|
Carbocyclic Nucleoside
Carbocyclic nucleosides (also referred to as carbanucleosides) are nucleoside analogues in which a methylene group has replaced the oxygen atom of the furanose ring. These analogues have the nucleobase attached at a simple alkyl carbon rather than being part of a hemiaminal ether linkage. As a result, they have increased chemical stability. They also have increased metabolic stability because they are unaffected by phosphorylases and hydrolases that cleave the glycosidic bond between the nucleobase and furanose ring of nucleosides. They retain many of the biological properties of the original nucleosides with respect to recognition by various enzymes and receptors. Carbocyclic nucleosides were originally limited to a five-membered ring system, matching the ring-size of the nucleosides; however, this term has been broadened to three-, four-, and six-membered rings. Natural products The 5-membered ring carbocyclic nucleosides aristeromycin, the analog of adenosine, and neplanocin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generic Ribonucleoside With Gycosidic Bond And Carbocyclic Ribonucleoside Analogue
Generic or generics may refer to: In business * Generic term, a common name used for a range or class of similar things not protected by trademark * Generic brand, a brand for a product that does not have an associated brand or trademark, other than the trading name of the business providing the product * Generic trademark, a trademark that sometimes or usually replaces a common term in colloquial usage * Generic drug, a drug identified by its chemical name rather than its brand name In computer programming * Generic function, a computer programming entity made up of all methods having the same name * Generic programming, a computer programming paradigm based on method/functions or classes defined irrespective of the concrete data types used upon instantiation ** Generics in Java In linguistics *A pronoun or other word used with a less specific meaning, such as: ** generic ''you'' ** generic ''he'' or generic ''she'' ** generic ''they'' * Generic mood, a grammatical mood used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varicella Zoster Virus
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV), also known as human herpesvirus 3 (HHV-3, HHV3) or ''Human alphaherpesvirus 3'' (taxonomically), is one of nine known herpes viruses that can infect humans. It causes chickenpox (varicella) commonly affecting children and young adults, and shingles (herpes zoster) in adults but rarely in children. VZV infections are species-specific to humans. The virus can survive in external environments for a few hours. VZV multiplies in the tonsils, and causes a wide variety of symptoms. Similar to the herpes simplex viruses, after primary infection with VZV (chickenpox), the virus lies dormant in neurons, including the cranial nerve ganglia, dorsal root ganglia, and autonomic ganglia. Many years after the person has recovered from initial chickenpox infection, VZV can ''reactivate'' to cause shingles. Epidemiology Chickenpox Primary varicella zoster virus infection results in chickenpox (varicella), which may result in complications including encephaliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herpesviridae
''Herpesviridae'' is a large family of DNA viruses that cause infections and certain diseases in animals, including humans. The members of this family are also known as herpesviruses. The family name is derived from the Greek word ''ἕρπειν'' ( 'to creep'), referring to spreading cutaneous lesions, usually involving blisters, seen in flares of herpes simplex 1, herpes simplex 2 and herpes zoster ( shingles). In 1971, the International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) established ''Herpesvirus'' as a genus with 23 viruses among four groups. As of 2020, 115 species are recognized, all but one of which are in one of the three subfamilies. Herpesviruses can cause both latent and lytic infections. Nine herpesvirus types are known to primarily infect humans, at least five of which – herpes simplex viruses 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2, also known as HHV-1 and HHV-2; both of which can cause orolabial herpes and genital herpes), varicella zoster virus (or HHV-3; the cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis B Virus
''Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, a species of the genus ''Orthohepadnavirus'' and a member of the ''Hepadnaviridae'' family of viruses. This virus causes the disease hepatitis B. Disease Despite there being a vaccine to prevent Hepatitis B, HBV remains a global health problem. Hepatitis B can be acute and later become chronic, leading to other diseases and health conditions. In addition to causing hepatitis, infection with HBV can lead to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. It has also been suggested that it may increase the risk of pancreatic cancer. Roles in disease Viral infection by ''Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) causes many hepatocyte changes due to the direct action of a protein encoded by the virus, HBx, and to indirect changes due to a large increase in intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) after infection. HBx appears to dysregulate a number of cellular pathways. HBx causes dysregulation in part by binding to genomic DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
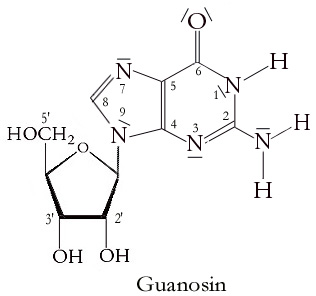
Guanosine
Guanosine (symbol G or Guo) is a purine nucleoside comprising guanine attached to a ribose (ribofuranose) ring via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Guanosine can be phosphorylated to become guanosine monophosphate (GMP), cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), guanosine diphosphate (GDP), and guanosine triphosphate (GTP). These forms play important roles in various biochemical processes such as synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, photosynthesis, muscle contraction, and intracellular signal transduction (cGMP). When guanine is attached by its N9 nitrogen to the C1 carbon of a deoxyribose ring it is known as deoxyguanosine. Physical and chemical properties Guanosine is a white, crystalline powder with no odor and mild saline taste. It is very soluble in acetic acid, slightly soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, benzene and chloroform. Functions Guanosine is required for an RNA splicing reaction in mRNA, when a "self-splicing" intron removes itself from the mRNA messag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entecavir
Entecavir (ETV), sold under the brand name Baraclude, is an antiviral medication used in the treatment of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. In those with both HIV/AIDS and HBV antiretroviral medication should also be used. Entecavir is taken by mouth as a tablet or solution. Common side effects include headache, nausea, high blood sugar, and decreased kidney function. Severe side effects include enlargement of the liver, high blood lactate levels, and liver inflammation if the medication is stopped. While there appears to be no harm from use during pregnancy, this use has not been well studied. Entecavir is in the nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) family of medications. It prevents the hepatitis B virus from multiplying by blocking reverse transcriptase. Entecavir was approved for medical use in 2005. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Available as a generic medication in the United States. Medical uses Entecavir is ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abacavir
Abacavir, sold under the brand name Ziagen among others, is a medication used to treat HIV/AIDS. Similar to other nucleoside analog reverse-transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), abacavir is used together with other HIV medications, and is not recommended by itself. It is taken by mouth as a tablet or solution and may be used in children over the age of three months. Abacavir is generally well tolerated. Common side effects include vomiting, insomnia (trouble sleeping), fever, and feeling tired. Other common side effects include loss of appetite, headache, nausea (feeling sick), diarrhea, rash, and lethargy (lack of energy). More severe side effects include hypersensitivity, liver damage, and lactic acidosis. Genetic testing can indicate whether a person is at higher risk of developing hypersensitivity. Symptoms of hypersensitivity include rash, vomiting, and shortness of breath. Abacavir is in the NRTI class of medications, which work by blocking reverse transcriptase, an enzyme n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prodrug
A prodrug is a medication or compound that, after intake, is metabolized (i.e., converted within the body) into a pharmacologically active drug. Instead of administering a drug directly, a corresponding prodrug can be used to improve how the drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted (ADME). Prodrugs are often designed to improve bioavailability when a drug itself is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. A prodrug may be used to improve how selectively the drug interacts with cells or processes that are not its intended target. This reduces adverse or unintended effects of a drug, especially important in treatments like chemotherapy, which can have severe unintended and undesirable side effects. History Many herbal extracts historically used in medicine contain glycosides (sugar derivatives) of the active agent, which are hydrolyzed in the intestines to release the active and more bioavailable aglycone. For example, salicin is a β-D-glucopyranosid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enantiomer
In chemistry, an enantiomer ( /ɪˈnænti.əmər, ɛ-, -oʊ-/ ''ih-NAN-tee-ə-mər''; from Ancient Greek ἐνάντιος ''(enántios)'' 'opposite', and μέρος ''(méros)'' 'part') – also called optical isomer, antipode, or optical antipode – is one of two stereoisomers that are non-superposable onto their own mirror image. Enantiomers are much like one's right and left hands, when looking at the same face, they cannot be superposed onto each other. No amount of reorientation will allow the four unique groups on the chiral carbon (see Chirality (chemistry)) to line up exactly. The number of stereoisomers a molecule has can be determined by the number of chiral carbons it has. Stereoisomers include both enantiomers and diastereomers. Diastereomers, like enantiomers, share the same molecular formula and are non-superposable onto each other however, they are not mirror images of each other. A molecule with chirality rotates plane-polarized light. A mixture of equals a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Vince (scientist)
Robert Vince (born November 20, 1940) is an American scientist known for his contributions to the research in the area of drug design. He is currently the director and professor at the Center for Drug Design at the Academic Health Center for the University of Minnesota. Biography Robert Vince was born in Auburn, New York, Auburn, New York. After graduating with a Bachelor of Science in Pharmacy in 1962, Vince joined the research group of Prof Howard J. Schaeffer at SUNY Buffalo in New York, where he obtained his doctoral degree in medicinal chemistry. He subsequently joined the University of Mississippi for a brief stint as assistant professor of medicinal chemistry. In 1967, he joined the medicinal chemistry faculty at the University of Minnesota.Singh, R.; Vince, R. “2-Azabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-3-one: Chemical Profile of a Versatile Synthetic Building Block and its Impact on the Development of Therapeutics" ''Chemical Reviews'' 2012, ''112,'' 4642–4686. In 2002, Vince est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racemic
In chemistry, a racemic mixture, or racemate (), is one that has equal amounts of left- and right-handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule or salt. Racemic mixtures are rare in nature, but many compounds are produced industrially as racemates. History The first known racemic mixture was racemic acid, which Louis Pasteur found to be a mixture of the two enantiomeric isomers of tartaric acid. He manually separated the crystals of a mixture by hand, starting from an aqueous solution of the sodium ammonium salt of racemate tartaric acid. Pasteur benefited from the fact that ammonium tartrate salt that gives enantiomeric crystals with distinct crystal forms (at 77 °F). Reasoning from the macroscopic scale down to the molecular, he reckoned that the molecules had to have non-superimposable mirror images. A sample with only a single enantiomer is an ''enantiomerically pure'' or ''enantiopure'' compound. Etymology From racemic acid found in grapes; from Latin ''racemus'', meani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse-transcriptase Inhibitors
Reverse-transcriptase inhibitors (RTIs) are a class of antiretroviral drugs used to treat HIV infection or AIDS, and in some cases hepatitis B. RTIs inhibit activity of reverse transcriptase, a viral DNA polymerase that is required for replication of HIV and other retroviruses. Mechanism of action When HIV infects a cell, reverse transcriptase copies the viral single stranded RNA genome into a double-stranded viral DNA. The viral DNA is then integrated into the host chromosomal DNA, which then allows host cellular processes, such as transcription and translation, to reproduce the virus. RTIs block reverse transcriptase's enzymatic function and prevent completion of synthesis of the double-stranded viral DNA, thus preventing HIV from multiplying. A similar process occurs with other types of viruses. The hepatitis B virus, for example, carries its genetic material in the form of DNA, and employs an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase to replicate. Some of the same compounds used as RTI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |