|
Bubble Bath
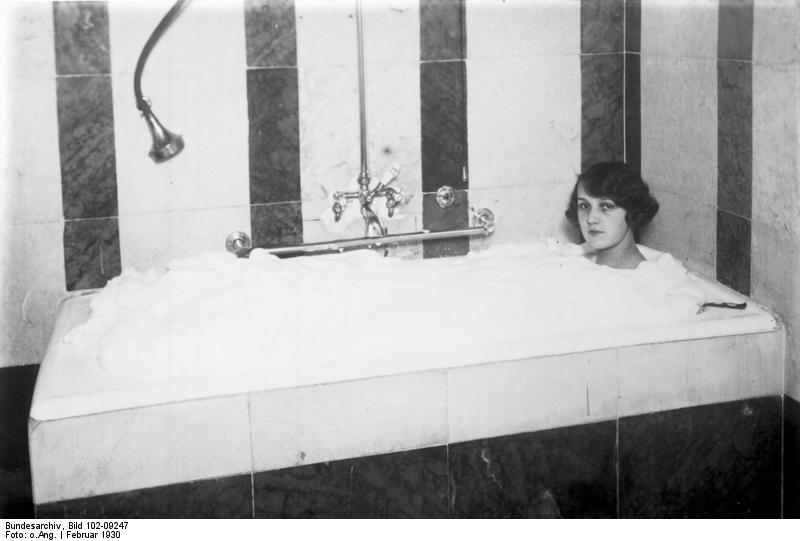
A bubble bath is a filled bathtub with a layer of surfactant foam on the surface of the water and consequently also the surfactant product used to produce the foam or soap. Less commonly, aerated or carbonated baths are called ''bubble baths''. Bubbles on top of the water, less ambiguously known as a foam bath (see photo), can be obtained by adding a product containing foaming surfactants to water and temporarily aerating it by agitation (often merely by the fall of water filling the tub). The practice is popular for personal bathing because of the belief that it cleanses the skin, that the foam insulates the bath water, keeping it warm for longer, and (as a lime soap dispersant) prevents or reduces deposits on the bath tub at and below the water level (called "bathtub ring" and soap scum, respectively) produced by soap and hard water. It can hide the body of the bather, preserving modesty or, in theatre and film, giving the appearance that a performer who is actually clothed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundesarchiv Bild 102-09247, Berlinerin Im Schaumbad
, type = Archive , seal = , seal_size = , seal_caption = , seal_alt = , logo = Bundesarchiv-Logo.svg , logo_size = , logo_caption = , logo_alt = , image = Bundesarchiv Koblenz.jpg , image_caption = The Federal Archives in Koblenz , image_alt = , formed = , preceding1 = , preceding2 = , dissolved = , superseding1 = , superseding2 = , agency_type = , jurisdiction = , status = Active , headquarters = PotsdamerStraße156075Koblenz , coordinates = , motto = , employees = , budget = million () , chief1_name = Michael Hollmann , chief1_position = President of the Federal Archives , chief2_name = Dr. Andrea Hänger , chief2_position ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonionic
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons. Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed atomic or monatomic ions, while two or more atoms form molecular ions or polyatomic ions. In the case of physical ionization in a fluid (gas or liquid), "ion pairs" are created by spontaneous molecule collisions, where each generated pair consists of a free electron and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathing
Bathing is the act of washing the body, usually with water, or the immersion of the body in water. It may be practiced for personal hygiene, religious ritual or therapeutic purposes. By analogy, especially as a recreational activity, the term is also applied to sun bathing and sea bathing. People bathe at a range of temperatures, according to custom or purpose, from very cold to very hot. In the western world, bathing is usually done at comfortable temperatures in a bathtub or shower. This type of bathing is done more or less daily for hygiene purposes. A ritual religious bath is sometimes referred to as immersion or baptism. The use of water for therapeutic purposes can be called a water treatment or hydrotherapy. Recreational water activities are also known as swimming and paddling. History Ancient world Throughout history, societies devised systems to enable water to be brought to population centers. The oldest accountable daily ritual of bathing can be traced to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bath Fizzies
{{No sources, date=October 2017 Bath fizzies are material products designed to effervesce in bathwater. They come in the form of: * amorphous grains of homogeneous mixture, packaged in a box, jar, or envelope; * single-use envelopes of mixed powders; and * solid boluses of homogeneous or inhomogeneous mixture called bath bombs. Bath fizzies date from the early 20th Century and may be considered a form of bath salts in that the products of their use include a salt solution in addition to the carbon dioxide bubbles which are their definitive feature. Their ingredients must include one or more acid(s) and one or more water-soluble bicarbonate, sesquicarbonate, and/or carbonate. In addition they commonly include coloring, fragrance, and/or other water-soluble, water-dispersible, and/or volatile ingredients for esthetic, cosmetic, or skin soothing purposes. This principle of effervescing while releasing other ingredients is the same that has been used by tableted products for child ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
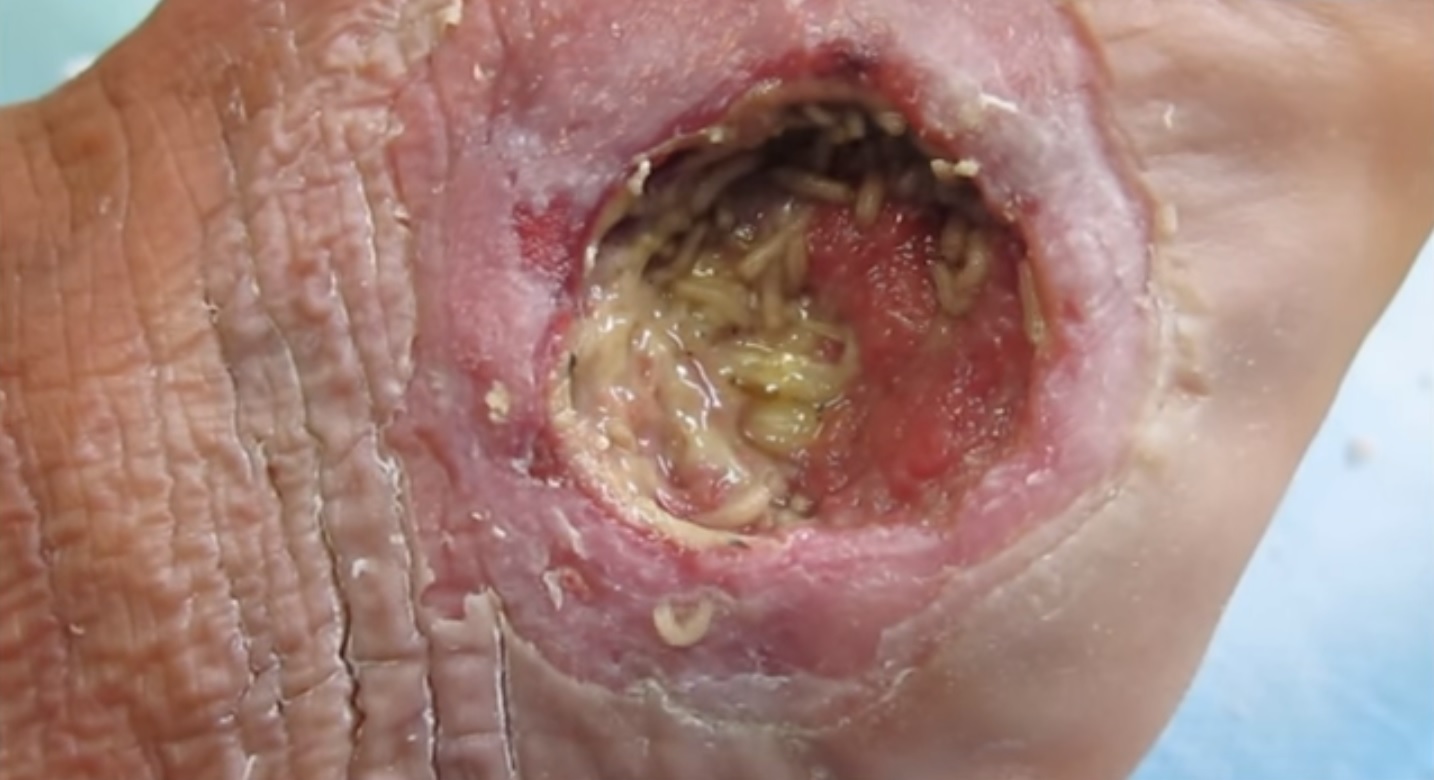
Debridement
Debridement is the medical removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue. Removal may be surgical, mechanical, chemical, autolytic (self-digestion), and by maggot therapy. In podiatry, practitioners such as chiropodists, podiatrists and foot health practitioners remove conditions such as calluses and verrucas. Debridement is an important part of the healing process for burns and other serious wounds; it is also used for treating some kinds of snake and spider bites. Sometimes the boundaries of the problem tissue may not be clearly defined. For example, when excising a tumor, there may be micrometastases along the edges of the tumor that are too small to be detected, but if not removed, could cause a relapse. In such circumstances, a surgeon may opt to debride a portion of the surrounding healthy tissue to ensure that the tumor is completely removed. Types There is lack of high quality evidence to compare th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacuzzi
Jacuzzi Brands LLC (; ), through its subsidiaries, is a global manufacturer and distributor of branded baths, hot tubs, pools, saunas and, formerly, aircraft. Founded in 1915 by the Italian family of the same name, Jacuzzi is a federally registered trademark of Jacuzzi Inc. as of September 5, 1978. History Jacuzzi Brothers was founded in 1915 by seven Italian brothers from Casarsa della Delizia, Friuli, in Northern Italy, led by Rachele, who had worked for James Smith McDonnell, and invented the first wood laminate propeller. The company made wooden propellers under military contracts, based at 2043 San Pablo Avenue, Berkeley, California. In 1920, the brothers also dabbled briefly with aircraft design and manufacture, with a single-seat monoplane and a seven-seat cabin monoplane. Both aircraft were noted for their use of laminated wood products for fuselage manufacture, but were essentially unsuccessful, with only one of each type being built. In 1921, Giocondo Jacuzzi, the pilo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bath Salts
Bath salts are water-soluble, pulverized minerals that are added to water to be used for bathing. They are said to improve cleaning, enhance the enjoyment of bathing, and serve as a vehicle for cosmetic agents. Bath salts have been developed which mimic the properties of natural mineral baths or hot springs. Some bath salts contain glycerine so the product will act as an emollient, humectant, or lubricant. Fragrances and colors are often added to bath salts; the fragrances are used to increase the users' enjoyment of the bathing experience. Description Substances often labeled as bath salts include magnesium sulfate (Epsom salts), sodium chloride (table salt), sodium bicarbonate (baking soda), sodium hexametaphosphate (Calgon, amorphous/glassy sodium metaphosphate), sodium sesquicarbonate, borax, and sodium citrate. Glycerin, or liquid glycerin, is another common ingredient in bath salts. Depending on their properties, the additives can be classified as emollient, humect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bath Bomb
A bath bomb is a consumer product used during bathing. It was invented and patented in 1989 by Mo Constantine, co-founder of Lush Cosmetics. It is a compacted mixture of wet and dry ingredients molded into any of several shapes and then dried. Bath water effervesces at the surface of a bath bomb immersed within it, with attendant dispersion of such ingredients as essential oil, moisturizer, scent, or colorant. History The bath bomb was invented in 1989 by Lush Cosmetics co-founder Mo Constantine. Working from her shed in Dorset, Constantine was inspired to create her 'Aqua Sizzlers' (which would later become 'Bath Bombs') after becoming intrigued by Alka-Seltzer tablets. While her first attempts looked much like Alka-Seltzer tablets, Mo and her husband Mark Constantine quickly began experimenting with a range of molds and ingredients.“We were up and down the high street, buying different shaped jelly moulds, anything. In the garden centre, Mark was saying ‘What are you l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bath Fizzies
{{No sources, date=October 2017 Bath fizzies are material products designed to effervesce in bathwater. They come in the form of: * amorphous grains of homogeneous mixture, packaged in a box, jar, or envelope; * single-use envelopes of mixed powders; and * solid boluses of homogeneous or inhomogeneous mixture called bath bombs. Bath fizzies date from the early 20th Century and may be considered a form of bath salts in that the products of their use include a salt solution in addition to the carbon dioxide bubbles which are their definitive feature. Their ingredients must include one or more acid(s) and one or more water-soluble bicarbonate, sesquicarbonate, and/or carbonate. In addition they commonly include coloring, fragrance, and/or other water-soluble, water-dispersible, and/or volatile ingredients for esthetic, cosmetic, or skin soothing purposes. This principle of effervescing while releasing other ingredients is the same that has been used by tableted products for child ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocamidopropyl Betaine
Cocamidopropyl betaine (CAPB) is a mixture of closely related organic compounds derived from coconut oil and dimethylaminopropylamine. CAPB is available as a viscous pale yellow solution and it is used as a surfactant in personal care products and animal husbandry. The name reflects that the major part of the molecule, the lauric acid group, is derived from coconut oil. Cocamidopropyl betaine to a significant degree has replaced cocamide DEA. Production Despite the name cocamidopropyl betaine, the molecule is not synthesized from betaine. Instead it is produced in a two step manner, beginning with the reaction of dimethylaminopropylamine (DMAPA) with fatty acids from coconut or palm kernel oil (lauric acid, or its methyl ester, is the main constituent). The primary amine in DMAPA is more reactive than the tertiary amine, leading to its selective addition to form an amide. In the second step chloroacetic acid reacts with the remaining tertiary amine to form a quaternary ammonium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betaines
A betaine () in chemistry is any neutral chemical compound with a positively charged cationic functional group, such as a quaternary ammonium or phosphonium cation (generally: onium ions) that bears no hydrogen atom and with a negatively charged functional group such as a carboxylate group that may not be adjacent to the cationic site. Historically, the term was reserved for trimethylglycine (TMG) which is involved in methylation reactions and detoxification of homocysteine. This is a modified amino acid consisting of glycine with three methyl groups serving as methyl donor for various metabolic pathways. The pronunciation of the compound reflects its origin and first isolation from sugar ''beets'' (''Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''vulgaris''), and does not derive from the Greek letter beta (β). It is commonly pronounced ''beta-INE'' or ''BEE-tayn''. In biological systems, many naturally occurring betaines serve as organic osmolytes. These are substances synthesized or taken up from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_02.jpg)