|
Business Performance Management
Business performance management (BPM), also known as corporate performance management (CPM) and enterprise performance management (EPM),) is a set of performance management and analytic processes that enables the management of an organization's performance to achieve one or more pre-selected goals. Gartner retired the concept of "CPM" and reclassified it as "financial planning and analysis (FP&A)," and "financial close" to reflect two concepts: increased focus on planning and the emergence of a new category of solutions supporting the management of the financial close. Business performance management is contained within approaches to business process management. History Before the Information Age in the late 20th century, businesses sometimes laboriously collected data from non-automated sources. As they lacked computing resources to analyze the data properly, they often made commercial decisions primarily by intuition (knowledge), intuition. As businesses started automating th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Buytendijk
Frank Buytendijk (The Hague, 1969) is a Dutch author of management books. He studied business and information technology at the Hogeschool Utrecht (University of Applied Sciences Utrecht), was a consultant at various firms in his home country, was a research analyst and held executive positions in various large, medium and small software companies. He has a background in business intelligence, corporate performance management and business process management. Buytendijk is also a visiting fellow at Cranfield University School of Management. In 2012, he was appointed fellow at The Data Warehousing Institute (TDWI). Currently, Buytendijk is a research vice president at analyst firm Gartner, where he served before as well between 2001 and 2006. Buytendijk wrote five books related to strategy, organizational behavior and performance management. A common theme throughout these books is the application of stakeholder theory in business. According tmanagementboek.nl Buytendijk's firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activity-based Costing
Activity-based costing (ABC) is a costing method that identifies activities in an organization and assigns the cost of each activity to all products and services according to the actual consumption by each. Therefore, this model assigns more indirect costs ( overhead) into direct costs compared to conventional costing. CIMA, the Chartered Institute of Management Accountants, defines ABC as an approach to the costing and monitoring of activities which involves tracing resource consumption and costing final outputs. Resources are assigned to activities, and activities to cost objects based on consumption estimates. The latter utilize cost drivers to attach activity costs to outputs. The Institute of Cost & Management Accountants of Bangladesh (ICMAB) defines activity-based costing as an accounting method which identifies the activities which a firm performs and then assigns indirect costs to cost objects. Objectives With ABC, a company can soundly estimate the cost elements o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overall Equipment Effectiveness
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a measure of how well a manufacturing operation is utilized (facilities, time and material) compared to its full potential, during the periods when it is scheduled to run. It identifies the percentage of manufacturing time that is truly productive. An OEE of 100% means that only good parts are produced (100% ''quality''), at the maximum speed (100% ''performance''), and without interruption (100% ''availability''). Measuring OEE is a manufacturing best practice. By measuring OEE and the underlying losses, important insights can be gained on how to systematically improve the manufacturing process. OEE is an effective metric for identifying losses, bench-marking progress, and improving the productivity of manufacturing equipment (i.e., eliminating waste). The best way for reliablOEE monitoring is to automatically collect all data directly from the machines. Total Effective Equipment Performance (TEEP) is a closely related measure which quant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dashboard (business)
In business computer information systems, a dashboard is a type of graphical user interface which often provides at-a-glance views of key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to a particular objective or business process. In other usage, "dashboard" is another name for "progress report" or "report" and considered a form of data visualization. In providing this overview, business owners can save time and improve their decision making by utilizing dashboards. The “dashboard” is often accessible by a web browser and is usually linked to regularly updating data sources. Well known dashboards include Google Analytics dashboards, used on 55% of all websites, which show activity on a website; such as visits, entry pages, bounce rate and traffic sources. The COVID-19 pandemic of 2020 brought other dashboards to the fore, with the Johns Hopkins coronavirus tracker and the UK government coronavirus tracker being good examples. The term dashboard originates from the automobile das ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Time (media)
Real time within the media is a method in which events are portrayed at the same rate at which they occur in the plot. For example, if a film told in real time is two hours long, then the plot of that movie covers two hours of fictional time. If a daily real time comic strip runs for six years, then the characters will be six years older at the end of the strip than they were at the beginning. This technique can be enforced with varying levels of precision. In some stories, every minute of screen time is a minute of fictional time. In other stories, such as the daily comic strip '' For Better or For Worse'', each day's strip does not necessarily correspond to a new day of fictional time, but each year of the strip does correspond to one year of fictional time. Real time fiction dates back to the climactic structure of classical Greek drama. Film, television and radio Often, use of split screens or picture-in-pictures are used to show events occurring at the same time, or the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Validity (statistics)
Validity is the main extent to which a concept, conclusion or measurement is well-founded and likely corresponds accurately to the real world. The word "valid" is derived from the Latin validus, meaning strong. The validity of a measurement tool (for example, a test in education) is the degree to which the tool measures what it claims to measure. Validity is based on the strength of a collection of different types of evidence (e.g. face validity, construct validity, etc.) described in greater detail below. In psychometrics, validity has a particular application known as test validity: "the degree to which evidence and theory support the interpretations of test scores" ("as entailed by proposed uses of tests"). It is generally accepted that the concept of scientific validity addresses the nature of reality in terms of statistical measures and as such is an epistemological and philosophical issue as well as a question of measurement. The use of the term in logic is narrower, relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability (statistics)
In statistics and psychometrics, reliability is the overall consistency of a measure. A measure is said to have a high reliability if it produces similar results under consistent conditions:"It is the characteristic of a set of test scores that relates to the amount of random error from the measurement process that might be embedded in the scores. Scores that are highly reliable are precise, reproducible, and consistent from one testing occasion to another. That is, if the testing process were repeated with a group of test takers, essentially the same results would be obtained. Various kinds of reliability coefficients, with values ranging between 0.00 (much error) and 1.00 (no error), are usually used to indicate the amount of error in the scores." For example, measurements of people's height and weight are often extremely reliable.The Marketing Accountability Standards Board (MASB) endorses this definition as part of its ongoinCommon Language: Marketing Activities and Metrics Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benchmarking
Benchmarking is the practice of comparing business processes and performance metrics to industry bests and best practices from other companies. Dimensions typically measured are quality, time and cost. Benchmarking is used to measure performance using a specific indicator (cost per unit of measure, productivity per unit of measure, cycle time of x per unit of measure or defects per unit of measure) resulting in a metric of performance that is then compared to others. Also referred to as "best practice benchmarking" or "process benchmarking", this process is used in management in which organizations evaluate various aspects of their processes in relation to best-practice companies' processes, usually within a peer group defined for the purposes of comparison. This then allows organizations to develop plans on how to make improvements or adapt specific best practices, usually with the aim of increasing some aspect of performance. Benchmarking may be a one-off event, but is often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operationalization
In research design, especially in psychology, social sciences, life sciences and physics, operationalization or operationalisation is a process of defining the measurement of a phenomenon which is not directly Measurement, measurable, though its existence is inferred by other phenomena. Operationalization thus defines a fuzzy concept so as to make it clearly distinguishable, measurable, and understandable by empirical observation. In a broader sense, it defines the Extension (semantics), extension of a concept—describing what is and is not an instance of that concept. For example, in medicine, the phenomenon of health might be operationalized by one or more indicators like body mass index or tobacco smoking. As another example, in visual processing the presence of a certain object in the environment could be inferred by measuring specific features of the light it reflects. In these examples, the phenomena are difficult to directly observe and measure because they are general/abstra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
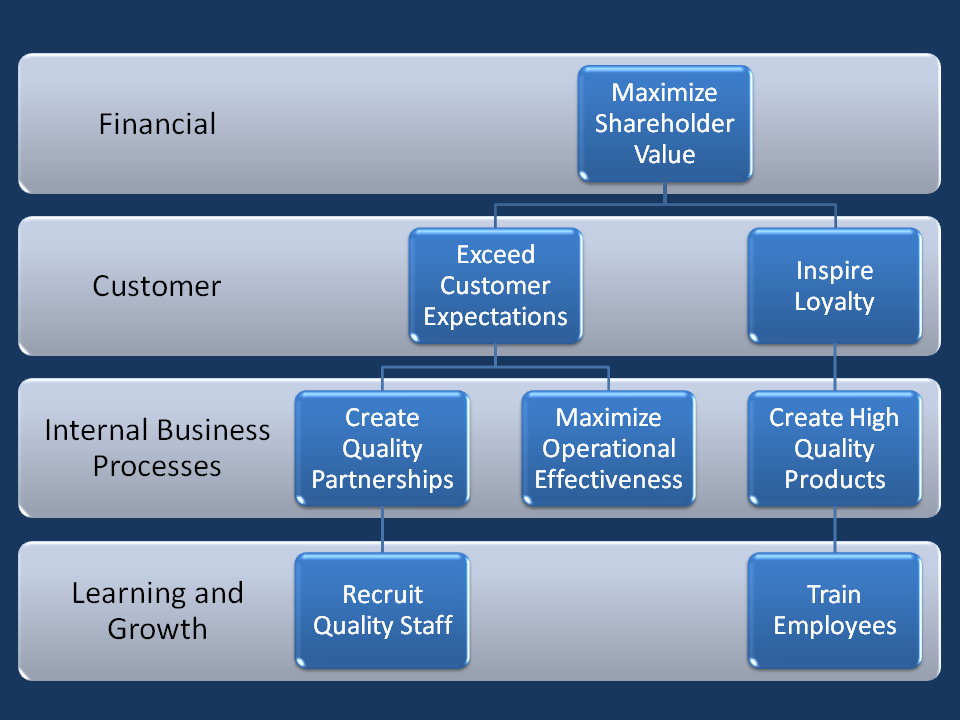
Strategy Map
A strategy map is a diagram that documents the strategic goals being pursued by an organization or management team. It is an element of the documentation associated with the Balanced Scorecard, and in particular is characteristic of the second generation of Balanced Scorecard designs that first appeared during the mid-1990s. The first diagrams of this type appeared in the early 1990s, and the idea of using this type of diagram to help document Balanced Scorecard was discussed in a paper by Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton in 1996. The strategy map idea featured in several books and articles during the late 1990s by Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton. Their original book in 1996, "The Balanced Scorecard, Translating strategy into action", contained diagrams which are later called strategy maps, but at this time they did not refer to them as such. Kaplan & Norton's second book, The Strategy Focused Organization, explicitly refers to strategy maps and includes a chapter on how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Strategic Measurement
Integration may refer to: Biology *Multisensory integration *Path integration * Pre-integration complex, viral genetic material used to insert a viral genome into a host genome *DNA integration, by means of site-specific recombinase technology, performed by a specific class of recombinase enzymes ("integrases") Economics and law *Economic integration, trade unification between different states *Horizontal integration and vertical integration, in microeconomics and strategic management, styles of ownership and control *Regional integration, in which states cooperate through regional institutions and rules * Integration clause, a declaration that a contract is the final and complete understanding of the parties *A step in the process of money laundering *Integrated farming, a farm management system * Integration (tax), a feature of corporate and personal income tax in some countries Engineering *Data integration * Digital integration *Enterprise integration *Integrated archit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |