|
Bismuth Selenide
Bismuth selenide (Bi2Se3) is a gray compound of bismuth and selenium also known as bismuth(III) selenide. It is a semiconductor and a thermoelectric material. In its pure state it has a topological insulator ground-state. While perfect stoichiometric bismuth selenide should be a semiconductor (with a gap of 0.3 eV) naturally occurring selenium vacancies act as electron donors and it often acts as a semimetal in its as grown phase. Topologically protected Dirac cone surface states have been observed in Bismuth selenide and its insulating derivatives leading to intrinsic topological insulators, which later became the subject of world-wide scientific research. Production Although bismuth selenide occurs naturally (as the mineral guanajuatite) at the Santa Catarina Mine in Guanajuato, Mexico as well as some sites in the United States and Europe, such deposits are rare and contain a significant level of sulfur atoms as an impurity. For this reason, most bismuth selenide used in rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bismuth(III) Oxide
Bismuth(III) oxide is perhaps the most industrially important compound of bismuth. It is also a common starting point for bismuth chemistry. It is found naturally as the mineral bismite (monoclinic) and sphaerobismoite (tetragonal, much more rare), but it is usually obtained as a by-product of the smelting of copper and lead ores. Dibismuth trioxide is commonly used to produce the " Dragon's eggs" effect in fireworks, as a replacement of red lead. Structure The structures adopted by differ substantially from those of arsenic(III) oxide, , and antimony(III) oxide, .Wells, A.F. (1984) ''Structural Inorganic Chemistry''. 5th. London, England: Oxford University Press. p.890 Bismuth oxide, has five crystallographic polymorphs. The room temperature phase, α- has a monoclinic crystal structure. There are three high temperature phases, a tetragonal β-phase, a body-centred cubic γ-phase, a cubic δ- phase and an ε-phase. The room temperature α-phase has a complex structure with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Review B
''Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics'' (also known as PRB) is a peer-reviewed, scientific journal, published by the American Physical Society (APS). The Editor of PRB is Laurens W. Molenkamp. It is part of the ''Physical Review'' family of journals. About the Physical Review Journals The current Editor in Chief is . PRB currently publishes over 4500 papers a year, making it one of the largest physics journals in the world. PRB ranked by the Eigenfactor, University of Washingto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bismuth Compounds
Bismuth compounds are compounds containing the element bismuth (Bi). Bismuth forms trivalent and pentavalent compounds, the trivalent ones being more common. Many of its chemical properties are similar to those of arsenic and antimony, although they are less toxic than derivatives of those lighter elements. Oxides and sulfides At elevated temperatures, the vapors of the metal combine rapidly with oxygen, forming the yellow trioxide, . Wiberg, p. 768. Greenwood, p. 553. When molten, at temperatures above 710 °C, this oxide corrodes any metal oxide and even platinum. Krüger, p. 185 On reaction with a base, it forms two series of oxyanions: , which is polymeric and forms linear chains, and . The anion in is a cubic octameric anion, , whereas the anion in is tetrameric. The dark red bismuth(V) oxide, , is unstable, liberating gas upon heating. The compound NaBiO3 is a strong oxidising agent. Greenwood, p. 578. Bismuth sulfide, , occurs naturally in bismuth ores. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
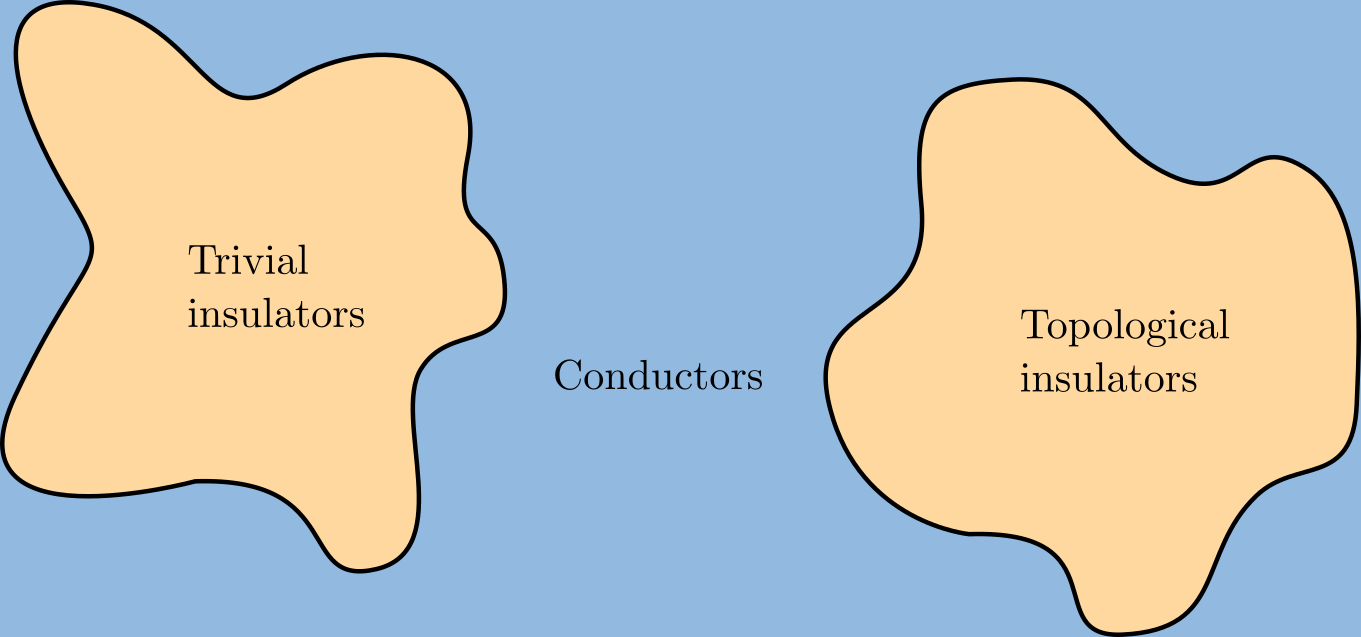
Topological Insulators
A topological insulator is a material whose interior behaves as an electrical insulator while its surface behaves as an electrical conductor, meaning that electrons can only move along the surface of the material. A topological insulator is an insulator for the same reason a "trivial" (ordinary) insulator is: there exists an energy gap between the valence and conduction bands of the material. But in a topological insulator, these bands are, in an informal sense, "twisted", relative to a trivial insulator. The topological insulator cannot be continuously transformed into a trivial one without untwisting the bands, which closes the band gap and creates a conducting state. Thus, due to the continuity of the underlying field, the border of a topological insulator with a trivial insulator (including vacuum, which is topologically trivial) is forced to support a conducting state. Since this results from a global property of the topological insulator's band structure, local (symmetry- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoelectric Effect
The thermoelectric effect is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice versa via a thermocouple. A thermoelectric device creates a voltage when there is a different temperature on each side. Conversely, when a voltage is applied to it, heat is transferred from one side to the other, creating a temperature difference. At the atomic scale, an applied temperature gradient causes charge carriers in the material to diffuse from the hot side to the cold side. This effect can be used to generate electricity, measure temperature or change the temperature of objects. Because the direction of heating and cooling is affected by the applied voltage, thermoelectric devices can be used as temperature controllers. The term "thermoelectric effect" encompasses three separately identified effects: the Seebeck effect, Peltier effect, and Thomson effect. The Seebeck and Peltier effects are different manifestations of the same physical process; textbooks may re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoelectric Materials
Thermoelectric materials show the thermoelectric effect in a strong or convenient form. The ''thermoelectric effect'' refers to phenomena by which either a temperature difference creates an electric potential or an electric current creates a temperature difference. These phenomena are known more specifically as the Seebeck effect (creating a voltage from temperature difference), Peltier effect (driving heat flow with an electric current), and Thomson effect (reversible heating or cooling within a conductor when there is both an electric current and a temperature gradient). While all materials have a nonzero thermoelectric effect, in most materials it is too small to be useful. However, low-cost materials that have a sufficiently strong thermoelectric effect (and other required properties) are also considered for applications including power generation and refrigeration. The most commonly used thermoelectric material is based on bismuth telluride (). Thermoelectric materials are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
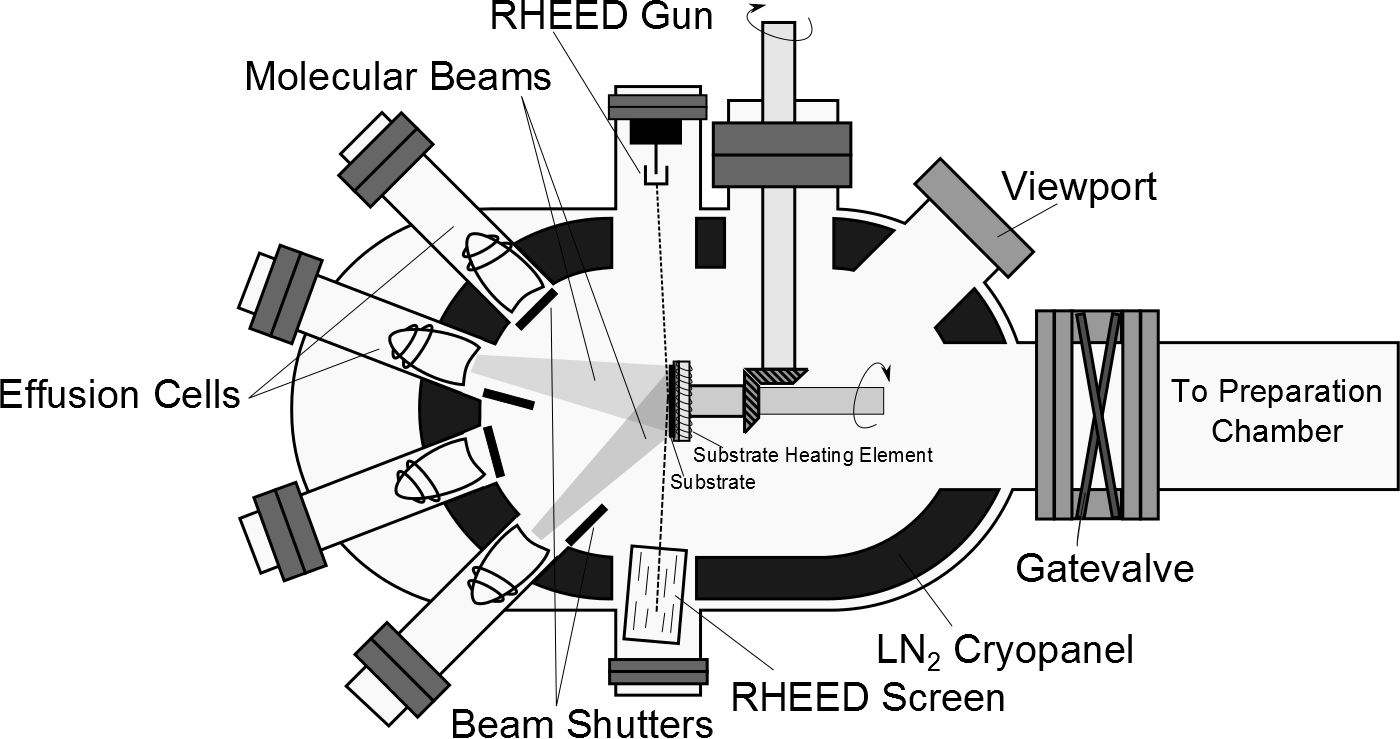
Bridgman–Stockbarger Method
The Bridgman–Stockbarger method, or Bridgman–Stockbarger technique, is named after Harvard physicist Percy Williams Bridgman (1882–1961) and MIT physicist Donald C. Stockbarger (1895–1952). The method includes two similar but distinct techniques primarily used for growing boules (single-crystal ingots), but which can be used for solidifying polycrystalline ingots as well. Overview The methods involve heating polycrystalline material above its melting point and slowly cooling it from one end of its container, where a seed crystal is located. A single crystal of the same crystallographic orientation as the seed material is grown on the seed and is progressively formed along the length of the container. The process can be carried out in a horizontal or vertical orientation, and usually involves a rotating crucible/ampoule to stir the melt. The Bridgman method is a popular way of producing certain semiconductor crystals such as gallium arsenide, for which the Czochralski me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Today, almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere The greatest commercial use of the element is the production o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and to the east by the Gulf of Mexico. Mexico covers ,Mexico ''''. . making it the world's 13th-largest country by are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanajuato
Guanajuato (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guanajuato ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Guanajuato), is one of the 32 states that make up the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 46 municipalities and its capital city is Guanajuato. Guanajuato is in central Mexico. It is bordered by the states of Jalisco to the west, Zacatecas to the northwest, San Luis Potosí to the north, Querétaro to the east, and Michoacán to the south. It covers an area of . The state is home to several historically important cities, especially those along the "Bicentennial Route", which retraces the path of Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla's insurgent army at the beginning of the Mexican War of Independence. This route begins at Dolores Hidalgo, and passes through the Sanctuary of Atotonilco, San Miguel de Allende, Celaya, and the capital of Guanajuato. Other important cities in the state include León, the state's biggest city, Salamanca, and Irapuato. The first town established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topological Insulator
A topological insulator is a material whose interior behaves as an electrical insulator while its surface behaves as an electrical conductor, meaning that electrons can only move along the surface of the material. A topological insulator is an insulator for the same reason a "trivial" (ordinary) insulator is: there exists an energy gap between the valence and conduction bands of the material. But in a topological insulator, these bands are, in an informal sense, "twisted", relative to a trivial insulator. The topological insulator cannot be continuously transformed into a trivial one without untwisting the bands, which closes the band gap and creates a conducting state. Thus, due to the continuity of the underlying field, the border of a topological insulator with a trivial insulator (including vacuum, which is topologically trivial) is forced to support a conducting state. Since this results from a global property of the topological insulator's band structure, local (symmetry- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_oxide_2.jpg)