistry and physics to economics and social science; they are used in calculus and numerical analysis to approximate other functions. In advanced mathematics, polynomials are used to construct polynomial rings and algebraic varieties, which are central concepts in algebra and algebraic geometry. Etymology The word ''polynomial'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can perform automated deductions (referred to as automated reasoning) and use mathematical and logical tests to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making). Using human characteristics as descriptors of machines in metaphorical ways was already practiced by Alan Turing with terms such as "memory", "search" and "stimulus". In contrast, a heuristic is an approach to problem solving that may not be fully specified or may not guarantee correct or optimal results, especially in problem domains where there is no well-defined correct or optimal result. As an effective method, an algorithm can be expressed within a finite amount of spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |