|
Callus (cell Biology)
Plant callus (plural ''calluses'' or ''calli'') is a growing mass of unorganized plant parenchyma cells. In living plants, callus cells are those cells that cover a plant wound. In biological research and biotechnology callus formation is induced from plant tissue samples (explants) after surface sterilization and plating onto tissue culture medium in vitro (in a closed culture vessel such as a Petri dish). The culture medium is supplemented with plant growth regulators, such as auxin, cytokinin, and gibberellin, to initiate callus formation or somatic embryogenesis. Callus initiation has been described for all major groups of land plants. Callus induction and tissue culture Plant species representing all major land plant groups have been shown to be capable of producing callus in tissue culture. A callus cell culture is usually sustained on gel medium. Callus induction medium consists of agar and a mixture of macronutrients and micronutrients for the given cell type. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
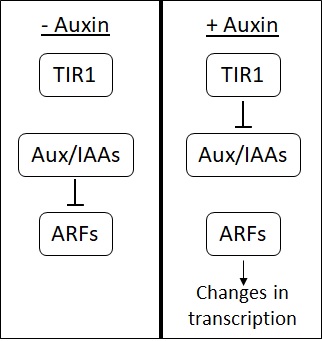
Auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essential for plant body development. The Dutch biologist Frits Warmolt Went first described auxins and their role in plant growth in the 1920s. Kenneth V. Thimann became the first to isolate one of these phytohormones and to determine its chemical structure as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). Went and Thimann co-authored a book on plant hormones, ''Phytohormones'', in 1937. Overview Auxins were the first of the major plant hormones to be discovered. They derive their name from the Greek word αυξειν (''auxein'' – "to grow/increase"). Auxin is present in all parts of a plant, although in very different concentrations. The concentration in each position is crucial developmental information, so it is subject to tight regulation through both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementary particles, theoretically with the same amount of matter, have nonetheless different masses. Mass in modern physics has multiple definitions which are conceptually distinct, but physically equivalent. Mass can be experimentally defined as a measure of the body's inertia, meaning the resistance to acceleration (change of velocity) when a net force is applied. The object's mass also determines the strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). In physics, mass is not the same as weight, even though mass is often determined by measuring the object's weight using a spring scale, rather than balance scale comparing it directly with known masses. An object on the Moon would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micronutrient
Micronutrients are essential dietary elements required by organisms in varying quantities throughout life to orchestrate a range of physiological functions to maintain health. Micronutrient requirements differ between organisms; for example, humans and other animals require numerous vitamins and dietary minerals, whereas plants require specific minerals. For human nutrition, micronutrient requirements are in amounts generally less than 100 milligrams per day, whereas macronutrients are required in gram quantities daily. The minerals for humans and other animals include 13 elements that originate from Earth's soil and are not synthesized by living organisms, such as calcium and iron. Micronutrient requirements for animals also include vitamins, which are organic compounds required in microgram or milligram amounts. Since plants are the primary origin of nutrients for humans and animals, some micronutrients may be in low levels and deficiencies can occur when dietary intake is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pv Callus Dark 3 3-11-2008
PV may refer to: Places * Paceville, Malta * Puerto Vallarta, Mexico * Postal village, a settlement that has a post office United States * Palos Verdes Peninsula, California * Prescott Valley, Arizona * Prairie Village, Kansas Politics * Partido Verde (other), several political parties * Peoples Voice, a political party in Singapore * Preferential voting (other), a category of electoral systems Science and technology * Photovoltaics, a technology for converting sunlight into electricity * Potential vorticity, in fluid dynamics * Presta valve, one of the two common tire valves * Process variable, in control systems * Programmed visibility, of traffic signals Biology and medicine * Parvalbumin, a calcium-binding albumin protein * Pathovar, a bacterial strain or set of strains with the same or similar characteristics * Pemphigus vulgaris, a chronic blistering skin disease * ''Per vaginam'', through/via the vagina * Periventricular nucleus, of the hypothalamu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Hormones
Plant hormone (or phytohormones) are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, from embryogenesis, the regulation of organ size, pathogen defense, stress tolerance and through to reproductive development. Unlike in animals (in which hormone production is restricted to specialized glands) each plant cell is capable of producing hormones. Went and Thimann coined the term "phytohormone" and used it in the title of their 1937 book. Phytohormones occur across the plant kingdom, and even in algae, where they have similar functions to those seen in higher plants. Some phytohormones also occur in microorganisms, such as unicellular fungi and bacteria, however in these cases they do not play a hormonal role and can better be regarded as secondary metabolites. Characteristics The word hormone is derived from Greek, meaning ''set in motion''. Plant hormones affect gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dedifferentiation
Dedifferentiation (pronounced dē-ˌdi-fə-ˌren-chē-ˈā-shən) is a transient process by which cells become less specialized and return to an earlier cell state within the same lineage. This suggests an increase in a cell potency, meaning that after dedifferentiation, cells may possess an ability to redifferentiate into more cell types than it did before. This is in contrast to differentiation, where differences in gene expression, morphology, or physiology arise in a cell, making its function increasingly specialized. The loss of specialization observed in dedifferentiation can be noted through changes in gene expression, physiology, function, proliferative activity, or morphology. While it can be induced in a laboratory setting through processes like direct reprogramming and the production of induced pluripotent stem cells, endogenous dedifferentiation processes also exist as a component of wound healing mechanisms. History References to dedifferentiation can be found a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesophyll Tissue
A leaf ( : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, flower, and fruit collectively form the shoot system. In most leaves, the primary photosynthetic tissue is the palisade mesophyll and is located on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of ''Eucalyptus'', palisade mesophyll is present on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral. Most leaves are flattened and have distinct upper ( adaxial) and lower ( abaxial) surfaces that differ in color, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases), the amount and structure of epicuticular wax and other features. Leaves are mostly green in color due to the presence of a compound called chlorophyll that is essential for photosynthesis as it absorbs light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicago Truncatula
''Medicago truncatula'', the barrelclover, strong-spined medick, barrel medic, or barrel medick, is a small annual legume native to the Mediterranean region that is used in genomic research. It is a low-growing, clover-like plant tall with trifoliate leaves. Each leaflet is rounded, long, often with a dark spot in the center. The flowers are yellow, produced singly or in a small inflorescence of two to five together; the fruit is a small, spiny pod. This species is studied as a model organism for legume biology because it has a small diploid genome, is self-fertile, has a rapid generation time and prolific seed production, is amenable to genetic transformation, and its genome has been sequenced. It forms symbioses with nitrogen-fixing rhizobia ('' Sinorhizobium meliloti'' and '' Sinorhizobium medicae'') and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi including '' Rhizophagus irregularis'' (previously known as '' Glomus intraradices''). The model plant ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' does not form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meristem
The meristem is a type of tissue found in plants. It consists of undifferentiated cells (meristematic cells) capable of cell division. Cells in the meristem can develop into all the other tissues and organs that occur in plants. These cells continue to divide until a time when they get differentiated and then lose the ability to divide. Differentiated plant cells generally cannot divide or produce cells of a different type. Meristematic cells are undifferentiated or incompletely differentiated. They are totipotent and capable of continued cell division. Division of meristematic cells provides new cells for expansion and differentiation of tissues and the initiation of new organs, providing the basic structure of the plant body. The cells are small, with no or small vacuoles and protoplasm fills the cell completely. The plastids (chloroplasts or chromoplasts), are undifferentiated, but are present in rudimentary form ( proplastids). Meristematic cells are packed closely together ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explant Culture
In biology, explant culture is a technique to organotypically culture cells from a piece or pieces of tissue or organ removed from a plant or animal. The term ''explant'' can be applied to samples obtained from any part of the organism. The extraction process is extensively sterilized, and the culture can be typically used for two to three weeks. The major advantage of explant culture is the maintenance of near ''in vivo'' environment in the laboratory for a short duration of time. This experimental setup allows investigators to perform experiments and easily visualize the impact of tests. This ''ex vivo'' model requires a highly maintained environment in order to recreate original cellular conditions. The composition of extracellular matrix, for example, must be precisely similar to that of ''in vivo'' conditions in order to induce naturally observed behaviors of cells. The growth medium also must be considered, as different solutions may be needed for different experiments. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatic (biology)
The term somatic - etymologically from the Ancient Greek words of "σωματικός" (sōmatikós, “bodily”) and σῶμα (sôma, “body”) - is often used in biology to refer to the cells of the body in contrast to the reproductive (germline) cells, which usually give rise to the egg or sperm (or other gametes in other organisms). These somatic cells are diploid, containing two copies of each chromosome, whereas germ cells are haploid, as they only contain one copy of each chromosome (in preparation for fertilisation). Although under normal circumstances all somatic cells in an organism contain identical DNA, they develop a variety of tissue-specific characteristics. This process is called differentiation, through epigenetic and regulatory alterations. The grouping of similar cells and tissues creates the foundation for organs. Somatic mutations are changes to the genetics of a multicellular organism that are not passed on to its offspring through the germline. Most ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin '' kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to form flaky white potassium peroxide in only seconds of exposure. It was first isolated from potash, the ashes of plants, from which its name derives. In the periodic table, potassium is one of the alkali metals, all of which have a single valence electron in the outer electron shell, that is easily removed to create an ion with a positive charge – a cation, that combines with anions to form salts. Potassium in nature occurs only in ionic salts. Elemental potassium reacts vigorously with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite hydrogen emitted in the reaction, and burning with a lilac- colored flame. It is found dissolved in sea water (which is 0.04% potassium by weight), and occurs in many minerals such as orth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)

