|
Blood Irradiation Therapy
Blood irradiation therapy is an alternative medical procedure in which the blood is exposed to low level light (often laser light) for therapeutic reasons. The practice was originally developed in the United States, but most recent research on it has been conducted in Germany (by UV lamps) and in Russia (in all variants). Low-level laser therapy has been tested for a wide range of conditions, but rigorous double-blinded studies have not yet been performed. Furthermore, it has been claimed that ultraviolet irradiation of blood kills bacteria by DNA damage and also activation of the immune system. Blood irradiation therapy is highly controversial, and has fallen from mainstream use since its heyday in the 1940s and 1950s. Blood irradiation therapy can be administered in three ways: extracorporeally, transcutaneously, and intravenously. The extracorporeal (outside the body) method removes blood from the body and irradiates it in a special cuvette (tube). This method is used for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematology
Hematology ( always spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the production of blood and its components, such as blood cells, hemoglobin, blood proteins, bone marrow, platelets, blood vessels, spleen, and the mechanism of coagulation. Such diseases might include hemophilia, blood clots ( thrombus), other bleeding disorders, and blood cancers such as leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma. The laboratory analysis of blood is frequently performed by a medical technologist or medical laboratory scientist. Specialization Physicians specialized in hematology are known as hematologists or haematologists. Their routine work mainly includes the care and treatment of patients with hematological diseases, although some may also work at the hematology laboratory viewing blood films and bone marrow slides unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poliomyelitis
Poliomyelitis, commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 70% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe symptoms develop such as headache, neck stiffness, and paresthesia. These symptoms usually pass within one or two weeks. A less common symptom is permanent paralysis, and possible death in extreme cases.. Years after recovery, post-polio syndrome may occur, with a slow development of muscle weakness similar to that which the person had during the initial infection. Polio occurs naturally only in humans. It is highly infectious, and is spread from person to person either through fecal-oral transmission (e.g. poor hygiene, or by ingestion of food or water contaminated by human feces), or via the oral-oral route. Those who are infected may spread the disease for up to six weeks even if no symptoms are present. The disease may be diagnosed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, the symptoms are often vague, such as tiredness, weakness, shortness of breath, headaches, and a reduced ability to exercise. When anemia is acute, symptoms may include confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out, loss of consciousness, and increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Symptoms of anemia depend on how quickly hemoglobin decreases. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause. Preoperative anemia can increase the risk of needing a blood transfusion following surgery. Anemia can be temporary or long term and can range from mild to severe. Anemia can be caused by blood loss, decreased red blood cell production, and increased red blood cell breakdown. Causes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
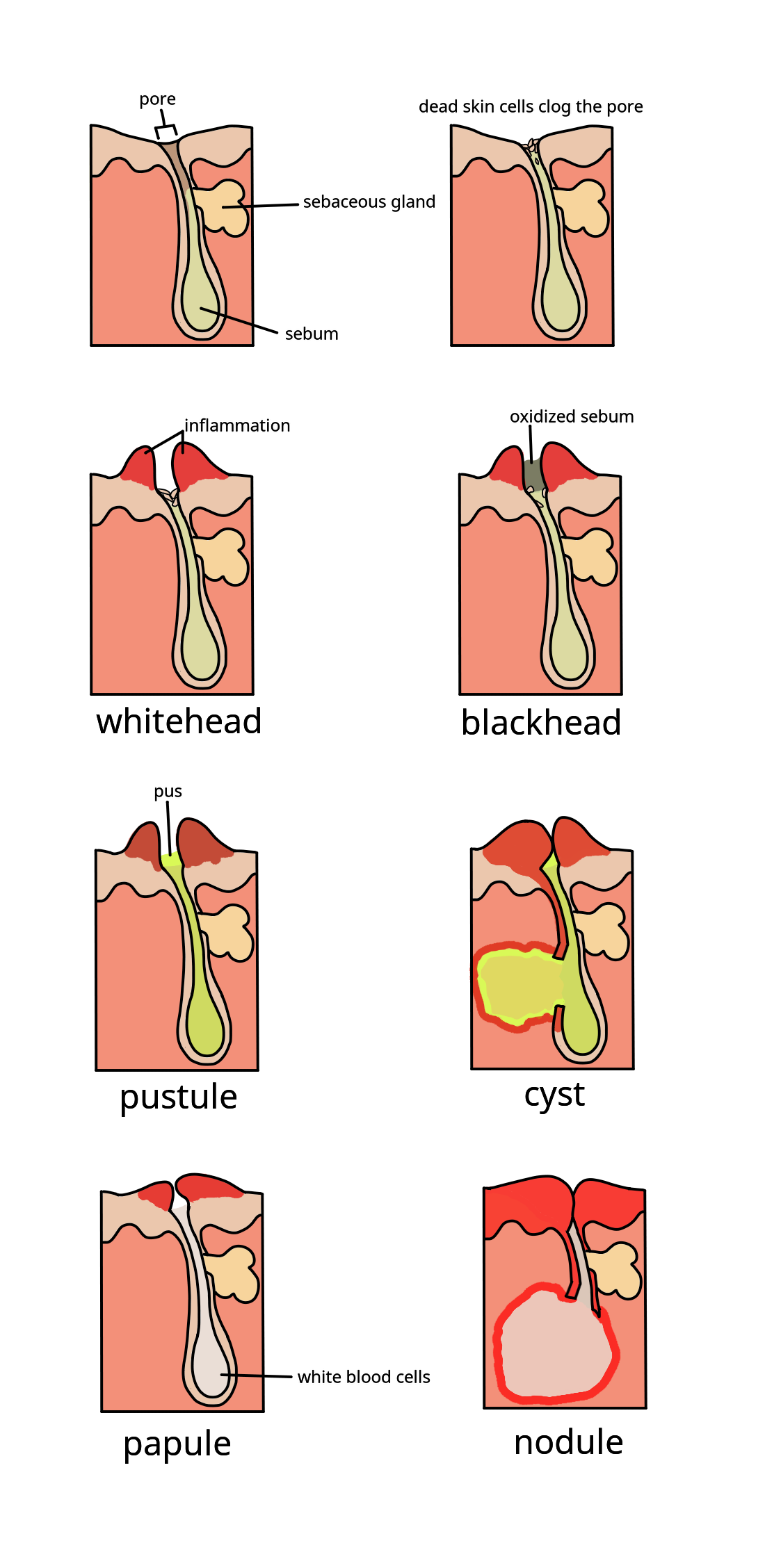
Acne Vulgaris
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and, in extreme cases, depression or thoughts of suicide. Susceptibility to acne is primarily genetic in 80% of cases. The roles of diet and cigarette smoking in the condition are unclear, and neither cleanliness nor exposure to sunlight appear to play a part. In both sexes, hormones called androgens appear to be part of the underlying mechanism, by causing increased production of sebum. Another common factor is the excessive growth of the bacterium ''Cutibacterium acnes'', which is present on the skin. Treatments for acne are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain. Other signs and symptoms may include fever, headaches, a poor sense of smell, sore throat, a feeling that phlegm is oozing out from the back of the nose to the throat along with a necessity to clear the throat frequently and frequent attacks of cough. Generally sinusitis starts off as a common viral infection like common cold. This infection generally subsides within 5 to 7 days. During this time the nasal structures can swell and facilitate the stagnation of fluids in sinuses that leads to acute sinusitis which lasts from 6th day of the infection to 15th day. From the 15th day to 45th day of the infection comes the subacute stage followed by chronic stage. Whenever a chronic stage patient's immunity takes a hit the infection moves to "acute on sinusitis" stage and moves back to chro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
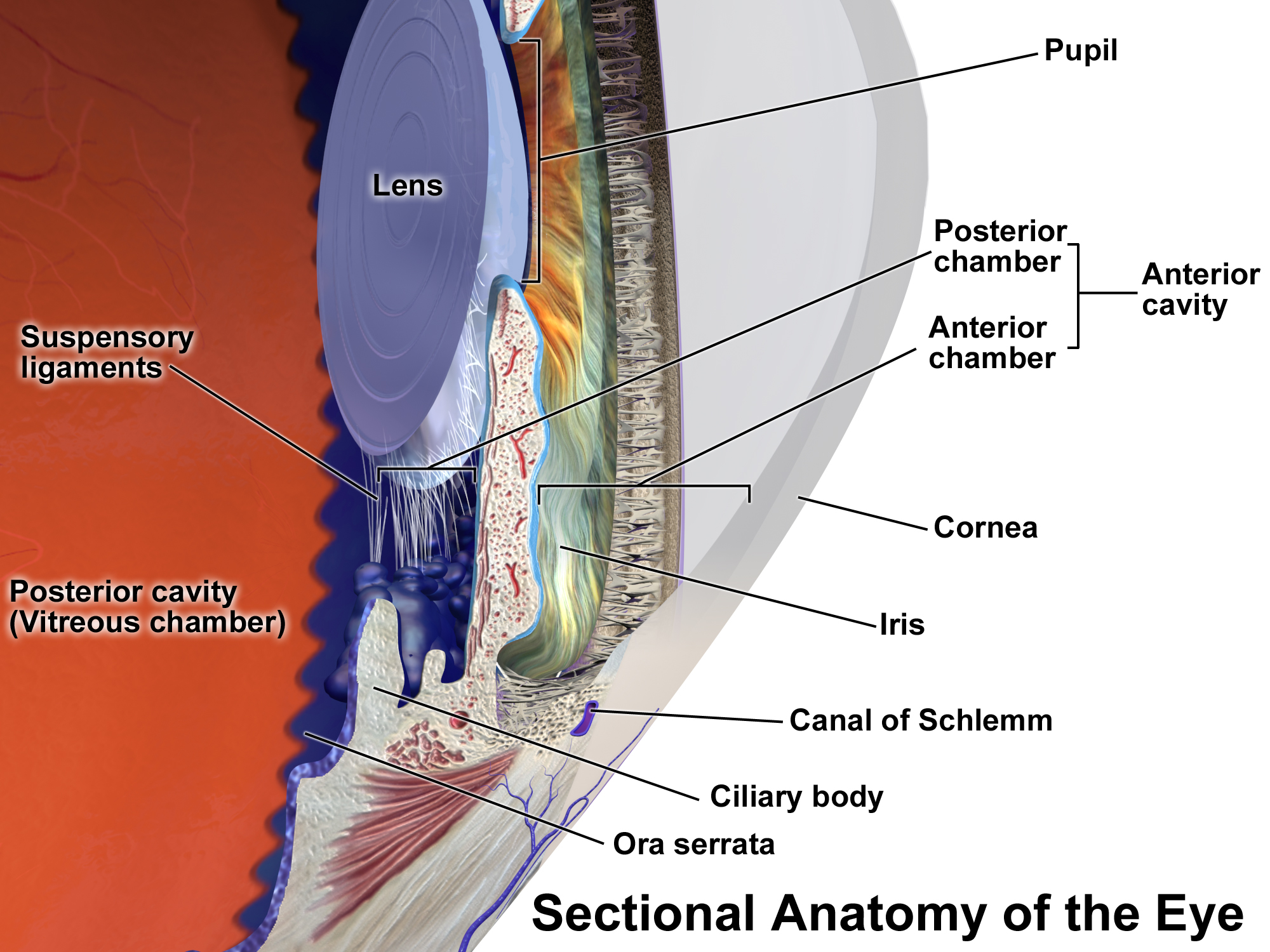
Uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and includes the Iris (anatomy), iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Uveitis is described anatomically, by the part of the eye affected, as anterior, intermediate uveitis, intermediate or posterior, or panuveitic if all parts are involved. Anterior uveitis (iridocyclytis) is the most common, with the incidence of uveitis overall affecting approximately 1:4500, most commonly those between the ages of 20-60. Symptoms include eye pain, eye redness, floaters and blurred vision, and ophthalmic examination may show dilated ciliary body, ciliary blood vessels and the presence of cells in the Anterior chamber of eyeball, anterior chamber. Uveitis may arise spontaneously, have a genetic component, or be associated with an autoimmune disease or infection. Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
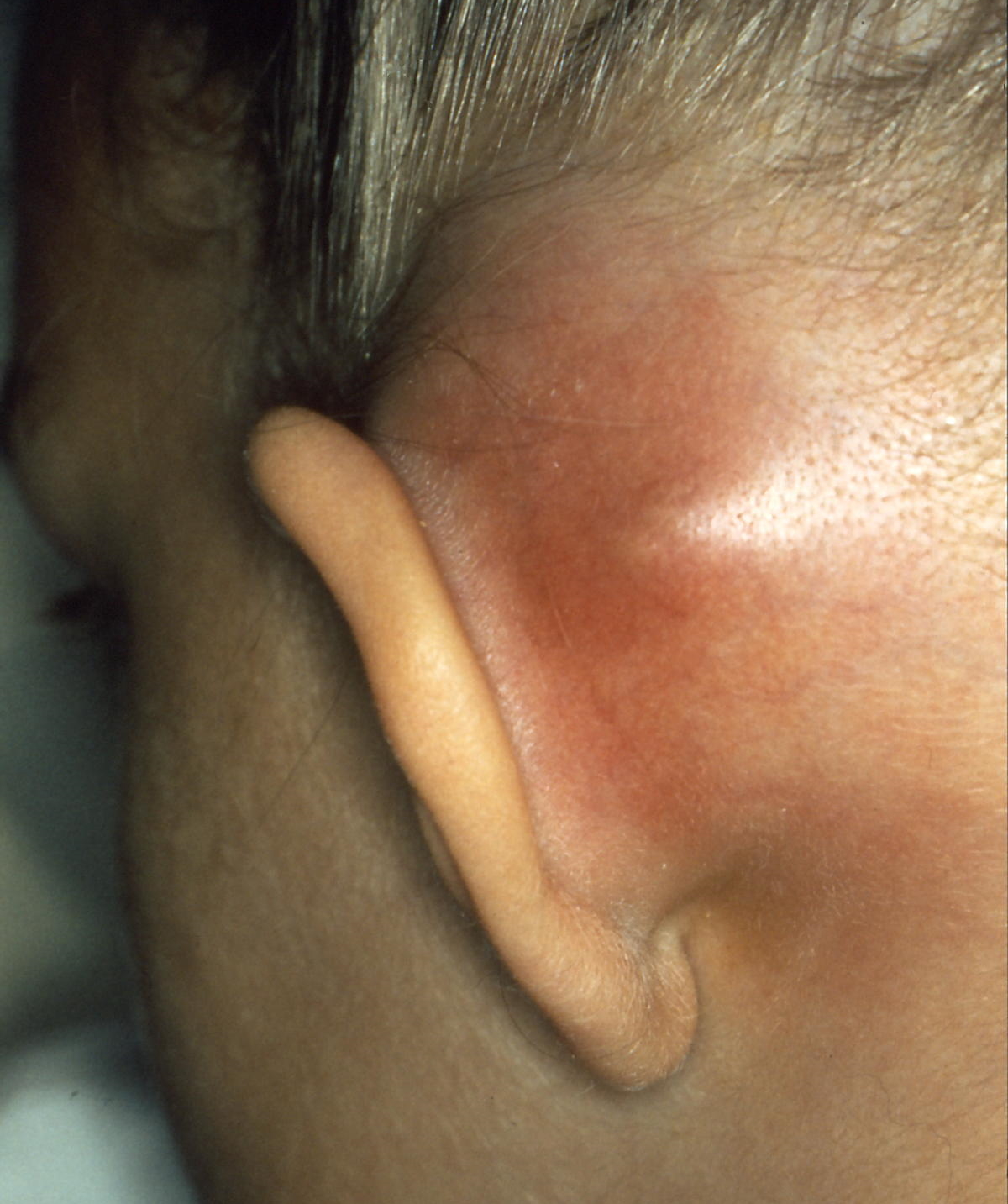
Mastoiditis
Mastoiditis is the result of an infection that extends to the air cells of the skull behind the ear. Specifically, it is an inflammation of the mucosal lining of the mastoid antrum and mastoid air cell system inside the mastoid process. The mastoid process is the portion of the temporal bone of the skull that is behind the ear. The mastoid process contains open, air-containing spaces. Mastoiditis is usually caused by untreated acute otitis media (middle ear infection) and used to be a leading cause of child mortality. With the development of antibiotics, however, mastoiditis has become quite rare in developed countries where surgical treatment is now much less frequent and more conservative, unlike former times. There is no evidence that the drop in antibiotic prescribing for otitis media has increased the incidence of mastoiditis, raising the possibility that the drop in reported cases is due to a confounding factor such as childhood immunizations against ''Haemophilus'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blepharitis
Blepharitis is one of the most common ocular conditions characterized by inflammation, scaling, reddening, and crusting of the eyelid. This condition may also cause swelling, burning, itching, or a grainy sensation when introducing foreign objects or substances to the eye. Although blepharitis by itself is not sight-threatening, it can lead to permanent alterations of the eyelid margin. The primary cause is bacteria and inflammation from congested meibomian oil glands at the base of each eyelash. Other conditions may give rise to blepharitis, whether they be infectious or noninfectious, including, but not limited to, bacterial infections or allergies. Different variations of blepharitis can be classified as seborrheic, staphylococcal, mixed, posterior or meibomitis, or parasitic. In a survey of US ophthalmologists and optometrists, 37% to 47% of patients seen by those surveyed had signs of blepharitis, which can affect all ages and ethnic groups. One single-center study of 90 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. It was historically referred to as consumption due to the weight loss associated with the disease. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is spread from one person to the next through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with Latent TB do not spread the disease. Active infection occurs more often in people with HIV/AIDS and in those who smoke. Diagnosis of ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone which affects 1 in 7 adults in the United States. It is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world. The most common symptoms are joint pain and stiffness. Usually the symptoms progress slowly over years. Initially they may occur only after exercise but can become constant over time. Other symptoms may include joint swelling, decreased range of motion, and, when the back is affected, weakness or numbness of the arms and legs. The most commonly involved joints are the two near the ends of the fingers and the joint at the base of the thumbs; the knee and hip joints; and the joints of the neck and lower back. Joints on one side of the body are often more affected than those on the other. The symptoms can interfere with work and normal daily activities. Unlike some other types of arthritis, only the joints, not internal organs, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |