|
Closed-end Funds
A closed-end fund (CEF) is a fund that raises capital by issuing a fixed number of shares which are not redeemable, and then invest that capital in financial assets such as stocks and bonds. Unlike open-end funds, new shares in a closed-end fund are not created by managers to meet demand from investors. Instead, the shares can be purchased and sold only in the market, which is the original design of the mutual fund, which predates open-end mutual funds but offers the same actively-managed pooled investments. In the United States, closed-end funds sold publicly must be registered under both the Securities Act of 1933 and the Investment Company Act of 1940. Closed-end funds are usually listed on a recognized stock exchange and can be bought and sold on that exchange. The price per share is determined by the market and is usually different from the underlying value or net asset value (NAV) per share of the investments held by the fund. The price is said to be at a discount or premi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open-end Fund
Open-end fund (or open-ended fund) is a collective investment scheme that can issue and redeem shares at any time. An investor will generally purchase shares in the fund directly from the fund itself, rather than from the existing shareholders. The term contrasts with a closed-end fund, which typically issues at the outset all the shares that it will issue, with such shares usually thereafter being tradable among investors. Open-ended funds are available in most developed countries, but the terminology and operating rules vary. US mutual funds, UK unit trusts and OEICs, European SICAVs, and hedge funds are all examples of open-ended funds. The price at which shares in an open-ended fund are issued or can be redeemed will vary in proportion to the net asset value of the fund and so directly reflects its performance. Fees There may be a percentage charge levied on the purchase of shares or units. Some of these fees are called an initial charge (UK) or 'front-end load' (US). So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NYSE
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE, nicknamed "The Big Board") is an American stock exchange in the Financial District, Manhattan, Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It is by far the List of stock exchanges, world's largest stock exchange by market capitalization of its listed companies at US$30.1 trillion as of February 2018. The average daily trading value was approximately 169 billion in 2013. The NYSE Trading room, trading floor is at the New York Stock Exchange Building on 11 Wall Street and 18 Broad Street (Manhattan), Broad Street and is a National Historic Landmark. An additional trading room, at 30 Broad Street, was closed in February 2007. The NYSE is owned by Intercontinental Exchange, an American holding company that it also lists (). Previously, it was part of NYSE Euronext (NYX), which was formed by the NYSE's 2007 merger with Euronext. History The earliest recorded organization of Security (finance), securities trading in New York ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listed Investment Company
A listed investment company (LIC) is an Australian '' closed-end'' collective investment scheme similar to investment trusts in the UK and closed-end funds in the United States. Instead of regularly issuing new shares or canceling shares as investors join and leave the fund, investors buy and sell to each other on the ASX. They are traded like other securities on the Australian stock exchange. See also * Collective investment schemes for generic information. Advantages * Listed Investment Companies are a closed end investment, meaning that management do not have to worry about people withdrawing funds. If people wish to exit the investment they can simply sell their shares, without affecting the amount of funds under management. This allows for management to take a more long term approach to investing if deemed favourable (Viney, 2007). * Traditional LICs employ this buy and hold strategy which can result in tax advantages (for example Australia's system of paying capital gains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutual Fund
A mutual fund is a professionally managed investment fund that pools money from many investors to purchase securities. The term is typically used in the United States, Canada, and India, while similar structures across the globe include the SICAV in Europe ('investment company with variable capital') and open-ended investment company (OEIC) in the UK. Mutual funds are often classified by their principal investments: money market funds, bond or fixed income funds, stock or equity funds, or hybrid funds. Funds may also be categorized as index funds, which are passively managed funds that track the performance of an index, such as a stock market index or bond market index, or actively managed funds, which seek to outperform stock market indices but generally charge higher fees. Primary structures of mutual funds are open-end funds, closed-end funds, unit investment trusts. Open-end funds are purchased from or sold to the issuer at the net asset value of each share as of the close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Investment Trust
An investment trust is a form of investment fund found mostly in the United Kingdom and Japan. Investment trusts are constituted as public limited companies and are therefore closed ended since the fund managers cannot redeem or create shares. The first investment trust was the Foreign & Colonial Investment Trust, started in 1868 "to give the investor of moderate means the same advantages as the large capitalists in diminishing the risk by spreading the investment over a number of stocks". In many respects, the investment trust was the progenitor of the investment company in the U.S. The name is somewhat misleading, given that (according to law) an investment "trust" is not in fact a "trust" in the legal sense at all, but a separate legal person or a company. This matters for the fiduciary duties owed by the board of directors and the equitable ownership of the fund's assets. In the United Kingdom, the term "investment trust" has a strict meaning under tax law. However, the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collective Investment Scheme
An investment fund is a way of investing money alongside other investors in order to benefit from the inherent advantages of working as part of a group such as reducing the risks of the investment by a significant percentage. These advantages include an ability to: * hire professional investment managers, who may offer better returns and more adequate risk management; * benefit from economies of scale, i.e., lower transaction costs; * increase the asset diversification to reduce some unsystematic risk. It remains unclear whether professional active investment managers can reliably enhance risk adjusted returns by an amount that exceeds fees and expenses of investment management. Terminology varies with country but investment funds are often referred to as investment pools, collective investment vehicles, collective investment schemes, managed funds, or simply funds. The regulatory term is undertaking for collective investment in transferable securities, or short collective invest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Mortgage Investment Trust
Scottish Mortgage Investment Trust is a publicly traded investment trust. It invests globally, looking for strong businesses with above-average returns. Scottish Mortgage is managed by Baillie Gifford & Co Limited, the Edinburgh-based investment management partnership. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. History The origins of Scottish Mortgage lie in a credit crisis, the Panic of 1907. By 1909 the growing popularity of the motorcar, including the Model T Ford The Ford Model T is an automobile that was produced by Ford Motor Company from October 1, 1908, to May 26, 1927. It is generally regarded as the first affordable automobile, which made car travel available to middle-class Americans. The relati ..., was creating significant demand for tyres, which rubber planters in Southeast Asia were keen to exploit, but credit was still difficult to obtain. In Edinburgh, the recently formed legal partnership between Colonel Augustus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adams Express Company
Adams Funds, formerly Adams Express Company, is an investment company made up of Adams Diversified Equity Fund, Inc.(NYSE: ADX), a publicly traded diversified equity fund, and Adams Natural Resources Fund Inc. (NYSE: PEO), formerly Petroleum & Resources Corp., a publicly traded closed-end fund focused on energy and natural resources stocks. Adams Funds traces its roots to Adams Express Company, a 19th-century freight and cargo transport business that was part of the pony express system. It became an investment company in 1929, just prior to the October 1929 stock market crash. Adams survived the Great Depression and is now one of the oldest closed-end funds at 91 years old. The firm uses a disciplined investment process consisting of three core tenets: identifying high-quality companies through a proprietary research process; employing rigorous analysis to assess company fundamentals; and executing a portfolio management strategy focusing on generating long-term capital appreciatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arbitrage
In economics and finance, arbitrage (, ) is the practice of taking advantage of a difference in prices in two or more markets; striking a combination of matching deals to capitalise on the difference, the profit being the difference between the market prices at which the unit is traded. When used by academics, an arbitrage is a transaction that involves no negative cash flow at any probabilistic or temporal state and a positive cash flow in at least one state; in simple terms, it is the possibility of a risk-free profit after transaction costs. For example, an arbitrage opportunity is present when there is the possibility to instantaneously buy something for a low price and sell it for a higher price. In principle and in academic use, an arbitrage is risk-free; in common use, as in statistical arbitrage, it may refer to ''expected'' profit, though losses may occur, and in practice, there are always risks in arbitrage, some minor (such as fluctuation of prices decreasing profit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
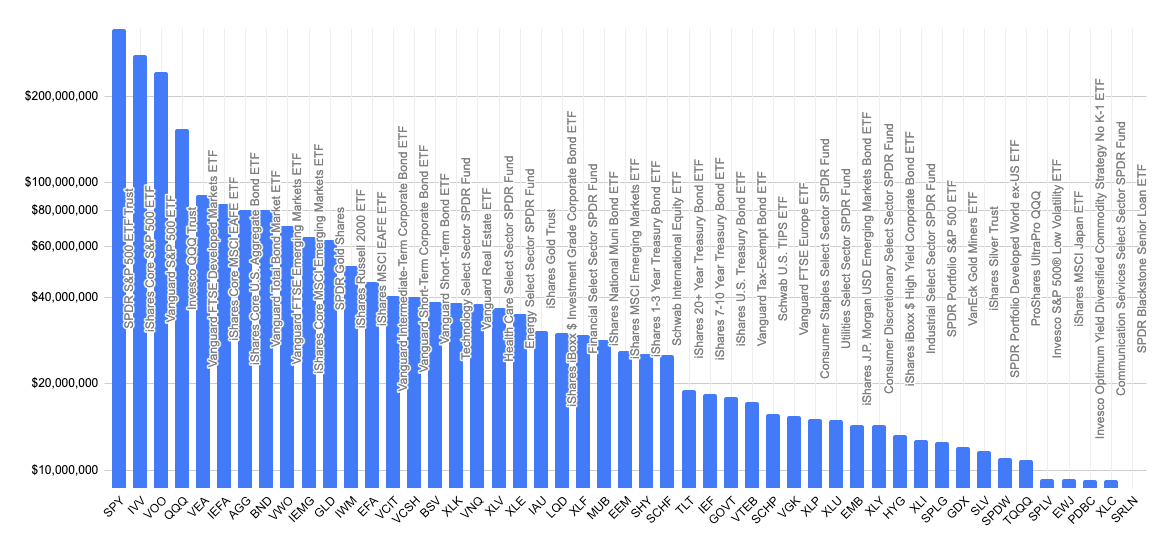
Exchange-traded Fund
An exchange-traded fund (ETF) is a type of investment fund and exchange-traded product, i.e. they are traded on stock exchanges. ETFs are similar in many ways to mutual funds, except that ETFs are bought and sold from other owners throughout the day on stock exchanges whereas mutual funds are bought and sold from the issuer based on their price at day's end. An ETF holds assets such as stocks, bonds, currencies, futures contracts, and/or commodities such as gold bars, and generally operates with an arbitrage mechanism designed to keep it trading close to its net asset value, although deviations can occasionally occur. Most ETFs are index funds: that is, they hold the same securities in the same proportions as a certain stock market index or bond market index. The most popular ETFs in the U.S. replicate the S&P 500, the total market index, the NASDAQ-100 index, the price of gold, the "growth" stocks in the Russell 1000 Index, or the index of the largest technology companies. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |