|
Bushy Cell
Bushy cells are two types of second order neuron found in the anterior part of the ventral cochlear nucleus, the AVCN. They can be ''globular'' or ''spherical'' giving outputs to different parts of the superior olivary complex. Structure Bushy cells are named after their appearance to bushes, having short dendrites. They are almost completely engulfed by the synaptic connections from the endbulbs of Held. Function Because of the large synaptic contact from the auditory nerve fibres, the output pattern from the bushy cell is almost the same as the auditory nerve input. Projections from the globular bushy cells extend to the superior olive on both sides of the brainstem where they give input to the bipolar neurons. The superior olive is an area seen to be of importance in the processing of binaural signals. Projections from the spherical bushy cells give excitatory input to the lateral and medial parts of the superior olive (the LSO and MSO). Again their very close synaptic coupli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventral Cochlear Nucleus
In the ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN), auditory nerve fibers enter the brain via the nerve root in the VCN. The ventral cochlear nucleus is divided into the anterior ventral (anteroventral) cochlear nucleus (AVCN) and the posterior ventral (posteroventral) cochlear nucleus (PVCN). In the VCN, auditory nerve fibers bifurcate, the ascending branch innervates the AVCN and the descending branch innervates the PVCN and then continue to the dorsal cochlear nucleus. The orderly innervation by auditory nerve fibers gives the AVCN a tonotopic organization along the dorsoventral axis. Fibers that carry information from the apex of the cochlea that are tuned to low frequencies contact neurons in the ventral part of the AVCN; those that carry information from the base of the cochlea that are tuned to high frequencies contact neurons in the dorsal part of the AVCN. Several populations of neurons populate the AVCN. Bushy cells receive input from auditory nerve fibers through particularly large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Olivary Complex
The superior olivary complex (SOC) or superior olive is a collection of brainstem nuclei that functions in multiple aspects of hearing and is an important component of the ascending and descending auditory pathways of the auditory system. The SOC is intimately related to the trapezoid body: most of the cell groups of the SOC are dorsal (posterior in primates) to this axon bundle while a number of cell groups are embedded in the trapezoid body. Overall, the SOC displays a significant interspecies variation, being largest in bats and rodents and smaller in primates. Physiology The superior olivary nucleus plays a number of roles in hearing. The medial superior olive (MSO) is a specialized nucleus that is believed to measure the time difference of arrival of sounds between the ears (the interaural time difference or ITD). The ITD is a major cue for determining the azimuth of sounds, i.e., localising them on the azimuthal plane – their degree to the left or the right. The lateral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bushes
A shrub (often also called a bush) is a small-to-medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from trees by their multiple stems and shorter height, less than tall. Small shrubs, less than 2 m (6.6 ft) tall are sometimes termed as subshrubs. Many botanical groups have species that are shrubs, and others that are trees and herbaceous plants instead. Some definitions state that a shrub is less than and a tree is over 6 m. Others use as the cut-off point for classification. Many species of tree may not reach this mature height because of hostile less than ideal growing conditions, and resemble a shrub-sized plant. However, such species have the potential to grow taller under the ideal growing conditions for that plant. In terms of longevity, most shrubs fit in a class between perennials and trees; some may only last about five y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calyx Of Held
The Calyx of Held is a particularly large synapse in the mammalian Auditory system, auditory central nervous system, so named after Hans Held who first described it in his 1893 article ''Die centrale Gehörleitung''Held, H. "Die centrale Gehörleitung" Arch. Anat. Physiol. Anat. Abt, 1893 because of its resemblance to the sepal, calyx of a flower. Globular bushy cells in the anterior cochlear nucleus, anteroventral cochlear nucleus (AVCN) send axons to the contralateral medial nucleus of the trapezoid body (MNTB), where they synapse via these calyces on MNTB principal cells. These principal cells then project to the ipsilateral Superior olivary nucleus, lateral superior olive (LSO), where they inhibit postsynaptic neurons and provide a basis for Interaural level difference, interaural level detection (ILD), required for high frequency sound localization. This synapse has been described as the largest in the brain. The related endbulb of Held is also a large axon terminal smaller sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auditory Nerve
The cochlear nerve (also auditory nerve or acoustic nerve) is one of two parts of the vestibulocochlear nerve, a cranial nerve present in amniotes, the other part being the vestibular nerve. The cochlear nerve carries auditory sensory information from the cochlea of the inner ear directly to the brain. The other portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve is the vestibular nerve, which carries spatial orientation information to the brain from the semicircular canals, also known as semicircular ducts. Anatomy and connections In terms of anatomy, an auditory nerve fiber is either bipolar or unipolar, with its distal projection being called the peripheral process, and its proximal projection being called the axon; these two projections are also known as the "peripheral axon" and the "central axon", respectively. The peripheral process is sometimes referred to as a dendrite, although that term is somewhat inaccurate. Unlike the typical dendrite, the peripheral process generates and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olivary Body
In anatomy, the olivary bodies or simply olives (Latin ''oliva'' and ''olivae'', singular and plural, respectively) are a pair of prominent oval structures in the medulla oblongata, the lower portion of the brainstem. They contain the olivary nuclei. Structure The olivary body is located on the anterior surface of the medulla lateral to the pyramid, from which it is separated by the antero-lateral sulcus and the fibers of the hypoglossal nerve. Behind (dorsally), it is separated from the postero-lateral sulcus by the ventral spinocerebellar fasciculus. In the depression between the upper end of the olive and the pons lies the vestibulocochlear nerve. In humans, it measures about 1.25 cm. in length, and between its upper end and the pons there is a slight depression to which the roots of the facial nerve are attached. The external arcuate fibers wind across the lower part of the pyramid and olive and enter the inferior peduncle. Olivary nuclei The olive consists of two pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch, and sometimes the diencephalon is included in the brainstem. The brainstem is very small, making up around only 2.6 percent of the brain's total weight. It has the critical roles of regulating cardiac, and respiratory function, helping to control heart rate and breathing rate. It also provides the main motor and sensory nerve supply to the face and neck via the cranial nerves. Ten pairs of cranial nerves come from the brainstem. Other roles include the regulation of the central nervous system and the body's sleep cycle. It is also of prime importance in the conveyance of motor and sensory pathways from the rest of the brain to the body, and from the body back to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
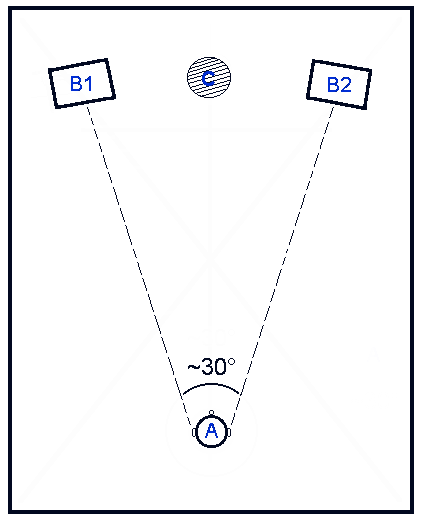
Interaural Time Difference
The interaural time difference (or ITD) when concerning humans or animals, is the difference in arrival time of a sound between two ears. It is important in the localization of sounds, as it provides a cue to the direction or angle of the sound source from the head. If a signal arrives at the head from one side, the signal has further to travel to reach the far ear than the near ear. This pathlength difference results in a time difference between the sound's arrivals at the ears, which is detected and aids the process of identifying the direction of sound source. When a signal is produced in the horizontal plane, its angle in relation to the head is referred to as its azimuth, with 0 degrees (0°) azimuth being directly in front of the listener, 90° to the right, and 180° being directly behind. Different methods for measuring ITDs *For an abrupt stimulus such as a click, onset ITDs are measured. An onset ITD is the time difference between the onset of the signal reaching two ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interaural Level Difference
Sound localization is a listener's ability to identify the location or origin of a detected sound in direction and distance. The sound localization mechanisms of the mammalian auditory system have been extensively studied. The auditory system uses several cues for sound source localization, including time difference and level difference (or intensity difference) between the ears, and spectral information. These cues are also used by other animals, such as birds and reptiles, but there may be differences in usage, and there are also localization cues which are absent in the human auditory system, such as the effects of ear movements. Animals with the ability to localize sound have a clear evolutionary advantage. How sound reaches the brain Sound is the perceptual result of mechanical vibrations traveling through a medium such as air or water. Through the mechanisms of compression and rarefaction, sound waves travel through the air, bounce off the pinna and concha of the exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_entre_izquierdo_(inferior)_y_correcto_(superior)_orejas.jpg)