|
Callicarpenal
Callicarpenal is a terpenoid that has been isolated from plants of the genus ''Callicarpa'' (beautyberry). It acts as an insect repellent against mosquitoes (''Aedes aegypti'' and '' Anopheles stephensi'') and fire ants. It also has activity against ticks (''Ixodes scapularis'' and ''Amblyomma americanum''). In comparison to the most commonly used insect repellent, DEET, callicarpenal is only about 21% less effective at preventing mosquito bites. Callicarpenal was discovered by scientists at the United States Department of Agriculture's Agricultural Research Service who were inspired by reports that ''Callicarpa americana ''Callicarpa americana'', the American beautyberry, is an open-habitat, native shrub of the Southern United States which is often grown as an ornamental in gardens and yards. American beautyberries produce large clusters of purple berries, whi ...'' (American beautyberry) was used as a folk remedy to prevent mosquito bites. References External link ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callicarpa
''Callicarpa'' (beautyberry) is a genus of shrubs and small trees in the family Lamiaceae.Heywood, V.H., Brummitt, R.K., Culham, A. & Seberg, O. 2007: Flowering Plant Families of the World. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. They are native to east and southeast Asia (where the majority of the species occur), Australia, Madagascar, southeast North America and South America. Growth The temperate species are deciduous, the tropical species evergreen. The leaves are simple, opposite, and 5–25 cm long. The flowers are in clusters, white to pinkish. The fruit is a berry, 2–5 mm diameter and pink to red-purple with a highly distinctive metallic lustre, are very conspicuous in clusters on the bare branches after the leaves fall. The berries last well into the winter or dry season and are an important survival food for birds and other animals, though they will not eat them until other sources are depleted. The berries are highly astringent but are made into wine and jelly. ''Call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
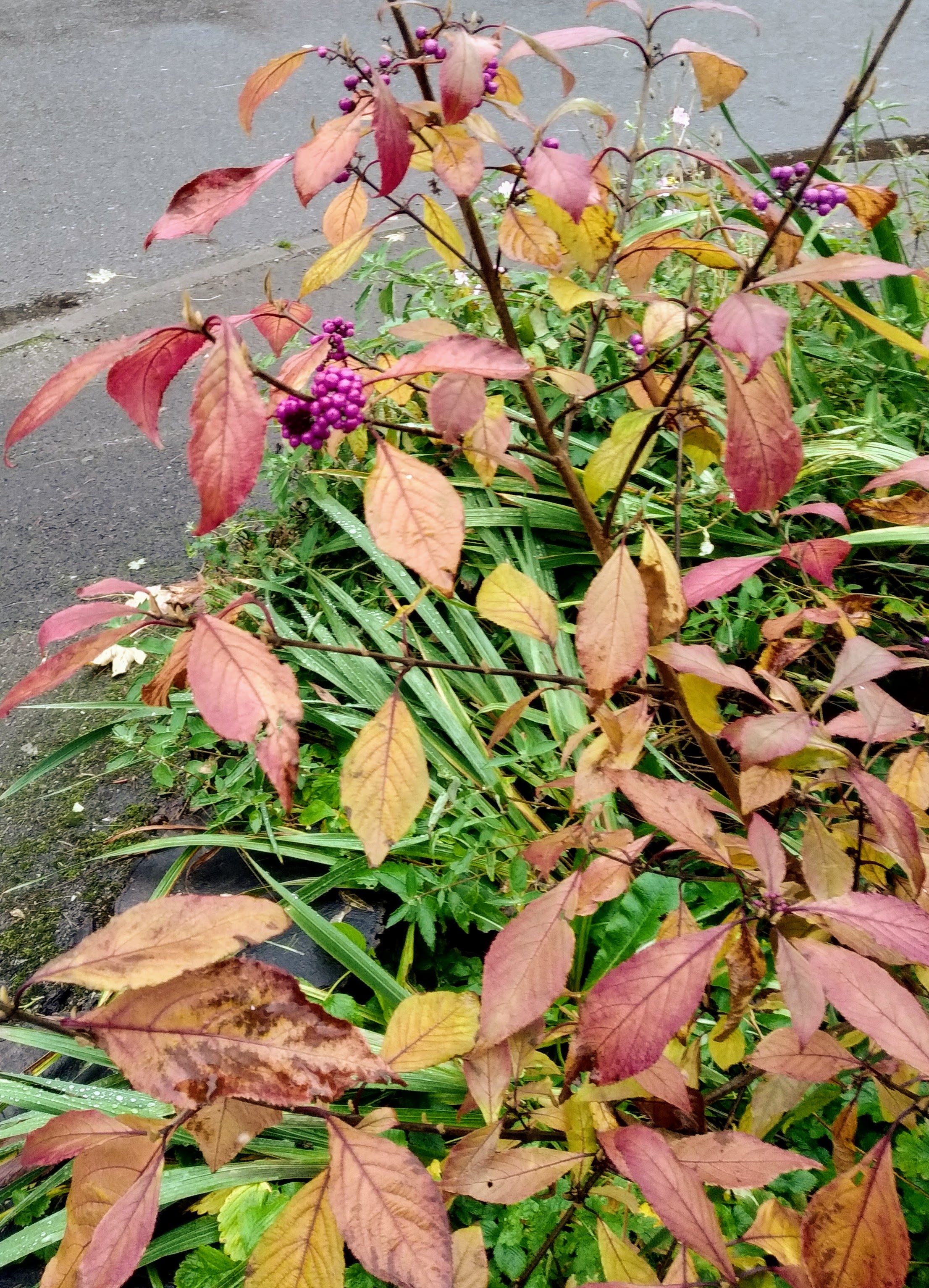
Callicarpa Americana
''Callicarpa americana'', the American beautyberry, is an open-habitat, native shrub of the Southern United States which is often grown as an ornamental in gardens and yards. American beautyberries produce large clusters of purple berries, which birds and deer eat, thus distributing the seeds. Uses The raw berries, while palatably sweet, are suitable for human consumption only in small amounts, because they are astringent. Some people have reported mild stomach cramps after consumption. The berries are also used in jellies and wine. The roots are used to make herbal tea. As a folk remedy it has been claimed that "fresh, crushed leaves of American beautyberry, ''Callicarpa americana'' ... helped keep biting insects away from animals such as horses and mules". A chemical compound isolated from the plant, callicarpenal, was effective as a mosquito repellent in a laboratory experiment using a simulated skin model. The berries ripen in September through October and are a favorite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terpenoid
The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeably with "terpenes", terpenoids contain additional functional groups, usually containing oxygen. When combined with the hydrocarbon terpenes, terpenoids comprise about 80,000 compounds. They are the largest class of plant secondary metabolites, representing about 60% of known natural products. Many terpenoids have substantial pharmacological bioactivity and are therefore of interest to medicinal chemists. Plant terpenoids are used for their aromatic qualities and play a role in traditional herbal remedies. Terpenoids contribute to the scent of eucalyptus, the flavors of cinnamon, cloves, and ginger, the yellow color in sunflowers, and the red color in tomatoes. Well-known terpenoids include citral, menthol, camphor, salvinorin A in the plant '' Salvia di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect Repellent
An insect repellent (also commonly called "bug spray") is a substance applied to skin, clothing, or other surfaces to discourage insects (and arthropods in general) from landing or climbing on that surface. Insect repellents help prevent and control the outbreak of insect-borne (and other arthropod-bourne) diseases such as malaria, Lyme disease, dengue fever, bubonic plague, river blindness, and West Nile fever. Pest animals commonly serving as vectors for disease include insects such as flea, fly, and mosquito; and ticks (arachnids). Some insect repellents are insecticides (bug killers), but most simply discourage insects and send them flying or crawling away. Nearly any would be fatal upon reaching the median lethal dose, but classification as an insecticide implies death even at lower doses. Effectiveness Synthetic repellents tend to be more effective and/or longer lasting than "natural" repellents. For protection against mosquito bites, the U.S. Centers for Diseas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning " gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "little fly". Mosquitoes have a slender segmented body, one pair of wings, one pair of halteres, three pairs of long hair-like legs, and elongated mouthparts. The mosquito life cycle consists of egg, larva, pupa, and adult stages. Eggs are laid on the water surface; they hatch into motile larvae that feed on aquatic algae and organic material. These larvae are important food sources for many freshwater animals, such as dragonfly nymphs, many fish, and some birds such as ducks. The adult females of most species have tube-like mouthparts (called a proboscis) that can pierce the skin of a host and feed on blood, which contains protein and iron needed to produce eggs. Thousands of mosquito species feed on the blood of various hosts � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aedes Aegypti
''Aedes aegypti'', the yellow fever mosquito, is a mosquito that can spread dengue fever, chikungunya, Zika fever, Mayaro and yellow fever viruses, and other disease agents. The mosquito can be recognized by black and white markings on its legs and a marking in the form of a lyre on the upper surface of its thorax. This mosquito originated in Africa, but is now found in tropical, subtropical and temperate regions throughout the world. Biology ''Aedes aegypti'' is a long, dark mosquito which can be recognized by white markings on its legs and a marking in the form of a lyre on the upper surface of its thorax. Females are larger than males. Microscopically females possess small palps tipped with silver or white scales, and their antennae have sparse short hairs, whereas those of males are feathery. ''Aedes aegypti'' can be mixed up with Aedes albopictus without a magnifying glass: The latter have a white stripe on the top of the mid thorax. Males live off fruit and only the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anopheles Stephensi
''Anopheles stephensi'' is a primary mosquito vector of malaria in urban India and is included in the same subgenus as ''Anopheles gambiae'', the primary malaria vector in Africa. ''A. gambiae'' consists of a complex of morphologically identical species of mosquitoes, along with all other major malaria vectors; however, ''A. stephensi'' has not yet been included in any of these complexes. Nevertheless, two races of ''A. stephensi'' exist based on differences in egg dimensions and the number of ridges on the eggs; ''A. s. stephensi'' ''sensu stricto'', the type form, is a competent malaria vector that takes place in urban areas, and ''A. s. mysorensis'', the variety form, exists in rural areas and exhibits considerable zoophilic behaviour, making it a poor malaria vector. However, ''A. s. mysorensis'' is a detrimental vector in Iran.Sinka, M.E., Bangs, M.J., Manguin, S., Chareonviriyaphap, T., Patil, A.P., Temperley, W.H., Gething, P. W., Elyazar, I.R.F., Kabaria, C.W., Harbach, R. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Ant
Fire ants are several species of ants in the genus ''Solenopsis'', which includes over 200 species. ''Solenopsis'' are stinging ants, and most of their common names reflect this, for example, ginger ants and tropical fire ants. Many of the names shared by this genus are often used interchangeably to refer to other species of ant, such as the term red ant, mostly because of their similar coloration despite not being in the genus Solenopsis. Both ''Myrmica rubra ''Myrmica rubra'', also known as the common red ant or erroneously the European fire ant, is a species of ant of the genus '' Myrmica'', found all over Europe and is now invasive in some parts of North America and Asia. It is mainly red in colou ...'' and ''Pogonomyrmex barbatus'' are common examples of non-Solenopsis ants being termed red ants. None of these names apply to all species of ''Solenopsis'' nor only to ''Solenopsis'' species; for example the colloquial names for several species of weaver ants in the genus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tick
Ticks (order Ixodida) are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by feeding on the blood of mammals, birds, and sometimes reptiles and amphibians. The timing of the origin of ticks is uncertain, though the oldest known tick fossils are from the Cretaceous period, around 100 million years old. Ticks are widely distributed around the world, especially in warm, humid climates. Ticks belong to two major families, the Ixodidae or hard ticks, and the Argasidae, or soft ticks. ''Nuttalliella,'' a genus of tick from southern Africa is the only member of the family Nuttalliellidae, and represents the most primitive living lineage of ticks. Adults have ovoid/pear-shaped bodies (idiosomas) which become engorged with blood when they feed, and eight legs. Their cephalothorax and abdomen are completely fused. In addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ixodes Scapularis
''Ixodes scapularis'' is commonly known as the deer tick or black-legged tick (although some people reserve the latter term for ''Ixodes pacificus'', which is found on the west coast of the US), and in some parts of the US as the bear tick. It was also named ''Ixodes dammini'' until it was shown to be the same species in 1993. It is a hard-bodied tick found in the eastern and northern Midwest of the United States as well as in southeastern Canada. It is a vector for several diseases of animals, including humans (Lyme disease, babesiosis, anaplasmosis, Powassan virus disease, etc.) and is known as the deer tick owing to its habit of parasitizing the white-tailed deer. It is also known to parasitize mice, lizards, migratory birds, etc. especially while the tick is in the larval or nymphal stage. Description The image shown here—and in fact, most images of ''Ixodes scapularis'' that are commonly available—show an adult female that is unengorged, that is, an adult female that h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
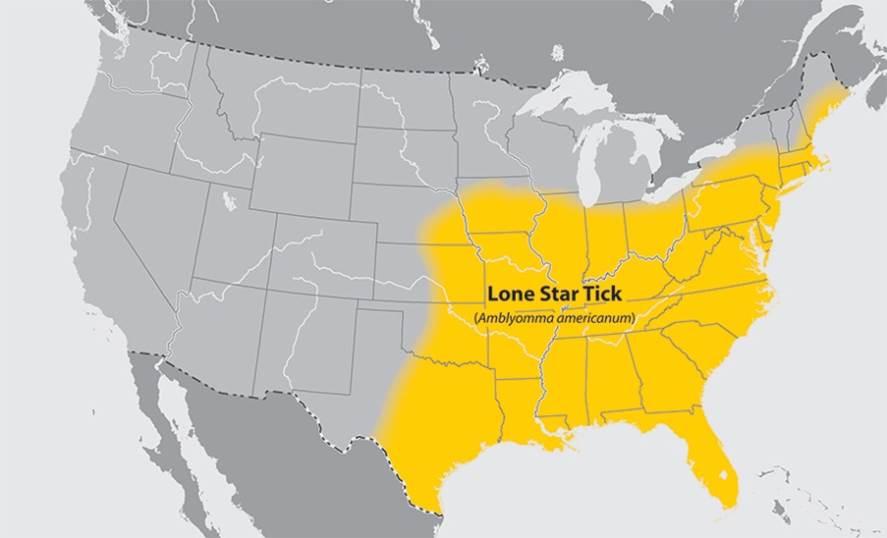
Amblyomma Americanum
''Amblyomma americanum'', also known as the lone star tick, the northeastern water tick, or the turkey tick, or the "Cricker Tick", is a type of tick indigenous to much of the eastern United States and Mexico, that bites painlessly and commonly goes unnoticed, remaining attached to its host for as long as seven days until it is fully engorged with blood. It is a member of the phylum Arthropoda, class Arachnida. The adult lone star tick is sexually dimorphic, named for a silvery-white, star-shaped spot or "lone star" present near the center of the posterior portion of the adult female shield (scutum); adult males conversely have varied white streaks or spots around the margins of their shields. ''A. americanum'' is also referred to as the turkey tick in some Midwestern U.S. states, where wild turkeys are a common host for immature ticks. It is the primary vector of ''Ehrlichia chaffeensis'', which causes human monocytic ehrlichiosis, and ''Ehrlichia ewingii'', which causes human a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DEET
''N'',''N''-Diethyl-''meta''-toluamide, also called DEET () or diethyltoluamide, is the most common active ingredient in insect repellents. It is a slightly yellow oil intended to be applied to the skin or to clothing and provides protection against mosquitoes, flies, ticks, fleas, chiggers, leeches and many biting insects. History DEET was developed in 1944 by Samuel Gertler of the United States Department of Agriculture for use by the United States Army, following its experience of jungle warfare during World War II. It was originally tested as a pesticide on farm fields, and entered military use in 1946 and civilian use in 1957. It was used in Vietnam and Southeast Asia. In its original form, known as "bug juice", the application solution was composed of 75% DEET and 25% ethanol. Later, a new version of the repellent was developed by the U.S. Army and the USDA. This formulation consisted of DEET and a mixture of polymers that extended its release and reduced its evaporation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |