|
Cheminformatics
Cheminformatics (also known as chemoinformatics) refers to the use of physical chemistry theory with computer and information science techniques—so called "'' in silico''" techniques—in application to a range of descriptive and prescriptive problems in the field of chemistry, including in its applications to biology and related molecular fields. Such '' in silico'' techniques are used, for example, by pharmaceutical companies and in academic settings to aid and inform the process of drug discovery, for instance in the design of well-defined combinatorial libraries of synthetic compounds, or to assist in structure-based drug design. The methods can also be used in chemical and allied industries, and such fields as environmental science and pharmacology, where chemical processes are involved or studied. History Cheminformatics has been an active field in various guises since the 1970s and earlier, with activity in academic departments and commercial pharmaceutical rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Cheminformatics
The ''Journal of Cheminformatics'' is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal that covers cheminformatics and molecular modelling. It was established in 2009 with David Wild (Indiana University) and Christoph Steinbeck (then at EMBL-EBI) as founding editors-in-chief, and was originally published by Chemistry Central. At the end of 2015, the Chemistry Central brand was retired and its titles, including ''Journal of Cheminformatics'', were merged with the SpringerOpen portfolio of open access journals. , the editors-in-chief are Rajarshi Guha (National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences) and Egon Willighagen (Maastricht University). The journal has issued a few special issues ("article collections") in 2011 and 2012, covering topics like PubChem, PubChem3D, the Resource Description Framework, and the International Chemical Identifier. In June 2021 Willighagen announced his intention to step down at the end of the year, explaining in an open letter that the publisher S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Space
Chemical space is a concept in cheminformatics referring to the property space spanned by all possible molecules and chemical compounds adhering to a given set of construction principles and boundary conditions. It contains millions of compounds which are readily accessible and available to researchers. It is a library used in the method of molecular docking. Theoretical spaces A chemical space often referred to in cheminformatics is that of potential pharmacologically active molecules. Its size is estimated to be in the order of 1060 molecules. There are no rigorous methods for determining the precise size of this space. The assumptions used for estimating the number of potential pharmacologically active molecules, however, use the Lipinski rules, in particular the molecular weight limit of 500. The estimate also restricts the chemical elements used to be Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen and Sulfur. It further makes the assumption of a maximum of 30 atoms to stay below 500 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combinatorial Libraries
Combinatorial chemistry comprises chemical synthetic methods that make it possible to prepare a large number (tens to thousands or even millions) of compounds in a single process. These compound libraries can be made as mixtures, sets of individual compounds or chemical structures generated by computer software. Combinatorial chemistry can be used for the synthesis of small molecules and for peptides. Strategies that allow identification of useful components of the libraries are also part of combinatorial chemistry. The methods used in combinatorial chemistry are applied outside chemistry, too. Introduction The basic principle of combinatorial chemistry is to prepare libraries of a very large number of compounds and identify those which are useful as potential drugs or agrochemicals. This relies on high-throughput screening which is capable of assessing the output at sufficient scale. Although combinatorial chemistry has only really been taken up by industry since the 1990s, its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
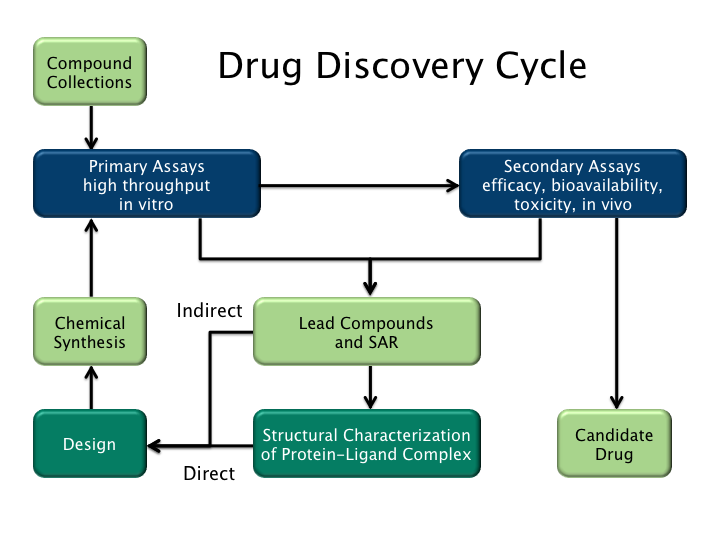
Drug Discovery
In the fields of medicine, biotechnology, and pharmacology, drug discovery is the process by which new candidate medications are discovered. Historically, drugs were discovered by identifying the active ingredient from traditional remedies or by serendipitous discovery, as with penicillin. More recently, chemical libraries of synthetic small molecules, natural products, or extracts were screened in intact cells or whole organisms to identify substances that had a desirable therapeutic effect in a process known as classical pharmacology. After sequencing of the human genome allowed rapid cloning and synthesis of large quantities of purified proteins, it has become common practice to use high throughput screening of large compounds libraries against isolated biological targets which are hypothesized to be disease-modifying in a process known as reverse pharmacology. Hits from these screens are then tested in cells and then in animals for efficacy. Modern drug discovery i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task (computing), tasks without explicit Machine code, instructions. Within a subdiscipline in machine learning, advances in the field of deep learning have allowed Neural network (machine learning), neural networks, a class of statistical algorithms, to surpass many previous machine learning approaches in performance. ML finds application in many fields, including natural language processing, computer vision, speech recognition, email filtering, agriculture, and medicine. The application of ML to business problems is known as predictive analytics. Statistics and mathematical optimisation (mathematical programming) methods comprise the foundations of machine learning. Data mining is a related field of study, focusing on exploratory data analysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topology (chemistry)
In chemistry, topology provides a way of describing and predicting the molecular structure within the constraints of three-dimensional (3-D) space. Given the determinants of chemical bonding and the Chemical property, chemical properties of the atoms, topology provides a model for explaining how the atoms ethereal wave functions must fit together. Molecular topology is a part of mathematical chemistry dealing with the algebraic description of chemical compounds so allowing a unique and easy characterization of them. Topology is insensitive to the details of a scalar field, and can often be determined using simplified calculations. Scalar fields such as electron density, Erwin Madelung, Madelung field, covalent field and the electrostatic potential can be used to model topology.Brown, David; Topology and Chemistry; Structural Chemistry Volume 13, Numbers 3–4, 339–355, Each scalar field has its own distinctive topology and each provides different information about the nature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structure-based Drug Design
Drug design, often referred to as rational drug design or simply rational design, is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. The drug is most commonly an organic small molecule that activates or inhibits the function of a biomolecule such as a protein, which in turn results in a therapeutic benefit to the patient. In the most basic sense, drug design involves the design of molecules that are complementary in shape and charge to the biomolecular target with which they interact and therefore will bind to it. Drug design frequently but not necessarily relies on computer modeling techniques. This type of modeling is sometimes referred to as computer-aided drug design. Finally, drug design that relies on the knowledge of the three-dimensional structure of the biomolecular target is known as structure-based drug design. In addition to small molecules, biopharmaceuticals including peptides and especially therapeutic antibodies are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structured Data Mining
Structure mining or structured data mining is the process of finding and extracting useful information from semi-structured data sets. Graph mining, sequential pattern mining and molecule mining are special cases of structured data mining. Description The growth of the use of semi-structured data has created new opportunities for data mining, which has traditionally been concerned with tabular data sets, reflecting the strong association between data mining and relational databases. Much of the world's interesting and mineable data does not easily fold into relational databases, though a generation of software engineers have been trained to believe this was the only way to handle data, and data mining algorithms have generally been developed only to cope with tabular data. XML, being the most frequent way of representing semi-structured data, is able to represent both tabular data and arbitrary trees. Any particular representation of data to be exchanged between two applications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unstructured Data
Unstructured data (or unstructured information) is information that either does not have a pre-defined data model or is not organized in a pre-defined manner. Unstructured information is typically plain text, text-heavy, but may contain data such as dates, numbers, and facts as well. This results in irregularities and ambiguities that make it difficult to understand using traditional programs as compared to data stored in fielded form in databases or annotation, annotated (Tag (metadata), semantically tagged) in documents. In 1998, Merrill Lynch said "unstructured data comprises the vast majority of data found in an organization, some estimates run as high as 80%." It is unclear what the source of this number is, but nonetheless it is accepted by some. Other sources have reported similar or higher percentages of unstructured data. , International Data Corporation, IDC and Dell EMC project that data will grow to 40 zettabytes by 2020, resulting in a 50-fold growth from the beginnin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Libraries
A digital library (also called an online library, an internet library, a digital repository, a library without walls, or a digital collection) is an online database of digital resources that can include text, still images, audio, video, digital documents, or other digital media formats or a library accessible through the internet. Objects can consist of digitized content like print or photographs, as well as originally produced digital content like word processor files or social media posts. In addition to storing content, digital libraries provide means for organizing, searching, and retrieving the content contained in the collection. Digital libraries can vary immensely in size and scope, and can be maintained by individuals or organizations. The digital content may be stored locally, or accessed remotely via computer networks. These information retrieval systems are able to exchange information with each other through interoperability and sustainability. History The earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structured Data
A data model is an abstract model that organizes elements of data and standardizes how they relate to one another and to the properties of real-world entities. For instance, a data model may specify that the data element representing a car be composed of a number of other elements which, in turn, represent the color and size of the car and define its owner. The corresponding professional activity is called generally ''data modeling'' or, more specifically, '' database design''. Data models are typically specified by a data expert, data specialist, data scientist, data librarian, or a data scholar. A data modeling language and notation are often represented in graphical form as diagrams. Michael R. McCaleb (1999)"A Conceptual Data Model of Datum Systems". National Institute of Standards and Technology. August 1999. A data model can sometimes be referred to as a data structure, especially in the context of programming languages. Data models are often complemented by function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |