|
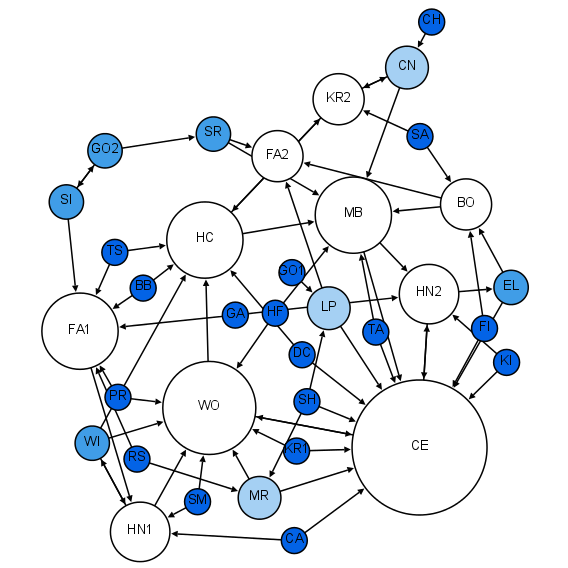
Blockmodel
Blockmodel (sometimes also block model) in blockmodeling (part of network science) is defined as a multitude of structures, which are obtained with: * identification of all vertices (e.g., units, nodes) within a cluster and at the same time representing each cluster as a vertex, from which vertices for another graph can be constructed; * combination of all the links (ties), represented in a block as a single link between positions, while at the same time constructing one tie for each block. In a case, when there are no ties in a block, there will be no ties between the two positions, that define the block. In principle, blockmodeling, as a process, is composed from three steps. In the first step, the number of units is determined. This is followed (in the second step) by selection or determination of permitted blocks, that will occur and perhaps also the locations in the matrix. The last, third step, using computer program, the partitioning of units is done, according to the pre- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blockmodeling
Blockmodeling is a set or a coherent framework, that is used for analyzing social structure and also for setting procedure(s) for partitioning (clustering) social network's units (nodes, vertices, actors), based on specific patterns, which form a distinctive structure through interconnectivity.Patrick Doreian, An Intuitive Introduction to Blockmodeling with Examples, ''BMS: Bulletin of Sociological Methodology'' / ''Bulletin de Méthodologie Sociologique'', January, 1999, No. 61 (January, 1999), pp. 5–34. It is primarily used in statistics, machine learning and network science. As an empirical procedure, blockmodeling assumes that all the units in a specific network can be grouped together to such extent to which they are equivalent. Regarding equivalency, it can be structural, regular or generalized.Anuška Ferligoj: Blockmodeling, http://mrvar.fdv.uni-lj.si/sola/info4/nusa/doc/blockmodeling-2.pdf Using blockmodeling, a network can be analyzed using newly created blockmodels, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrick Doreian
Patrick Doreian is an American mathematician and social scientist, whose specialty is network analysis. His specific research interests include blockmodeling, social structure and network processes. Doreian, Professor Emeritus from the University of Pittsburgh in Sociology and Statistics, was during his research career focused on social network research, especially regarding temporal networks, scientific collaboration, partitioning networks, signed networks, network autocorrelation and the US Supreme Court. He was also an (co)editor of '' The Journal of Mathematical Sociology'' (1982–2005) and ''Social Networks'' (2006–2015). He was also a Centennial professor at the London School of Economics (2002) and a visiting professor at the University of California-Irvine and the University of Ljubljana. Work With Thomas J. Fararo in 1984, he introduced tripartite structural analysis. With Norman P. Hummon in 1989, he proposed a main path analysis, a mathematical tool, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Model
A statistical model is a mathematical model that embodies a set of statistical assumptions concerning the generation of Sample (statistics), sample data (and similar data from a larger Statistical population, population). A statistical model represents, often in considerably idealized form, the data-generating process. A statistical model is usually specified as a mathematical relationship between one or more random variables and other non-random variables. As such, a statistical model is "a formal representation of a theory" (Herman J. Adèr, Herman Adèr quoting Kenneth A. Bollen, Kenneth Bollen). All Statistical hypothesis testing, statistical hypothesis tests and all Estimator, statistical estimators are derived via statistical models. More generally, statistical models are part of the foundation of statistical inference. Introduction Informally, a statistical model can be thought of as a statistical assumption (or set of statistical assumptions) with a certain property: that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cluster Analysis
Cluster analysis or clustering is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster) are more similar (in some sense) to each other than to those in other groups (clusters). It is a main task of exploratory data analysis, and a common technique for statistics, statistical data analysis, used in many fields, including pattern recognition, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning. Cluster analysis itself is not one specific algorithm, but the general task to be solved. It can be achieved by various algorithms that differ significantly in their understanding of what constitutes a cluster and how to efficiently find them. Popular notions of clusters include groups with small Distance function, distances between cluster members, dense areas of the data space, intervals or particular statistical distributions. Clustering can therefore be formulated as a multi-object ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex (graph Theory)
In discrete mathematics, and more specifically in graph theory, a vertex (plural vertices) or node is the fundamental unit of which graphs are formed: an undirected graph consists of a set of vertices and a set of edges (unordered pairs of vertices), while a directed graph consists of a set of vertices and a set of arcs (ordered pairs of vertices). In a diagram of a graph, a vertex is usually represented by a circle with a label, and an edge is represented by a line or arrow extending from one vertex to another. From the point of view of graph theory, vertices are treated as featureless and indivisible objects, although they may have additional structure depending on the application from which the graph arises; for instance, a semantic network is a graph in which the vertices represent concepts or classes of objects. The two vertices forming an edge are said to be the endpoints of this edge, and the edge is said to be incident to the vertices. A vertex ''w'' is said to be ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph (discrete Mathematics)
In discrete mathematics, and more specifically in graph theory, a graph is a structure amounting to a Set (mathematics), set of objects in which some pairs of the objects are in some sense "related". The objects correspond to mathematical abstractions called ''Vertex (graph theory), vertices'' (also called ''nodes'' or ''points'') and each of the related pairs of vertices is called an ''edge'' (also called ''link'' or ''line''). Typically, a graph is depicted in diagrammatic form as a set of dots or circles for the vertices, joined by lines or curves for the edges. Graphs are one of the objects of study in discrete mathematics. The edges may be directed or undirected. For example, if the vertices represent people at a party, and there is an edge between two people if they shake hands, then this graph is undirected because any person ''A'' can shake hands with a person ''B'' only if ''B'' also shakes hands with ''A''. In contrast, if an edge from a person ''A'' to a person ''B'' m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Node (computer Network)
A node is a basic unit of a data structure, such as a linked list or tree data structure. Nodes contain data and also may link to other nodes. Links between nodes are often implemented by pointers. Nodes and Trees Nodes are often arranged into tree structures. A node represents the information contained in a single data structure. These nodes may contain a value or condition, or possibly serve as another independent data structure. Nodes are represented by a single parent node. The highest point on a tree structure is called a root node, which does not have a parent node, but serves as the parent or 'grandparent' of all of the nodes below it in the tree. The height of a node is determined by the total number of edges on the path from that node to the furthest leaf node, and the height of the tree is equal to the height of the root node. Node depth is determined by the distance between that particular node and the root node. The root node is said to have a depth of zero. Data c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix (plural matrices) is a rectangular array or table of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns, which is used to represent a mathematical object or a property of such an object. For example, \begin1 & 9 & -13 \\20 & 5 & -6 \end is a matrix with two rows and three columns. This is often referred to as a "two by three matrix", a "-matrix", or a matrix of dimension . Without further specifications, matrices represent linear maps, and allow explicit computations in linear algebra. Therefore, the study of matrices is a large part of linear algebra, and most properties and operations of abstract linear algebra can be expressed in terms of matrices. For example, matrix multiplication represents composition of linear maps. Not all matrices are related to linear algebra. This is, in particular, the case in graph theory, of incidence matrices, and adjacency matrices. ''This article focuses on matrices related to linear algebra, and, unle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Science
Network science is an academic field which studies complex networks such as telecommunication networks, computer networks, biological networks, cognitive and semantic networks, and social networks, considering distinct elements or actors represented by ''nodes'' (or ''vertices'') and the connections between the elements or actors as ''links'' (or ''edges''). The field draws on theories and methods including graph theory from mathematics, statistical mechanics from physics, data mining and information visualization from computer science, inferential modeling from statistics, and social structure from sociology. The United States National Research Council defines network science as "the study of network representations of physical, biological, and social phenomena leading to predictive models of these phenomena." Background and history The study of networks has emerged in diverse disciplines as a means of analyzing complex relational data. The earliest known paper in this f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equivalence Relation
In mathematics, an equivalence relation is a binary relation that is reflexive, symmetric and transitive. The equipollence relation between line segments in geometry is a common example of an equivalence relation. Each equivalence relation provides a partition of the underlying set into disjoint equivalence classes. Two elements of the given set are equivalent to each other if and only if they belong to the same equivalence class. Notation Various notations are used in the literature to denote that two elements a and b of a set are equivalent with respect to an equivalence relation R; the most common are "a \sim b" and "", which are used when R is implicit, and variations of "a \sim_R b", "", or "" to specify R explicitly. Non-equivalence may be written "" or "a \not\equiv b". Definition A binary relation \,\sim\, on a set X is said to be an equivalence relation, if and only if it is reflexive, symmetric and transitive. That is, for all a, b, and c in X: * a \sim a ( ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intuition
Intuition is the ability to acquire knowledge without recourse to conscious reasoning. Different fields use the word "intuition" in very different ways, including but not limited to: direct access to unconscious knowledge; unconscious cognition; gut feelings; inner sensing; inner insight to unconscious pattern-recognition; and the ability to understand something instinctively, without any need for conscious reasoning.Intuition and consciousness – Rosenblatt AD, Thickstun JT. Psychoanal Q. 1994 Oct;63(4):696-714. Intuitive knowledge tends to be approximate. The word ''intuition'' comes from the Latin verb ''intueri'' translated as "consider" or from the late middle English word ''intuit'', "to contemplate". Use of intuition is sometimes referred to as responding to a "gut feeling" or "trusting your gut".Wilding, M.How to Stop Overthinking and Start Trusting your Gut ''Harvard Business Review'', published 10 March 2022, accessed 21 September 2022 Psychology Freud According to Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substance
Substance may refer to: * Matter, anything that has mass and takes up space Chemistry * Chemical substance, a material with a definite chemical composition * Drug substance ** Substance abuse, drug-related healthcare and social policy diagnosis or label ** Substance dependence, drug-related healthcare and social policy diagnosis or label Arts, entertainment, and media Music * ''Substance'' (Blank & Jones album), 2002 * ''Substance'' (Joy Division album), 1988 * '' Substance 1987'', a New Order album * "Substance", a song by Haste the Day on the album ''That They May Know You'' * "Substance" (song), a 2022 song by Demi Lovato Other media * '' SubStance'', an interdisciplinary journal on literature published by the University of Wisconsin Press * '' Metal Gear Solid 2: Substance'', an update of the video game ''Metal Gear Solid 2: Sons of Liberty'' Religion and philosophy * Dravya, a term used in Jainism to refer a substance * Ousia ''Ousia'' (; grc, οὐσία) is a ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |