|
Circumconic
In Euclidean geometry, a circumconic is a conic section that passes through the three vertices of a triangle, and an inconic is a conic section inscribed in the sides, possibly extended, of a triangle.Weisstein, Eric W. "Inconic." From MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Inconic.html Suppose are distinct non-collinear points, and let denote the triangle whose vertices are . Following common practice, denotes not only the vertex but also the angle at vertex , and similarly for and as angles in . Let a= , BC, , b=, CA, , c=, AB, , the sidelengths of . In trilinear coordinates, the general circumconic is the locus of a variable point X = x:y:z satisfying an equation :uyz + vzx + wxy = 0, for some point . The isogonal conjugate of each point on the circumconic, other than , is a point on the line :ux + vy + wz = 0. This line meets the circumcircle of in 0,1, or 2 points according as the circumconic is an ellipse, parabola, or hyperbola. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excircle
In geometry, the incircle or inscribed circle of a triangle is the largest circle that can be contained in the triangle; it touches (is tangent to) the three sides. The center of the incircle is a triangle center called the triangle's incenter. An excircle or escribed circle of the triangle is a circle lying outside the triangle, tangent to one of its sides and tangent to the extensions of the other two. Every triangle has three distinct excircles, each tangent to one of the triangle's sides. The center of the incircle, called the incenter, can be found as the intersection of the three internal angle bisectors. The center of an excircle is the intersection of the internal bisector of one angle (at vertex , for example) and the external bisectors of the other two. The center of this excircle is called the excenter relative to the vertex , or the excenter of . Because the internal bisector of an angle is perpendicular to its external bisector, it follows that the center of the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
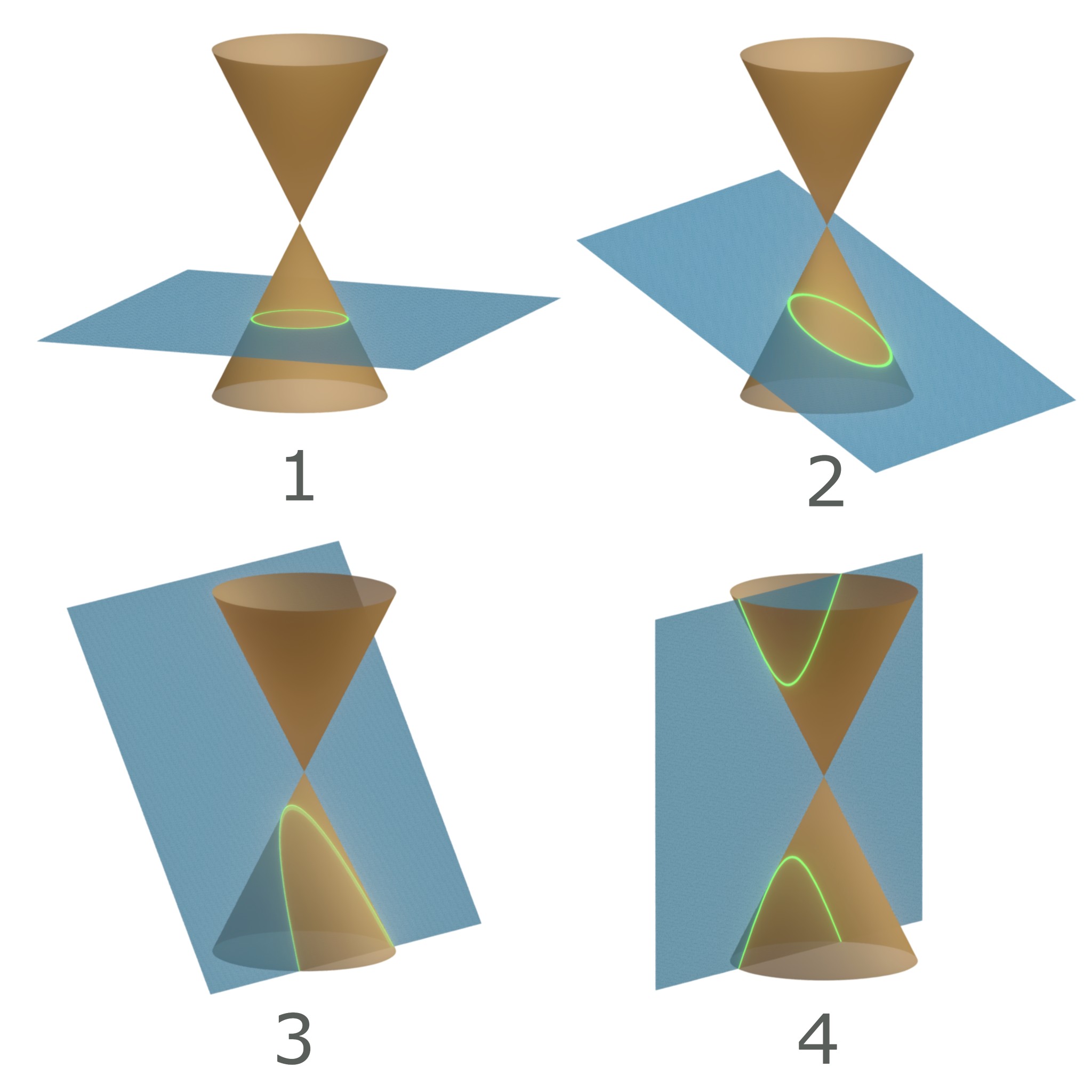
Conic Section
In mathematics, a conic section, quadratic curve or conic is a curve obtained as the intersection of the surface of a cone with a plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a special case of the ellipse, though historically it was sometimes called a fourth type. The ancient Greek mathematicians studied conic sections, culminating around 200 BC with Apollonius of Perga's systematic work on their properties. The conic sections in the Euclidean plane have various distinguishing properties, many of which can be used as alternative definitions. One such property defines a non-circular conic to be the set of those points whose distances to some particular point, called a ''focus'', and some particular line, called a ''directrix'', are in a fixed ratio, called the ''eccentricity''. The type of conic is determined by the value of the eccentricity. In analytic geometry, a conic may be defined as a plane algebraic curve of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inscribed Figure
{{unreferenced, date=August 2012 An inscribed triangle of a circle In geometry, an inscribed planar shape or solid is one that is enclosed by and "fits snugly" inside another geometric shape or solid. To say that "figure F is inscribed in figure G" means precisely the same thing as "figure G is circumscribed about figure F". A circle or ellipse inscribed in a convex polygon (or a sphere or ellipsoid inscribed in a convex polyhedron) is tangent to every side or face of the outer figure (but see Inscribed sphere for semantic variants). A polygon inscribed in a circle, ellipse, or polygon (or a polyhedron inscribed in a sphere, ellipsoid, or polyhedron) has each vertex on the outer figure; if the outer figure is a polygon or polyhedron, there must be a vertex of the inscribed polygon or polyhedron on each side of the outer figure. An inscribed figure is not necessarily unique in orientation; this can easily be seen, for example, when the given outer figure is a circle, in which case ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incircle
In geometry, the incircle or inscribed circle of a triangle is the largest circle that can be contained in the triangle; it touches (is tangent to) the three sides. The center of the incircle is a triangle center called the triangle's incenter. An excircle or escribed circle of the triangle is a circle lying outside the triangle, tangent to one of its sides and tangent to the extensions of the other two. Every triangle has three distinct excircles, each tangent to one of the triangle's sides. The center of the incircle, called the incenter, can be found as the intersection of the three internal angle bisectors. The center of an excircle is the intersection of the internal bisector of one angle (at vertex , for example) and the external bisectors of the other two. The center of this excircle is called the excenter relative to the vertex , or the excenter of . Because the internal bisector of an angle is perpendicular to its external bisector, it follows that the center of the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trilinear Coordinates
In geometry, the trilinear coordinates of a point relative to a given triangle describe the relative directed distances from the three sidelines of the triangle. Trilinear coordinates are an example of homogeneous coordinates. The ratio is the ratio of the perpendicular distances from the point to the sides (extended if necessary) opposite vertices and respectively; the ratio is the ratio of the perpendicular distances from the point to the sidelines opposite vertices and respectively; and likewise for and vertices and . In the diagram at right, the trilinear coordinates of the indicated interior point are the actual distances (, , ), or equivalently in ratio form, for any positive constant . If a point is on a sideline of the reference triangle, its corresponding trilinear coordinate is 0. If an exterior point is on the opposite side of a sideline from the interior of the triangle, its trilinear coordinate associated with that sideline is negative. It is impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Triangle
In Euclidean geometry, the medial triangle or midpoint triangle of a triangle is the triangle with vertices at the midpoints of the triangle's sides . It is the case of the midpoint polygon of a polygon with sides. The medial triangle is not the same thing as the median triangle, which is the triangle whose sides have the same lengths as the medians of . Each side of the medial triangle is called a ''midsegment'' (or ''midline''). In general, a midsegment of a triangle is a line segment which joins the midpoints of two sides of the triangle. It is parallel to the third side and has a length equal to half the length of the third side. Properties The medial triangle can also be viewed as the image of triangle transformed by a homothety centered at the centroid with ratio -1/2. Thus, the sides of the medial triangle are half and parallel to the corresponding sides of triangle ABC. Hence, the medial triangle is inversely similar and shares the same centroid and medians with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipse
In mathematics, an ellipse is a plane curve surrounding two focus (geometry), focal points, such that for all points on the curve, the sum of the two distances to the focal points is a constant. It generalizes a circle, which is the special type of ellipse in which the two focal points are the same. The elongation of an ellipse is measured by its eccentricity (mathematics), eccentricity e, a number ranging from e = 0 (the Limiting case (mathematics), limiting case of a circle) to e = 1 (the limiting case of infinite elongation, no longer an ellipse but a parabola). An ellipse has a simple algebraic solution for its area, but only approximations for its perimeter (also known as circumference), for which integration is required to obtain an exact solution. Analytic geometry, Analytically, the equation of a standard ellipse centered at the origin with width 2a and height 2b is: : \frac+\frac = 1 . Assuming a \ge b, the foci are (\pm c, 0) for c = \sqrt. The standard parametric e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euclidean Geometry
Euclidean geometry is a mathematical system attributed to ancient Greek mathematics, Greek mathematician Euclid, which he described in his textbook on geometry: the ''Euclid's Elements, Elements''. Euclid's approach consists in assuming a small set of intuitively appealing axioms (postulates) and deducing many other propositions (theorems) from these. Although many of Euclid's results had been stated earlier,. Euclid was the first to organize these propositions into a logic, logical system in which each result is ''mathematical proof, proved'' from axioms and previously proved theorems. The ''Elements'' begins with plane geometry, still taught in secondary school (high school) as the first axiomatic system and the first examples of mathematical proofs. It goes on to the solid geometry of three dimensions. Much of the ''Elements'' states results of what are now called algebra and number theory, explained in geometrical language. For more than two thousand years, the adjective " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthocenter
In geometry, an altitude of a triangle is a line segment through a vertex and perpendicular to (i.e., forming a right angle with) a line containing the base (the side opposite the vertex). This line containing the opposite side is called the ''extended base'' of the altitude. The intersection of the extended base and the altitude is called the ''foot'' of the altitude. The length of the altitude, often simply called "the altitude", is the distance between the extended base and the vertex. The process of drawing the altitude from the vertex to the foot is known as ''dropping the altitude'' at that vertex. It is a special case of orthogonal projection. Altitudes can be used in the computation of the area of a triangle: one half of the product of an altitude's length and its base's length equals the triangle's area. Thus, the longest altitude is perpendicular to the shortest side of the triangle. The altitudes are also related to the sides of the triangle through the trigonometri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiepert Conics
In triangle geometry, the Kiepert conics are two special conics associated with the reference triangle. One of them is a hyperbola, called the Kiepert hyperbola and the other is a parabola, called the Kiepert parabola. The Kiepert conics are defined as follows: :If the three triangles A^\prime BC, AB^\prime C and ABC^\prime, constructed on the sides of a triangle ABC as bases, are similar, isosceles and similarly situated, then the triangles ABC and A^\prime B^\prime C^\prime are in perspective. As the base angle of the isosceles triangles varies between -\pi/2 and \pi/2, the locus of the center of perspectivity of the triangles ABC and A^\prime B^\prime C^\prime is a hyperbola called the Kiepert hyperbola and the envelope of their axis of perspectivity is a parabola called the Kiepert parabola. It has been proved that the Kiepert hyperbola is the hyperbola passing through the vertices, the centroid and the orthocenter of the reference triangle and the Kiepert parabola is the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumcenter
In geometry, the circumscribed circle or circumcircle of a polygon is a circle that passes through all the vertices of the polygon. The center of this circle is called the circumcenter and its radius is called the circumradius. Not every polygon has a circumscribed circle. A polygon that does have one is called a cyclic polygon, or sometimes a concyclic polygon because its vertices are concyclic. All triangles, all regular simple polygons, all rectangles, all isosceles trapezoids, and all right kites are cyclic. A related notion is the one of a minimum bounding circle, which is the smallest circle that completely contains the polygon within it, if the circle's center is within the polygon. Every polygon has a unique minimum bounding circle, which may be constructed by a linear time algorithm. Even if a polygon has a circumscribed circle, it may be different from its minimum bounding circle. For example, for an obtuse triangle, the minimum bounding circle has the longest side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Václav Jeřábek
Václav Jeřábek (1845–1931) was a Czech mathematician, specialized in constructive geometry. Life and work Jeřábek studied at the lower school of Pardubice and at the higher school of Písek, then he was to Vienna and studied at Imperial and Royal Polytechnic Institute where he graduated. Although he participated in several leading intellectual circles of Vienna, he remained a Czech with a clear view of patriotism. He began his teaching at the ''Realschule'' of Litomyšl (1870), being transferred two years after to the ''Realschule'' of Telč. In 1881, he was appointed professor of the ''Czech Realschule'' in Brno, and became its director in 1901. He retired in 1907, and suffering of a cataract, he died almost completely blind, MacTutor History of Mathematics. in 1931. Jeřábek was one of the men who kept the Czech geometry at the scientific level. He published scientific articles in Czech, German and French, and longer lectures. He is well remembered by the Jerabek hype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |