|
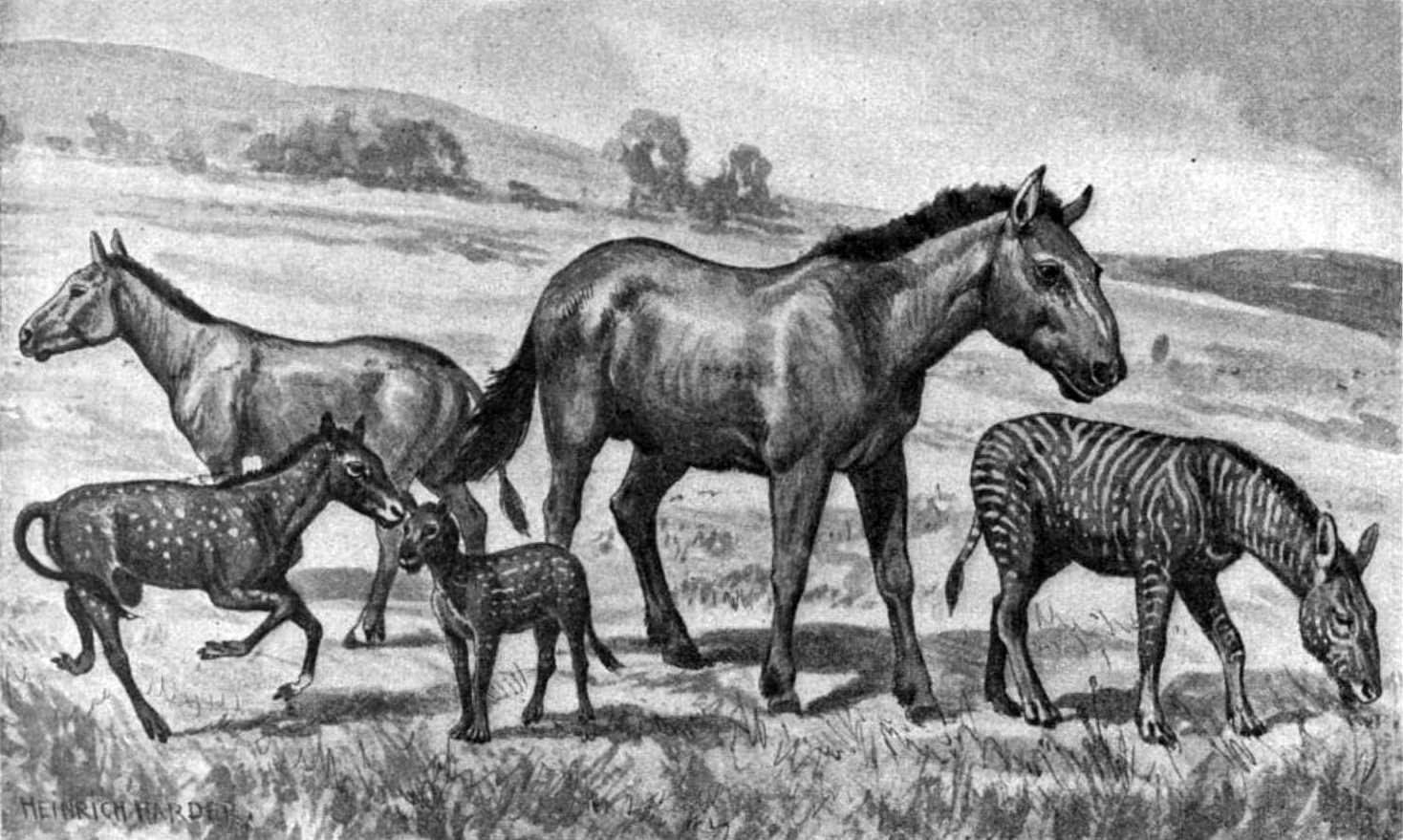
Chestnut (horse Anatomy)
The chestnut, also known as a night eye, is a callosity on the body of a horse or other equine, found on the inner side of the leg above the knee on the foreleg and, if present, below the hock on the hind leg. It is believed to be a vestigial toe, and along with the ergot form the three toes of some other extinct Equidae. Darren Naish dissents from this belief, noting that the chestnut is "not associated with the metacarpus or metatarsus, the only places where digits occur." Chestnuts vary in size and shape and are sometimes compared to the fingerprints in humans. For purposes of identification some breed registries require photographs of them among other individual characteristics. However, because chestnuts grow over time and horse groomers often peel or trim off the outer layers for neatness, their appearance is subject to change. Distribution among equines The evolution of the horse involved a reduction in the number of toes to one, along with other changes to the ances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chestnut On The Leg Of A Horse
The chestnuts are the deciduous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Castanea'', in the beech family Fagaceae. They are native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. The name also refers to the edible nuts they produce. The unrelated horse chestnuts (genus ''Aesculus'') are not true chestnuts, but are named for producing nuts of similar appearance that are mildly poisonous to humans. True chestnuts should also not be confused with water chestnuts, which are tubers of an aquatic herbaceous plant in the sedge family Cyperaceae. Other species commonly mistaken for chestnut trees are the chestnut oak (''Quercus prinus'') and the American beech (''Fagus grandifolia''),Chestnut Tree in chestnuttree.net. both of which are also in the Fagaceae family. |
Vestigiality
Vestigiality is the retention, during the process of evolution, of genetically determined structures or attributes that have lost some or all of the ancestral function in a given species. Assessment of the vestigiality must generally rely on comparison with homologous features in related species. The emergence of vestigiality occurs by normal evolutionary processes, typically by loss of function of a feature that is no longer subject to positive selection pressures when it loses its value in a changing environment. The feature may be selected against more urgently when its function becomes definitively harmful, but if the lack of the feature provides no advantage, and its presence provides no disadvantage, the feature may not be phased out by natural selection and persist across species. Examples of vestigial structures (also called degenerate, atrophied, or rudimentary organs) are the loss of functional wings in island-dwelling birds; the human vomeronasal organ; and the hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspian Pony
The Caspian is an Iranian breed of pony or small horse of Oriental type. The breed was created in 1965 by Louise Firouz, an American living in Iran, from a base stock of a small number of small horses found in the Elburz Mountains. In 2011, the remains of a small horse dating back to 3400 B.C.E. were found at Gohar Tappeh, Iran, giving rise to claims that today's Caspian originates from the oldest known breed of the domestic horse. It is also one of the rarest horse breeds and its population status is critically endangered. History The Caspian is said to originate from the mountainous regions of northern Iran, which explains how the breed is tough, athletic, and nimble. Indeed, the oldest known specimen of a Caspian-like horse was found in 2011, in a cemetery dating back to 3400 B.C.E., in the archaeological dig at Gohar Tappeh in the province of Mazandaran in northern Iran, between the cities of Neka and Behshahr. Small horses were depicted in ancient art where they appe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
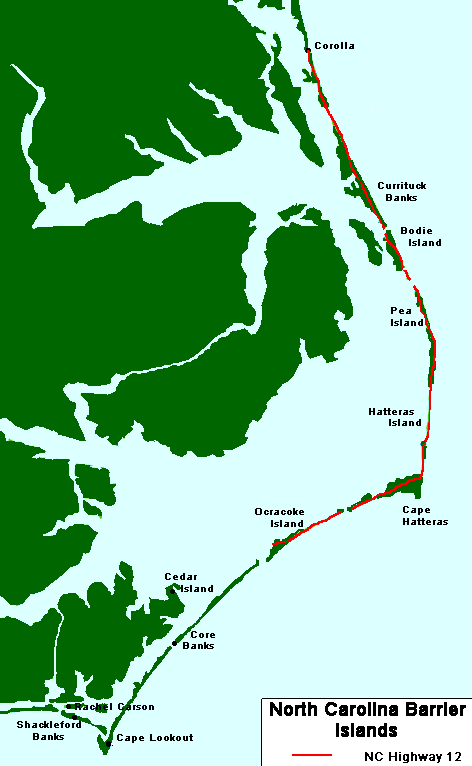
Banker Horse
The Banker horse is a breed of feral horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') living on barrier islands in North Carolina's Outer Banks. It is small, hardy, and has a docile temperament. Descended from domesticated Spanish horses and possibly brought to the Americas in the 16th century, the ancestral foundation bloodstock may have become feral after surviving shipwrecks or being abandoned on the islands by one of the exploratory expeditions led by Lucas Vázquez de Ayllón or Sir Richard Grenville. Populations are found on Ocracoke Island, Shackleford Banks, Currituck Banks, Cedar Island, and in the Rachel Carson Estuarine Sanctuary. Bankers are allowed to remain on the islands due to their historical significance even though they can trample plants and ground-nesting animals and are not considered to be indigenous. They survive by grazing on marsh grasses, which supply them with water as well as food, supplemented by temporary freshwater pools. To prevent overpopulation and inbreed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Breed
A horse breed is a selectively bred population of domesticated horses, often with pedigrees recorded in a breed registry. However, the term is sometimes used in a broader sense to define landrace animals of a common phenotype located within a limited geographic region, or even feral "breeds" that are naturally selected. Depending on definition, hundreds of "breeds" exist today, developed for many different uses. Horse breeds are loosely divided into three categories based on general temperament: spirited "hot bloods" with speed and endurance; "cold bloods," such as draft horses and some ponies, suitable for slow, heavy work; and "warmbloods," developed from crosses between hot bloods and cold bloods, often focusing on creating breeds for specific riding purposes, particularly in Europe. Horse breeds are groups of horses with distinctive characteristics that are transmitted consistently to their offspring, such as conformation, color, performance ability, or disposition. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Przewalski's Horse
Przewalski's horse (, , (Пржевальский ), ) (''Equus ferus przewalskii'' or ''Equus przewalskii''), also called the takhi, Mongolian wild horse or Dzungarian horse, is a rare and endangered horse originally native to the steppes of Central Asia. It is named after the Russian geographer and explorer Nikolay Przhevalsky. Once extinct in the wild, it has been reintroduced to its native habitat since the 1990s in Mongolia at the Khustain Nuruu National Park, Takhin Tal Nature Reserve, and Khomiin Tal, as well as several other locales in Central Asia and Eastern Europe. Several genetic characteristics of Przewalski's horse differ from what is seen in modern domestic horses, indicating neither is an ancestor of the other. For example, the Przewalski has 33 chromosome pairs, compared to 32 for the domestic horse. Their ancestral lineages split from a common ancestor between 38,000 and 160,000 years ago, long before the domestication of the horse. Przewalski's horse was long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domestic Horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature, ''Eohippus'', into the large, single-toed animal of today. Humans began domesticating horses around 4000 BCE, and their domestication is believed to have been widespread by 3000 BCE. Horses in the subspecies ''caballus'' are domesticated, although some domesticated populations live in the wild as feral horses. These feral populations are not true wild horses, as this term is used to describe horses that have never been domesticated. There is an extensive, specialized vocabulary used to describe equine-related concepts, covering everything from anatomy to life stages, size, colors, markings, breeds, locomotion, and behavior. Horses are adapted to run, allowing them to quickly escape predators, and poss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zebra
Zebras (, ) (subgenus ''Hippotigris'') are African equines with distinctive black-and-white striped coats. There are three living species: the Grévy's zebra (''Equus grevyi''), plains zebra (''E. quagga''), and the mountain zebra (''E. zebra''). Zebras share the genus ''Equus'' with horses and asses, the three groups being the only living members of the family Equidae. Zebra stripes come in different patterns, unique to each individual. Several theories have been proposed for the function of these stripes, with most evidence supporting them as a deterrent for biting flies. Zebras inhabit eastern and southern Africa and can be found in a variety of habitats such as savannahs, grasslands, woodlands, shrublands, and mountainous areas. Zebras are primarily grazers and can subsist on lower-quality vegetation. They are preyed on mainly by lions, and typically flee when threatened but also bite and kick. Zebra species differ in social behaviour, with plains and mountain zebra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asinus
''Asinus'' is a subgenus of '' Equus'' (single-toed (hooved) grazing animal) that encompasses several subspecies of the Equidae commonly known as wild asses, characterized by long ears, a lean, straight-backed build, lack of a true withers, a coarse mane and tail, and a reputation for considerable toughness and endurance. The common donkey is the best-known domesticated representative of the subgenus, with both domesticated and feral varieties. Among the wild ass species, several never-domesticated species live in Asia and Africa. Taxonomy * Genus: ''Equus'' ** Subgenus: ''Asinus'' *** African wild ass, ''Equus africanus'' **** Nubian wild ass, ''Equus africanus africanus'' **** Somali wild ass, ''Equus africanus somaliensis'' **** Atlas wild ass, †''Equus africanus atlanticus'' (extinct) **** Donkey, ''Equus africanus asinus'' ***Onager or Asiatic wild ass, ''Equus hemionus'' **** Mongolian wild ass or khulan, ''Equus hemionus hemionus'' **** Indian wild ass or khur, ''E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extant Taxon
Neontology is a part of biology that, in contrast to paleontology, deals with living (or, more generally, '' recent'') organisms. It is the study of extant taxa (singular: extant taxon): taxa (such as species, genera and families) with members still alive, as opposed to (all) being extinct. For example: * The moose (''Alces alces'') is an extant species, and the dodo (''Raphus cucullatus'') is an extinct species. * In the group of molluscs known as the cephalopods, there were approximately 600 extant species and 7,500 extinct species. A taxon can be classified as extinct if it is broadly agreed or certified that no members of the group are still alive. Conversely, an extinct taxon can be reclassified as extant if there are new discoveries of living species ("Lazarus species"), or if previously-known extant species are reclassified as members of the taxon. Most biologists, zoologists, and botanists are in practice neontologists, and the term neontologist is used large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equid
Equidae (sometimes known as the horse family) is the taxonomic family of horses and related animals, including the extant horses, asses, and zebras, and many other species known only from fossils. All extant species are in the genus '' Equus'', which originated in North America. Equidae belongs to the order Perissodactyla, which includes the extant tapirs and rhinoceros, and several extinct families. The term equid refers to any member of this family, including any equine. Evolution The oldest known fossils assigned to Equidae were found in North America, and date from the early Eocene epoch, 54 million years ago. They were once assigned to the genus ''Hyracotherium'', but the type species of that genus is now regarded as a palaeothere. The other species have been split off into different genera. These early equids were fox-sized animals with three toes on the hind feet, and four on the front feet. They were herbivorous browsers on relatively soft plants, and already adapted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |