|
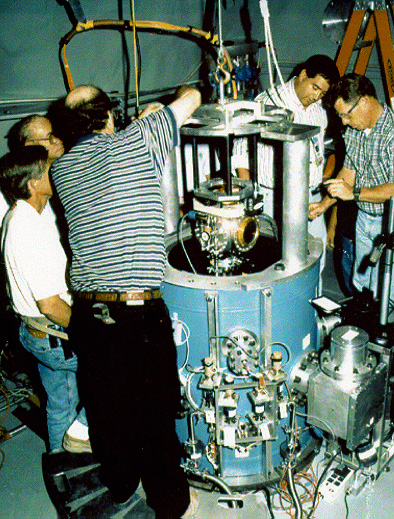
Bomb Tower
A bomb tower is a lightly constructed tower, often 100 to 700 feet (30 to 210 meters) high, built to hold a nuclear weapon for an above ground nuclear test. The tower holds the bomb for the purpose of the investigation of its destructive effects (such as burst height and distance with given explosive yield) and for the adjustment of measuring instruments, such as high-speed camera A high-speed camera is a device capable of capturing moving images with exposures of less than 1/1,000 second or frame rates in excess of 250 fps. It is used for recording fast-moving objects as photographic images onto a storage medium. After r ...s. Normally, the bomb tower disintegrates completely on detonation due to the enormous heat of the explosion. References Nuclear weapons testing Towers {{struct-type-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinity Tower
Trinity Tower is a skyscraper situated at the intersection of H.R. Rasuna Said Road and Jl. Prof. Dr. Satrio Road in Jakarta, Indonesia. The building was known as the Daswin building during its construction period. It was developed by PT Windas Development, which consists of Japan-based real estate giant Mitsubishi Estate, Indonesian manufacturing company and property developer Gesit Group and diversified conglomerate Santini Group. The project was the first opportunity for Mitsubishi Estate to develop an office building in Indonesia. Built with earthquake resistant technology and a green building concept, the tower is constructed on a land area of 1.6 hectares. The tower has three floors of retail, thirteen floors of parking and a basement floor, with total floor area of over . See also *List of tallest buildings in Indonesia *List of tallest buildings in Jakarta Jakarta is the capital of Indonesia and the largest city by population in Southeast Asia. The city is a blend as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tower
A tower is a tall Nonbuilding structure, structure, taller than it is wide, often by a significant factor. Towers are distinguished from guyed mast, masts by their lack of guy-wires and are therefore, along with tall buildings, self-supporting structures. Towers are specifically distinguished from buildings in that they are built not to be habitable but to serve other functions using the height of the tower. For example, the height of a clock tower improves the visibility of the clock, and the height of a tower in a fortified building such as a castle increases the visibility of the surroundings for defensive purposes. Towers may also be built for observation tower, observation, leisure, or telecommunication purposes. A tower can stand alone or be supported by adjacent buildings, or it may be a feature on top of a larger structure or building. Etymology Old English ''torr'' is from Latin ''turris'' via Old French ''tor''. The Latin term together with Greek language, Greek τύ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first test of a fission ("atomic") bomb released an amount of energy approximately equal to . The first thermonuclear ("hydrogen") bomb test released energy approximately equal to . Nuclear bombs have had yields between 10 tons TNT (the W54) and 50 megatons for the Tsar Bomba (see TNT equivalent). A thermonuclear weapon weighing as little as can release energy equal to more than . A nuclear device no larger than a conventional bomb can devastate an entire city by blast, fire, and radiation. Since they are weapons of mass destruction, the proliferation of nuclear weapons is a focus of international relations policy. Nuclear weapons have been d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Testing
Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine nuclear weapons' effectiveness, yield, and explosive capability. Testing nuclear weapons offers practical information about how the weapons function, how detonations are affected by different conditions, and how personnel, structures, and equipment are affected when subjected to nuclear explosions. However, nuclear testing has often been used as an indicator of scientific and military strength. Many tests have been overtly political in their intention; most nuclear weapons states publicly declared their nuclear status through a nuclear test. The first nuclear device was detonated as a test by the United States at the Trinity site in New Mexico on July 16, 1945, with a yield approximately equivalent to 20 kilotons of TNT. The first thermonuclear weapon technology test of an engineered device, codenamed "Ivy Mike", was tested at the Enewetak Atoll in the Marshall Islands on November 1, 1952 (local date), also by the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burst Height
An air burst or airburst is the detonation of an explosive device such as an anti-personnel artillery shell or a nuclear weapon in the air instead of on contact with the ground or target. The principal military advantage of an air burst over a ground burst is that the energy from the explosion (as well as any shell fragments) is distributed more evenly over a wider area; however, the peak energy is lower at ground zero. History Air burst artillery has a long history. The shrapnel shell was invented by Henry Shrapnel of the British Army in about 1780 to increase the effectiveness of canister shot. It was widely used by the time of the War of 1812 and stayed in use until it was superseded during the First World War. Modern shells, though sometimes called "shrapnel shells", actually produce fragments and splinters, not shrapnel. Air bursts were used in the First World War to shower enemy positions and men with shrapnel balls to kill the largest possible number with a single b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Weapon Yield
The explosive yield of a nuclear weapon is the amount of energy released when that particular nuclear weapon is detonated, usually expressed as a TNT equivalent (the standardized equivalent mass of trinitrotoluene which, if detonated, would produce the same energy discharge), either in kilotonnes (kt—thousands of tonnes of TNT), in megatonnes (Mt—millions of tonnes of TNT), or sometimes in terajoules (TJ). An explosive yield of one terajoule is equal to . Because the accuracy of any measurement of the energy released by TNT has always been problematic, the conventional definition is that one kilotonne of TNT is held simply to be equivalent to 1012 calories. The yield-to-weight ratio is the amount of weapon yield compared to the mass of the weapon. The practical maximum yield-to-weight ratio for fusion weapons (thermonuclear weapons) has been estimated to six megatonnes of TNT per tonne of bomb mass (25 TJ/kg). Yields of 5.2 megatonnes/tonne and higher have been reported ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-speed Camera
A high-speed camera is a device capable of capturing moving images with exposures of less than 1/1,000 second or frame rates in excess of 250 frames per second, fps. It is used for recording fast-moving objects as photographic images onto a storage medium. After recording, the images stored on the medium can be played back in slow motion. Early high-speed cameras used film to record the high-speed events, but were superseded by entirely electronic devices using either a charge-coupled device (CCD) or a CMOS active pixel sensor, recording, typically, over 1,000 frames per second, fps onto DRAM, to be played back slowly to study the motion for scientific study of transient phenomena. Overview A high-speed camera can be classified as: # A high-speed film camera which records to film, # A high-speed video camera which records to electronic memory, # A high-speed framing camera which records images on multiple image planes or multiple locations on the same image plane (generally film o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Weapons Testing
Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine nuclear weapons' effectiveness, Nuclear weapon yield, yield, and explosive capability. Testing nuclear weapons offers practical information about how the weapons function, how detonations are affected by different conditions, and how personnel, structures, and equipment are affected when subjected to Nuclear explosion, nuclear explosions. However, nuclear testing has often been used as an indicator of scientific and military strength. Many tests have been overtly political in their intention; most List of countries with nuclear weapons, nuclear weapons states publicly declared their nuclear status through a nuclear test. The first nuclear device was detonated as a test by the United States at the Trinity site in New Mexico on July 16, 1945, with a yield approximately TNT equivalent, equivalent to 20 kilotons of TNT. The first thermonuclear weapon technology test of an engineered device, codenamed "Ivy Mike", was teste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |