|
Carbaryl
Carbaryl (1-naphthyl methylcarbamate) is a chemical in the carbamate family used chiefly as an insecticide. It is a white crystalline solid previously sold under the brand name Sevin, which was a trademark of the Bayer Company. The Sevin trademark has since been acquired by GardenTech, which has eliminated carbaryl from most Sevin formulations. Union Carbide discovered carbaryl and introduced it commercially in 1958. Bayer purchased Aventis CropScience in 2002, a company that included Union Carbide pesticide operations. Carbaryl was the third-most-used insecticide in the United States for home gardens, commercial agriculture, and forestry and rangeland protection. As a veterinary drug, it is known as carbaril ( INN). Production Carbaryl is often inexpensively produced by direct reaction of methyl isocyanate with 1-naphthol. :C10H7OH + CH3NCO → C10H7OC(O)NHCH3 Alternatively, 1-naphthol can be treated with excess phosgene to produce 1-naphthyl chloroformate, which is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhopal Disaster
The Bhopal disaster, also referred to as the Bhopal gas tragedy, was a chemical accident on the night of 2–3 December 1984 at the Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) pesticide plant in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India. Considered the world's worst industrial disaster, over 500,000 people in the small towns around the plant were exposed to the highly toxic gas methyl isocyanate (). Estimates vary on the death toll, with the official number of immediate deaths being 2,259. In 2008, the Government of Madhya Pradesh paid compensation to the family members of 3,787 victims killed in the gas release, and to 574,366 injured victims. A government affidavit in 2006 stated that the leak caused 558,125 injuries, including 38,478 temporary partial injuries and approximately 3,900 severely and permanently disabling injuries. Others estimate that 8,000 died within two weeks, and another 8,000 or more have since died from gas-related diseases. The owner of the factory, UCIL, was majority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Isocyanate
Methyl isocyanate (MIC) is an organic compound with the molecular formula CH3NCO. Synonyms are isocyanatomethane and methyl carbylamine. Methyl isocyanate is an intermediate chemical in the production of carbamate pesticides (such as carbaryl, carbofuran, methomyl, and aldicarb). It has also been used in the production of rubbers and adhesives. As an extremely toxic and irritating compound, it is very hazardous to human health. It was the principal toxicant involved in the infamous Bhopal gas disaster, which officially killed around 20,000 people in total. It is also a very potent lachrymatory agent. Physical properties Methyl isocyanate is a colorless, poisonous, lachrymatory (tearing agent), flammable liquid.Union Carbide Corporation "Methyl Isocyanate" Product Information Publication, F-41443, November 1967. It is soluble in water to 6–10 parts per 100 parts, but it also reacts with water (see Reactions below). Manufacture Methyl isocyanate is usually manufactu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1-naphthol
1-Naphthol, or α-naphthol, is a fluorescent organic compound with the formula . It is a white solid. It is an isomer of 2-naphthol differing by the location of the hydroxyl group on the naphthalene ring. The naphthols are naphthalene homologues of phenol, with the hydroxyl group being more reactive than in the phenols. Both isomers are soluble in simple alcohols, ethers, and chloroform. They are precursors to a variety of useful compounds. Naphthols (both 1 and 2 isomers) are used as biomarkers for livestock and humans exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Production 1-Naphthol is prepared by two main routes. In one method, naphthalene is nitrated to give 1-nitronaphthalene, which is hydrogenated to the amine followed by hydrolysis: : : : Alternatively, naphthalene is hydrogenated to tetralin, which is oxidized to 1-tetralone, which undergoes dehydrogenation. Occurrence and degradation 1-Naphthol is a metabolite of the insecticide carbaryl and naphthalene. Along w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylamine
Methylamine is an organic compound with a formula of . This colorless gas is a derivative of ammonia, but with one hydrogen atom being replaced by a methyl group. It is the simplest primary amine. Methylamine is sold as a solution in methanol, ethanol, tetrahydrofuran, or water, or as the anhydrous gas in pressurized metal containers. Industrially, methylamine is transported in its anhydrous form in pressurized railcars and tank trailers. It has a strong odor similar to rotten fish. Methylamine is used as a building block for the synthesis of numerous other commercially available compounds. Industrial production Methylamine is prepared commercially by the reaction of ammonia with methanol in the presence of an aluminosilicate catalyst. Dimethylamine and trimethylamine are co-produced; the reaction kinetics and reactant ratios determine the ratio of the three products. The product most favored by the reaction kinetics is trimethylamine. : In this way, an estimated 115,000 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
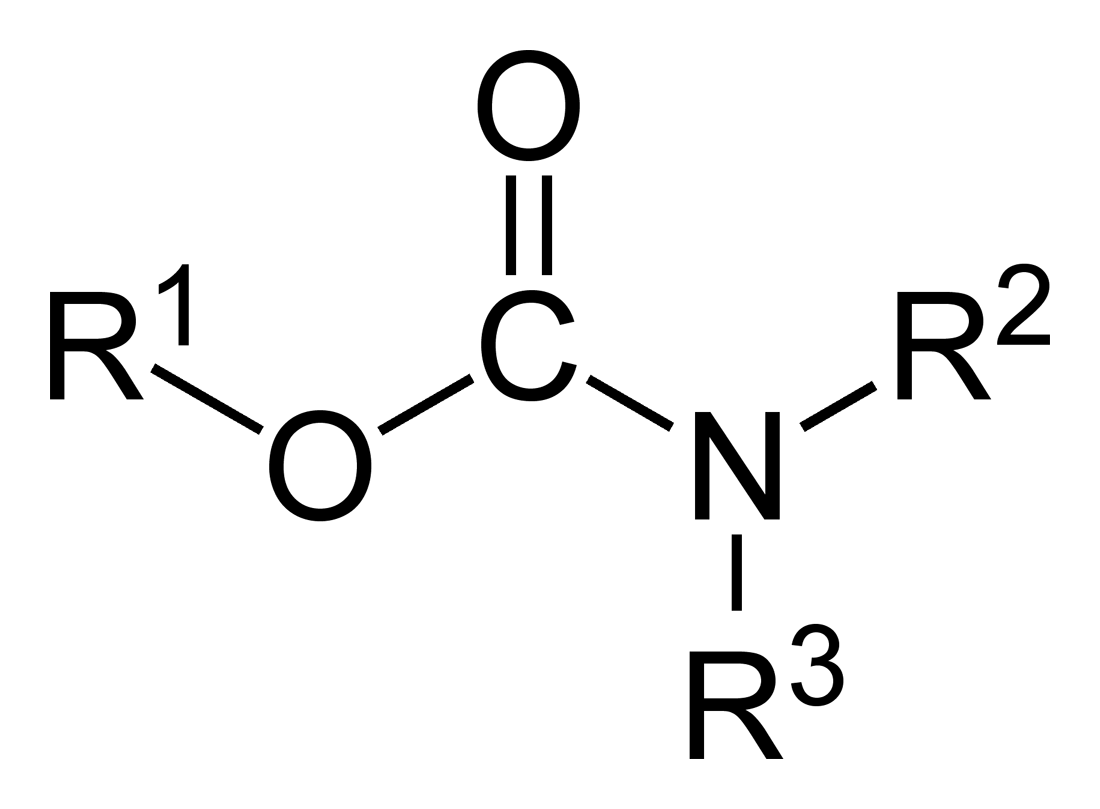
Carbamate
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose units are joined by carbamate groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters or ionic) are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbonate is not. Adding a calcium salt to an ammonium carbamate/carbonate solution will precipitate some calcium carbonat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
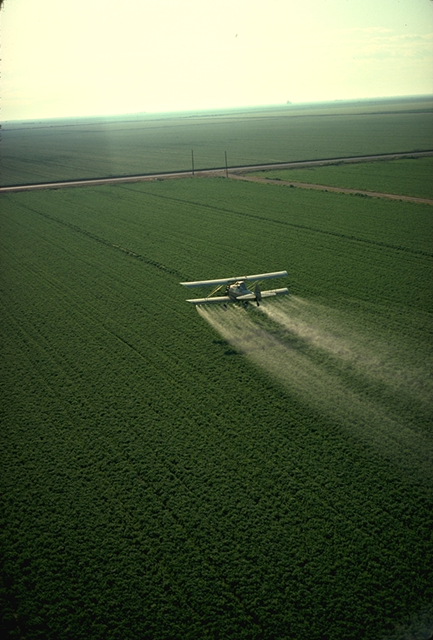
Pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are meant to control pests. This includes herbicide, insecticide, nematicide, molluscicide, piscicide, avicide, rodenticide, bactericide, insect repellent, animal repellent, microbicide, fungicide, and lampricide. The most common of these are herbicides which account for approximately 80% of all pesticide use. Most pesticides are intended to serve as plant protection products (also known as crop protection products), which in general, protect plants from weeds, fungi, or insects. As an example, the fungus '' Alternaria solani'' is used to combat the aquatic weed '' Salvinia''. In general, a pesticide is a chemical (such as carbamate) or biological agent (such as a virus, bacterium, or fungus) that deters, incapacitates, kills, or otherwise discourages pests. Target pests can include insects, plant pathogens, weeds, molluscs, birds, mammals, fish, nematodes (roundworms), and microbes that destroy property, cause nuisance, or spr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honeybee
A honey bee (also spelled honeybee) is a eusocial flying insect within the genus ''Apis'' of the bee clade, all native to Afro-Eurasia. After bees spread naturally throughout Africa and Eurasia, humans became responsible for the current cosmopolitan distribution of honey bees, introducing multiple subspecies into South America (early 16th century), North America (early 17th century), and Australia (early 19th century). Honey bees are known for their construction of perennial colonial nests from wax, the large size of their colonies, and surplus production and storage of honey, distinguishing their hives as a prized foraging target of many animals, including honey badgers, bears and human hunter-gatherers. Only eight surviving species of honey bee are recognized, with a total of 43 subspecies, though historically 7 to 11 species are recognized. Honey bees represent only a small fraction of the roughly 20,000 known species of bees. The best known honey bee is the wester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers. Zooplankton can be contrasted with phytoplankton, which are the plant component of the plankton community ("phyto" comes from the Greek word for ''plant''). Zooplankton are heterotrophic (other-feeding), whereas phytoplankton are autotrophic (self-feeding). This means zooplankton cannot manufacture their own food but must eat other plants or animals instead — in particular they eat phytoplankton. Zooplankton are generally larger than phytoplankton, most are microscopic, but some (such as jellyfish) are macroscopic and can be seen with the naked eye. Many protozoans (single-celled protists that prey on other microscopic life) are zooplankton, including zooflagellat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
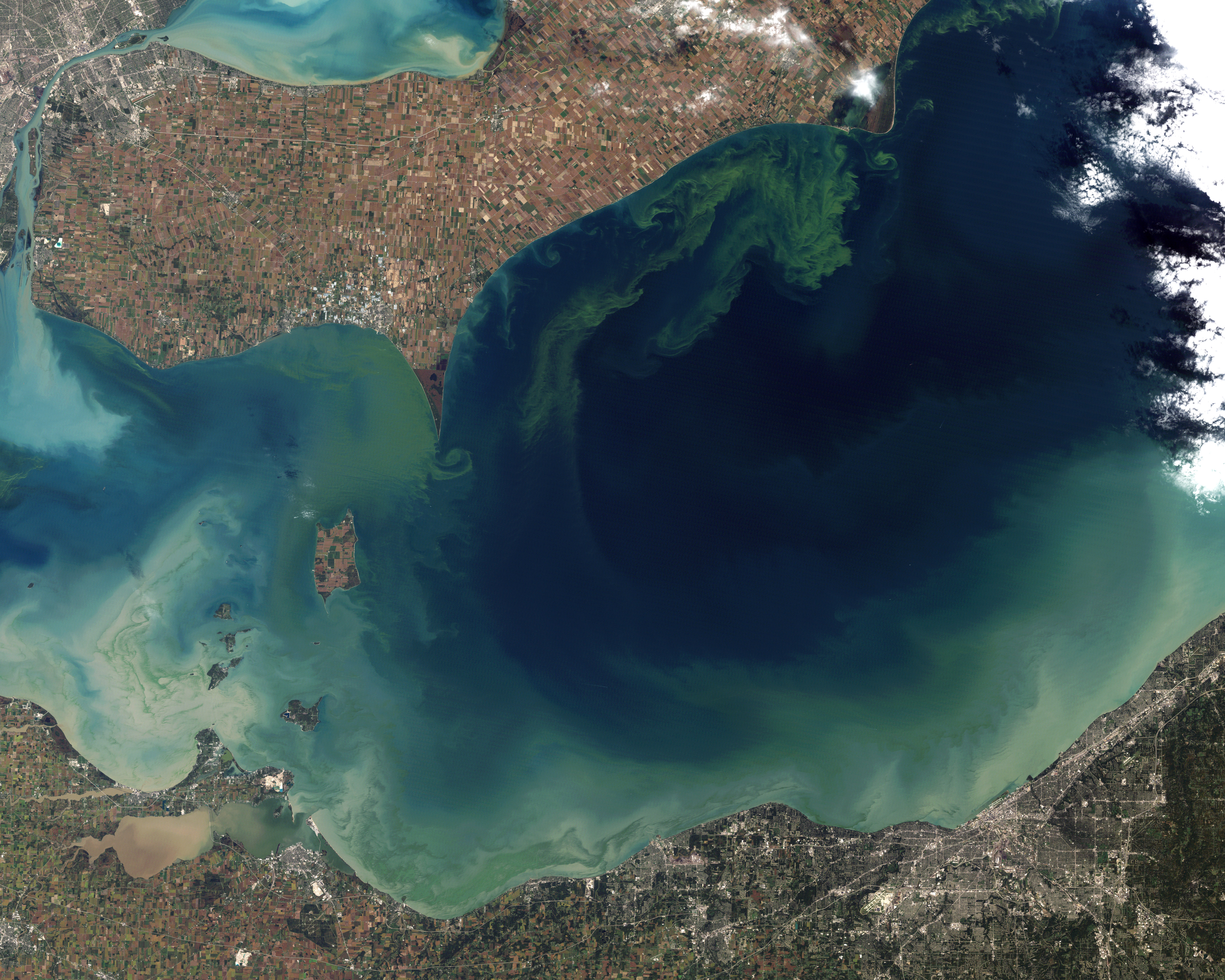
Algal Bloom
An algal bloom or algae bloom is a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae in freshwater or marine water systems. It is often recognized by the discoloration in the water from the algae's pigments. The term ''algae'' encompasses many types of aquatic photosynthetic organisms, both macroscopic multicellular organisms like seaweed and microscopic unicellular organisms like cyanobacteria. ''Algal bloom'' commonly refers to the rapid growth of microscopic unicellular algae, not macroscopic algae. An example of a macroscopic algal bloom is a kelp forest. Algal blooms are the result of a nutrient, like nitrogen or phosphorus from various sources (for example fertilizer runoff or other forms of nutrient pollution), entering the aquatic system and causing excessive growth of algae. An algal bloom affects the whole ecosystem. Consequences range from the benign feeding of higher trophic levels to more harmful effects like blocking sunlight from reaching other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bufo Woodhousii
Woodhouse's toad (''Anaxyrus woodhousii'') is a medium-sized () true toad native to the United States and Mexico. There are three recognized subspecies. ''A. woodhousii'' tends to hybridize with '' Anaxyrus americanus'' where their ranges overlap. Taxonomy Woodhouse's toad was first described in 1854 by the French herpetologist Charles Frédéric Girard. He gave it the name ''Bufo woodhousii'' in honor of the American physician and naturalist Samuel Washington Woodhouse. The large genus ''Bufo'' was split by Frost ''et al.'' in 2006, with the North American species being included in the genus '' Anaxyrus'' and this toad becoming ''A. woodhousii''. There are three recognised subspecies: *Rocky Mountain toad – ''Anaxyrus woodhousii woodhousii'' ( Girard, 1854) *East Texas toad – ''Anaxyrus woodhousii velatus'' (Bragg and Sanders, 1951)Bragg, A. N., and O. Sanders. 1951. A new subspecies of the ''Bufo woodhousii'' group of toads (Salientia: Bufonidae). Wasmann Journal of Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algae Eater
Algae eater or algivore is a common name for any bottom-dwelling or filter-feeding aquatic animal species that specialize in feeding on algae and phytoplanktons. Algae eaters are important for the fishkeeping hobby and many are commonly kept by aquarium hobbyists to improve water quality. They are also important primary consumers that relay the biomass and energy from photosynthetic autotrophes up into the food web, as well as protecting the aquatic ecosystem against algae blooms. Freshwater Fish Some of the common and most popular freshwater aquarium algae eaters include: * Many loricariid catfish of South America, such as genera '' Otocinclus'', '' Ancistrus'', and '' Plecostomus'', constantly graze algae and biofilm, although many species of "plecos", which attain an adult length of over 10 inches, eat much less frequently as they near adulthood. * The Siamese algae eater (''Crossocheilus oblongus'') is a more gregarious and tolerant cyprinid that ranges up to . It is on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRC Press
The CRC Press, LLC is an American publishing group that specializes in producing technical books. Many of their books relate to engineering, science and mathematics. Their scope also includes books on business, forensics and information technology. CRC Press is now a division of Taylor & Francis, itself a subsidiary of Informa. History The CRC Press was founded as the Chemical Rubber Company (CRC) in 1903 by brothers Arthur, Leo and Emanuel Friedman in Cleveland, Ohio, based on an earlier enterprise by Arthur, who had begun selling rubber laboratory aprons in 1900. The company gradually expanded to include sales of laboratory equipment to chemists. In 1913 the CRC offered a short (116-page) manual called the ''Rubber Handbook'' as an incentive for any purchase of a dozen aprons. Since then the ''Rubber Handbook'' has evolved into the CRC's flagship book, the ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics''. In 1964, Chemical Rubber decided to focus on its publishing ventures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)