|
Bis(chloromethyl) Ether
Bis(chloromethyl) ether is an organic compound with the chemical formula (CH2Cl)2O. It is a colourless liquid with an unpleasant suffocating odour and it is one of the chloroalkyl ethers. Bis(chloromethyl) ether was once produced on a large scale, but was found to be highly carcinogenic and thus such production has ceased. Synthesis It was produced industrially from paraformaldehyde and a mixture of chlorosulfonic acid and sulfuric acid. It is also produced as a byproduct in the Blanc chloromethylation reaction, formed when formaldehyde (the monomer, paraformaldehyde or formalin) and concentrated hydrochloric acid are mixed, and is a known impurity in technical grade chloromethyl methyl ether. Because of their carcinogenic potency, the industrial production of chloromethyl ethers ended in most countries in the early 1980s. Bis(chloromethyl) ether was no exception to this with production in the U.S.A. ending in 1982. Uses Bis(chloromethyl) ether has been extensively used in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide), are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive. Although organic compounds make up only a small percentage of Earth's crust, they are of central importance because all known life is based on organic compounds. Living t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
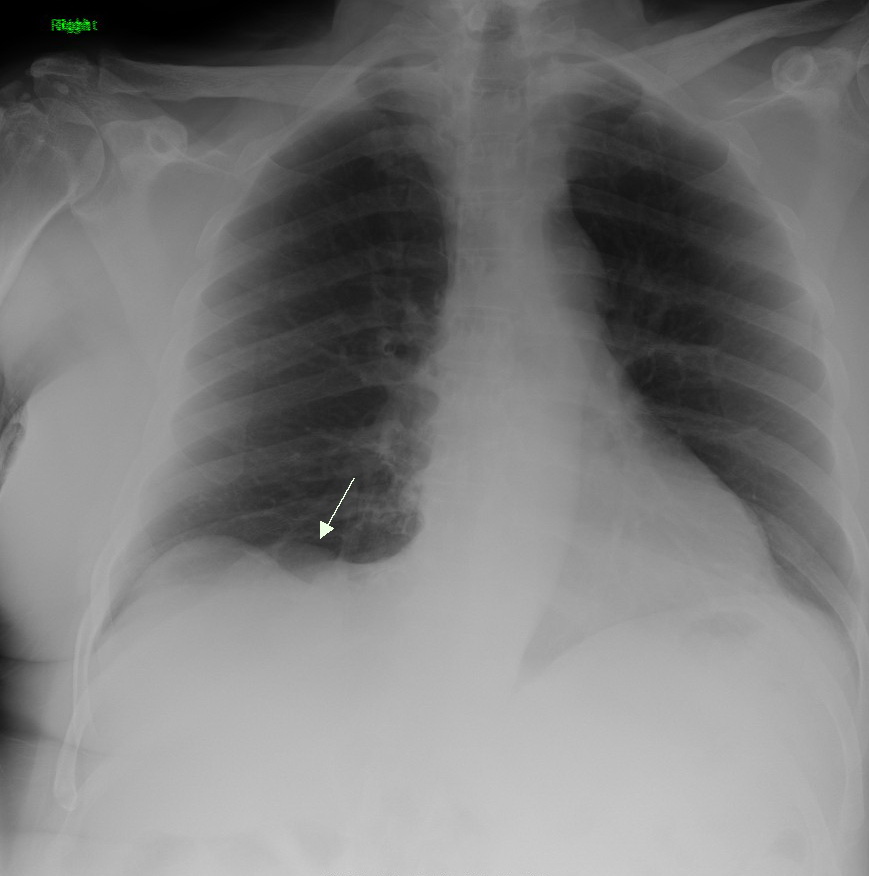
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissue (biology), tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malignant cells that originate as epithelial cells, or from tissues composed of epithelial cells. Other lung cancers, such as the rare sarcomas of the lung, are generated by the malignant transformation of connective tissues (i.e. nerve, fat, muscle, bone), which arise from mesenchymal cells. Lymphomas and melanomas (from lymphoid and melanocyte cell lineages) can also rarely result in lung cancer. In time, this uncontrolled neoplasm, growth can metastasis, metastasize (spreading beyond the lung) either by direct extension, by entering the lymphatic circulation, or via hematogenous, bloodborne spread – into nearby tissue or other, more distant parts of the body. Most cancers that originate from within the lungs, known as primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethers
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl or aryl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin. Structure and bonding Ethers feature bent C–O–C linkages. In dimethyl ether, the bond angle is 111° and C–O distances are 141 pm. The barrier to rotation about the C–O bonds is low. The bonding of oxygen in ethers, alcohols, and water is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organochlorides
An organochloride, organochlorine compound, chlorocarbon, or chlorinated hydrocarbon is an organic compound containing at least one covalently bonded atom of chlorine. The chloroalkane class (alkanes with one or more hydrogens substituted by chlorine) provides common examples. The wide structural variety and divergent chemical properties of organochlorides lead to a broad range of names, applications, and properties. Organochlorine compounds have wide use in many applications, though some are of profound environmental concern, with TCDD being one of the most notorious. Physical and chemical properties Chlorination modifies the physical properties of hydrocarbons in several ways. These compounds are typically denser than water due to the higher atomic weight of chlorine versus hydrogen. Aliphatic organochlorides are often alkylating agents as chlorine can act as a leaving group, which can result in cellular damage. Natural occurrence Many organochlorine compounds have been isolate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkylating Agents
Alkylation is the transfer of an alkyl group from one molecule to another. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or their equivalents). Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting alkylation. Alkyl groups can also be removed in a process known as dealkylation. Alkylating agents are often classified according to their nucleophilic or electrophilic character. In oil refining contexts, alkylation refers to a particular alkylation of isobutane with olefins. For upgrading of petroleum, alkylation produces a premium blending stock for gasoline. In medicine, alkylation of DNA is used in chemotherapy to damage the DNA of cancer cells. Alkylation is accomplished with the class of drugs called alkylating antineoplastic agents. Nucleophilic alkylating agents Nucleophilic alkylating agents deliver the equivalent of an alkyl anion (carbanion). The formal "alkyl anion" attacks an electrophile, forming a new covalent bond be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IARC Group 1 Carcinogens
IARC may refer to: * International Aerial Robotics Competition * International Age Rating Coalition * International Agency for Research on Cancer * International Arctic Research Center * Israel Amateur Radio Club * iArc, South Korean architecture firm {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bis(chloroethyl) Ether
Bis(chloroethyl) ether is an organic compound with the formula O(CH2CH2Cl)2. It is an ether with two 2-chloroethyl substituents. It is a colorless liquid with the odor of a chlorinated solvent. Reactions and applications Bis(chloroethyl) ether is less reactive than the corresponding sulfur mustard S(CH2CH2Cl)2. In the presence of base, it reacts with catechol to form dibenzo-18-crown-6: : Bis(chloroethyl) ether can be used in the synthesis of the cough suppressant fedrilate. It is combined with benzyl cyanide and two molar equivalents of sodamide in a ring-forming reaction. When treated with strong base, it gives divinyl ether, an anesthetic: :O(CH2CH2Cl)2 + 2 KOH → O(CH=CH2)2 + 2 KCl + 2 H2O Toxicity The is 74 mg/kg (oral, rat). Bis(chloroethyl) ether is considered as a potential carcinogen. See also * Bis(chloromethyl) ether * Sulfur mustard Mustard gas or sulfur mustard is a chemical compound belonging to a family of cytotoxic and blister agents known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloromethyl Methyl Ether
Chloromethyl methyl ether (CMME) is a compound with formula CH3OCH2Cl. A colorless liquid, it is a chloroalkyl ether. It is used as an alkylating agent. In organic synthesis, it is used for introducing the methoxymethyl ether (MOM) protecting group, and is thus often called MOM-Cl or MOM chloride. It also finds application as a chloromethylating agent in some variants of the Blanc chloromethylation. Preparation A convenient synthesis of chloromethyl methyl ether ''in situ'' involves the reaction of dimethoxymethane and acetyl chloride in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst This route affords a methyl acetate solution of chloromethyl methyl ether of high purity. A similar method, using a high-boiling acyl chloride, can be used to prepare pure, dimethoxymethane being the only contaminant. In contrast, the classical procedure reported in ''Organic Syntheses'' employing formaldehyde, methanol, and hydrogen chloride yields material significantly contaminated with the dangero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Government Publishing Office
The United States Government Publishing Office (USGPO or GPO; formerly the United States Government Printing Office) is an agency of the legislative branch of the United States Federal government. The office produces and distributes information products and services for all three branches of the Federal Government, including U.S. passports for the Department of State as well as the official publications of the Supreme Court, the Congress, the Executive Office of the President, executive departments, and independent agencies. An act of Congress changed the office's name to its current form in 2014. History The Government Printing Office was created by congressional joint resolution () on June 23, 1860. It began operations March 4, 1861, with 350 employees and reached a peak employment of 8,500 in 1972. The agency began transformation to computer technology in the 1980s; along with the gradual replacement of paper with electronic document distribution, this has led to a stea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emergency Planning And Community Right-to-Know Act
The Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act of 1986 is a United States federal law passed by the 99th United States Congress located at Title 42, Chapter 116 of the U.S. Code, concerned with emergency response preparedness. On October 17, 1986, President Ronald Reagan signed into law the Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act of 1986 (SARA). This act amended the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act of 1980 (CERCLA), commonly known as Superfund. A free-standing law, the Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act of 1986 (EPCRA) was commonly known as SARA Title III. Its purpose is to encourage and support emergency planning efforts at the state and local levels and to provide the public and local governments with information concerning potential chemical hazards present in their communities. Background During the early morning hours of December 3, 1984, a Union Carbide plant in a village just South of Bhopal, India rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Extremely Hazardous Substances
This is the list of extremely hazardous substances defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (42 U.S.C. 11002). The list can be found as an appendix to 40 C.F.R. 355. Updates as of 2006 can be seen on the Federal Register, 71 FR 47121 (August 16, 2006). The data were provided by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). __NOTOC__ A * Acetone cyanohydrin * Acetone thiosemicarbazide * Acrolein * Acrylamide * Acrylonitrile * Acryloyl chloride * Adiponitrile * Aldicarb * Aldrin * Allyl alcohol * Allylamine * Aluminum phosphide * Aminopterin * Amiton * Amiton oxalate * Ammonia * Amphetamine * Aniline * Aniline, 2,4,6-trimethyl- * Antimony pentafluoride * Antimycin A * ANTU (Alpha-Naphthylthiourea) * Arsenic pentoxide * Arsenous oxide * Arsenous trichloride * Arsine * Azinphos-ethyl * Azinphos-methyl B * Benzal chloride * Benzenamine, 3-(trifluoromethyl)- * Benzenearsonic acid * Benzimidazole, 4,5-dichloro-2-(tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obidoxime
Obidoxime is a member of the oxime family used to treat nerve gas poisoning. Oximes are drugs known for their ability to reverse the binding of organophosphorus compounds to the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE). AChE is an enzyme that removes acetylcholine from the synapse after it creates the required stimulation on the next nerve cell. If it gets inhibited, acetylcholine is not removed after the stimulation and multiple stimulations are made, resulting in muscle contractions and paralysis. Organophosphates (such as nerve gases) are well-known inhibitors of AChE. They bind to a specific place on the enzyme and prevent it from functioning normally by changing the OH group on the serine residue and by protonating (quaternary nitrogen, R4N+) the nearby nitrogen atom located in the histidine residue. Function Oximes such as obidoxime, pralidoxime and asoxime (HI-6) are used to restore enzyme functionality. They have greater affinity for the organic phosphate residue tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |