|
Boring (manufacturing)
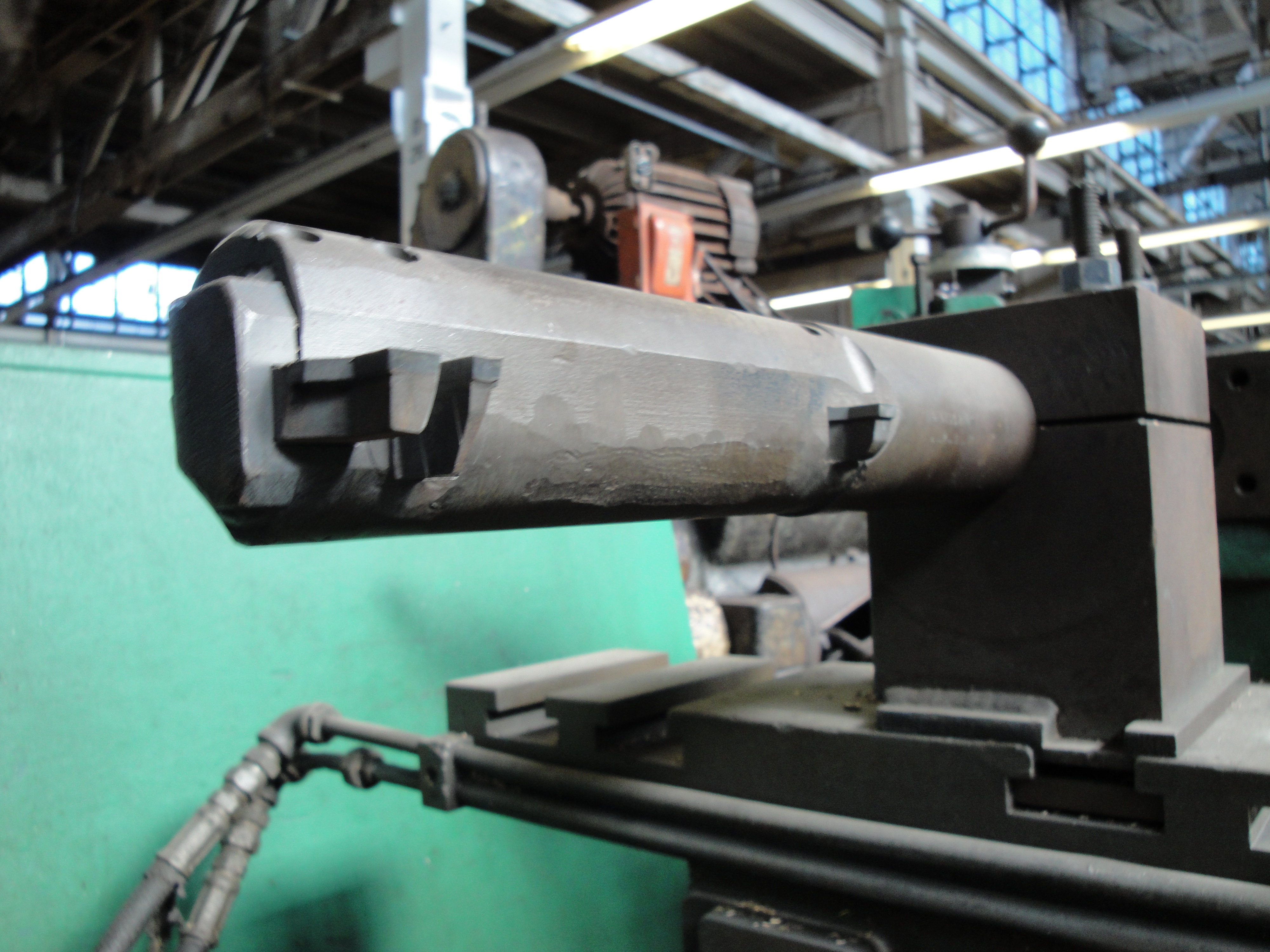
In machining, boring is the process of enlarging a hole that has already been drilled (or cast) by means of a single-point cutting tool (or of a boring head containing several such tools), such as in boring a gun barrel or an engine cylinder. Boring is used to achieve greater accuracy of the diameter of a hole, and can be used to cut a tapered hole. Boring can be viewed as the internal-diameter counterpart to turning, which cuts external diameters. There are various types of boring. The boring bar may be supported on both ends (which only works if the existing hole is a through hole), or it may be supported at one end (which works for both, through holes and blind holes). Lineboring (line boring, line-boring) implies the former. Backboring (back boring, back-boring) is the process of reaching through an existing hole and then boring on the "back" side of the workpiece (relative to the machine headstock). Because of the limitations on tooling design imposed by the fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
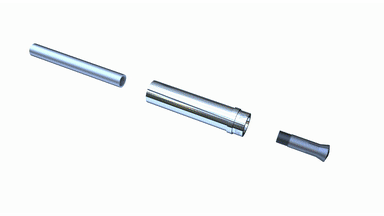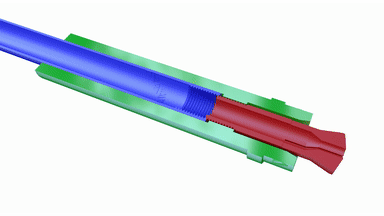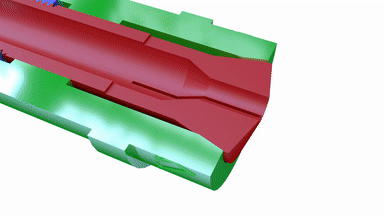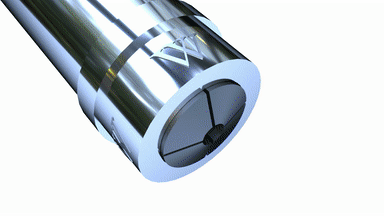
Boring Bar 001
Boring may refer to: *Something that causes boredom Engineering and science * Boring (earth), drilling a hole, tunnel, or well in the earth ** Tunnel boring machine, a machine used in boring tunnels * Boring (manufacturing), enlarging a hole that has already been drilled * Drilling, a cutting process that uses a drill bit to cut a hole of circular cross-section * Boring, a mechanism of bioerosion Places * Boring, Maryland, U.S. * Boring, Oregon, U.S. ** Boring Lava Field * Boring, Tennessee, U.S. Other uses * Boring (surname) * "Boring" (''The Young Ones''), an episode of ''The Young Ones'' * "Boring", a song by Pink from ''Funhouse'' * "Boring (It's Too Late)", a song by Medina from ''Forever'' See also * * Bore (other) * Bored (other) * Boredom (other) * Boreing (other) * Drilling (other) * Earth-boring dung beetle, a family of beetles that excavate burrows in which to lay their eggs * The Boring Company, designer of boring equi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jig Borer
The jig borer is a type of machine tool invented at the end of World War I to enable the quick and precise location of hole centers. It was invented independently in Switzerland and the United States. It resembles a specialized species of milling machine that provides tool and die makers with a higher degree of positioning precision (repeatability) and accuracy than those provided by general machines. Although capable of light milling, a jig borer is more suited to highly accurate drilling, boring, and reaming, where the quill or headstock does not see the significant side loading that it would with mill work. The result is a machine designed more for location accuracy than heavy material removal. A typical jig borer has a work table of around which can be moved using large handwheels (with micrometer-style readouts and verniers) on particularly carefully made shafts with a strong degree of gearing; this allows positions to be set on the two axes to an accuracy of . It is general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Dimensioning And Tolerancing
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) is a system for defining and communicating engineering tolerances and relationships. It uses a symbolic language on engineering drawings and computer-generated three-dimensional solid models that explicitly describe nominal geometry and its allowable variation. It tells the manufacturing staff and machines what degree of accuracy and precision is needed on each controlled feature of the part. GD&T is used to define the nominal (theoretically perfect) geometry of parts and assemblies, to define the allowable variation in form and possible size of individual features, and to define the allowable variation between features. *Dimensioning specifications define the nominal, as-modeled or as-intended geometry. One example is a basic dimension. *Tolerancing specifications define the allowable variation for the form and possibly the size of individual features, and the allowable variation in orientation and location between features. Two exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
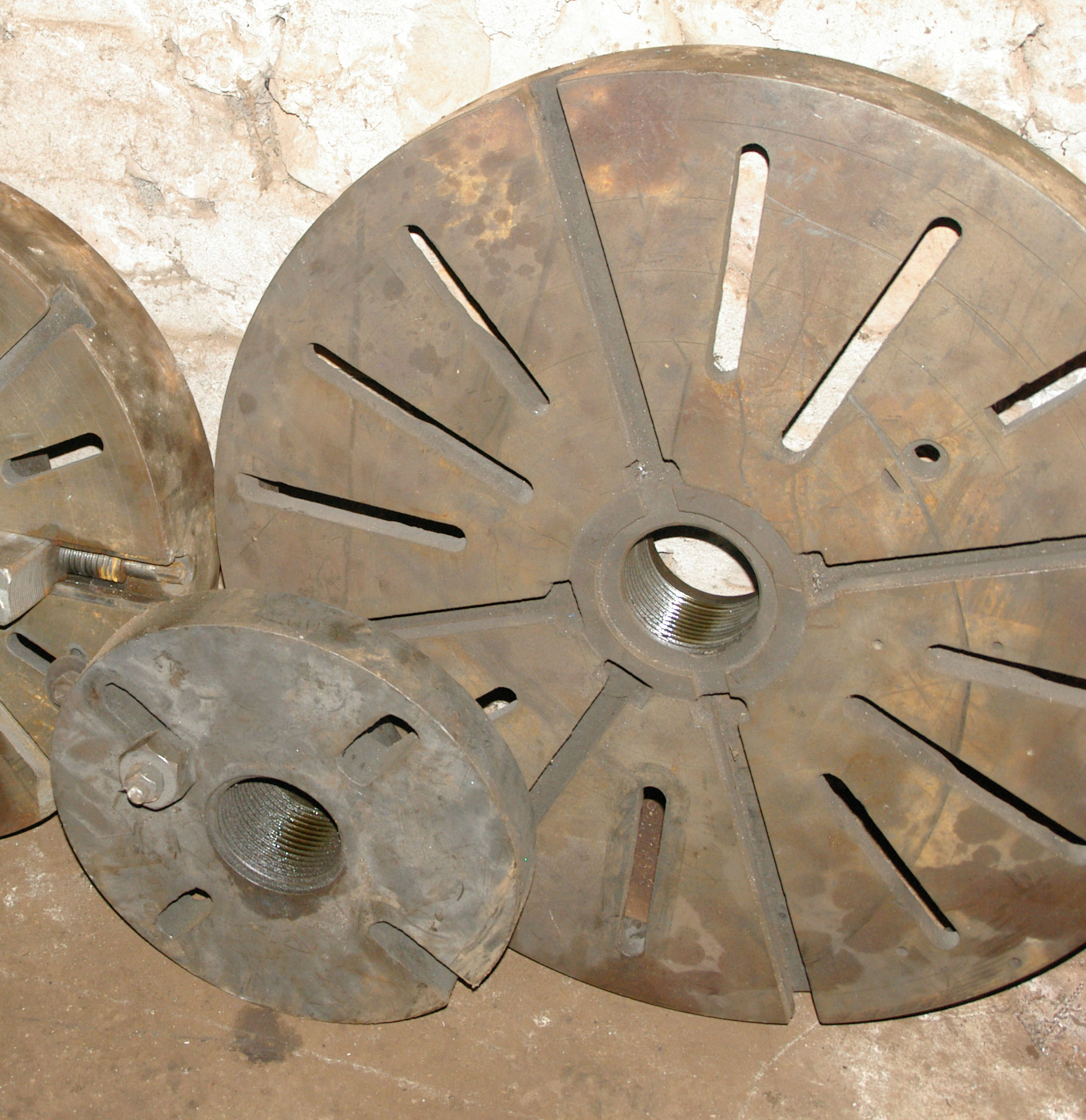
Lathe Faceplate
A lathe faceplate is a basic workholding accessory for a wood or metal turning lathe. It is a circular metal (usually cast iron) plate which fixes to the end of the lathe spindle. The workpiece is then clamped to the faceplate, typically using t-slot nuts in slots in the faceplate, or less commonly threaded holes in the faceplate itself. The faceplate may be attached to the lathe in several ways: the two most common are a thread and a precision cone arrangement, and threaded studs and a circular recess fitting a flange on the end of the spindle. Increasingly common is the camlock arrangement, in which shaped studs and cams replace threaded studs for rapid exchanging of the faceplate with other accessories, such as three or four jaw chucks. The faceplate was the ancestor of lathe chucks, an arrangement of three or more adjustable 'dogs' bolted to the faceplate providing a primitive chuck arrangement. The smaller plate in the upper photo is specifically a 'dog face' with slots ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collet
A collet is a segmented sleeve, band or ''collar''. One of the two radial surfaces of a collet is usually tapered (i.e a truncated cone) and the other is cylindrical. The term ''collet'' commonly refers to a type of chuck that uses collets to hold either a workpiece or a tool (such as a drill) but has other mechanical applications. An external collet is a sleeve with a cylindrical inner surface and a conical outer surface. The collet can be squeezed against a matching taper such that its inner surface contracts to a slightly smaller diameter, squeezing the tool or workpiece to hold it securely. Most often the collet is made of spring steel, with one or more kerf cuts along its length to allow it to expand and contract. This type of collet holds the external surface of the tool or workpiece being clamped. This is the most usual type of collet chuck. An external collet clamps against the internal surface or bore of a hollow cylinder. The collet's taper is internal and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-point Cutting Tool
A tool bit is a non-rotary cutting tool used in Lathe (metal), metal lathes, shapers, and Planer (metalworking), planers. Such cutters are also often referred to by the set-phrase name of single-point cutting tool, as distinguished from other cutting tools such as a saw or water jet cutter. The Blade, cutting edge is ground to suit a particular machining operation and may be resharpened or reshaped as needed. The ground tool bit is held rigidly by a tool holder while it is cutting. Geometry Rake angle, Back rake is to help control the direction of the chip, which naturally curves into the work due to the difference in length from the outer and inner parts of the cut. It also helps counteract the pressure against the tool from the work by pulling the tool into the work. Side rake along with back rake controls the chip flow and partly counteracts the resistance of the work to the movement of the cutter and can be optimized to suit the particular material being cut. Brass for exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-code
G-code (also RS-274) is the most widely used computer numerical control (CNC) programming language. It is used mainly in computer-aided manufacturing to control automated machine tools, and has many variants. G-code instructions are provided to a machine controller (industrial computer) that tells the motors where to move, how fast to move, and what path to follow. The two most common situations are that, within a machine tool such as a lathe or mill, a cutting tool is moved according to these instructions through a toolpath cutting away material to leave only the finished workpiece and/or an unfinished workpiece is precisely positioned in any of up to nine axes around the three dimensions relative to a toolpath and, either or both can move relative to each other. The same concept also extends to noncutting tools such as forming or burnishing tools, photoplotting, additive methods such as 3D printing, and measuring instruments. Implementations The first implementation of a nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subroutine
In computer programming, a function or subroutine is a sequence of program instructions that performs a specific task, packaged as a unit. This unit can then be used in programs wherever that particular task should be performed. Functions may be defined within programs, or separately in libraries that can be used by many programs. In different programming languages, a function may be called a routine, subprogram, subroutine, method, or procedure. Technically, these terms all have different definitions, and the nomenclature varies from language to language. The generic umbrella term ''callable unit'' is sometimes used. A function is often coded so that it can be started several times and from several places during one execution of the program, including from other functions, and then branch back (''return'') to the next instruction after the ''call'', once the function's task is done. The idea of a subroutine was initially conceived by John Mauchly during his work on ENIAC, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun Drill
Gun drills (through coolant drill) are straight fluted drills which allow cutting fluid (either compressed air or a suitable liquid) to be injected through the drill's hollow body to the cutting face. They are used for deep hole drilling—a depth-to-diameter ratio of 300:1 or more is possible. Gun barrels are the obvious example; hence the name. Other uses include moldmaking, diemaking, and the manufacture of combustion engine parts such as crankcase, cylinder head, and woodwind musical instruments, such as uilleann pipes, as gun drills can drill long straight holes in metal, wood, and some plastics. The coolant provides lubrication and cooling to the cutting edges and removes the swarf or chips from the hole. Modern gun drills use carbide tips to prolong life and reduce total cost when compared with steel tips. Speed of drilling depends on the material being drilled, rotational speed, and the drill diameter; a high speed drill can cut a hole in P20 steel at 30 inch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutting Fluid
Cutting fluid is a type of coolant and lubricant designed specifically for metalworking processes, such as machining and stamping. There are various kinds of cutting fluids, which include oils, oil-water emulsions, pastes, gels, aerosols (mists), and air or other gases. Cutting fluids are made from petroleum distillates, animal fats, plant oils, water and air, or other raw ingredients. Depending on context and on which type of cutting fluid is being considered, it may be referred to as cutting fluid, cutting oil, cutting compound, coolant, or lubricant. Most metalworking and machining processes can benefit from the use of cutting fluid, depending on workpiece material. Common exceptions to this are cast iron and brass, which may be machined dry (though this is not true of all brasses, and any machining of brass will likely benefit from the presence of a cutting fluid). The properties that are sought after in a good cutting fluid are the ability to: * Keep the workpiece at a sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drilling
Drilling is a cutting process where a drill bit is spun to cut a hole of circular cross-section in solid materials. The drill bit is usually a rotary cutting tool, often multi-point. The bit is pressed against the work-piece and rotated at rates from hundreds to thousands of revolutions per minute. This forces the cutting edge against the work-piece, cutting off chips (swarf) from the hole as it is drilled. In rock drilling, the hole is usually not made through a circular cutting motion, though the bit is usually rotated. Instead, the hole is usually made by hammering a drill bit into the hole with quickly repeated short movements. The hammering action can be performed from outside the hole ( top-hammer drill) or within the hole (down-the-hole drill, DTH). Drills used for horizontal drilling are called drifter drills. In rare cases, specially-shaped bits are used to cut holes of non-circular cross-section; a square cross-section is possible. Process Drilled holes are char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cemented Carbide
Cemented carbides are a class of hard materials used extensively for cutting tools, as well as in other industrial applications. It consists of fine particles of carbide cemented into a composite by a binder metal. Cemented carbides commonly use tungsten carbide (WC), titanium carbide (TiC), or tantalum carbide (TaC) as the aggregate. Mentions of "carbide" or "tungsten carbide" in industrial contexts usually refer to these cemented composites. Most of the time, carbide cutters will leave a better surface finish on a part and allow for faster machining than high-speed steel or other tool steels. Carbide tools can withstand higher temperatures at the cutter-workpiece interface than standard high-speed steel tools (which is a principal reason enabling the faster machining). Carbide is usually superior for the cutting of tough materials such as carbon steel or stainless steel, as well as in situations where other cutting tools would wear away faster, such as high-quantity productio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |