|
Benefactive Case
The benefactive case (abbreviated , or sometimes when it is a core argument) is a grammatical case used where English would use "for", "for the benefit of", or "intended for", e.g. "She opened the door ''for Tom''" or "This book is ''for Bob''". The benefactive case expresses that the referent of the noun it marks receives the benefit of the situation expressed by the clause. This meaning is often incorporated in a dative case. In Latin this type of dative is called the ''dativus commodi''. An example of a language with a benefactive case is Basque, which has a benefactive case ending in ''-entzat''. Quechua is another example, and the benefactive case ending in Quechua is ''-paq''. Tangkhul-Naga (from the Tibeto-Burman group of languages) has the benefactive case marker '. In Aymara, the benefactive case is marked with -''taki'', expressing that the referent of the inflected noun benefits from the situation expressed by the verb, or, when there is no verb, that the noun to wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Glossing Abbreviations
This article lists common abbreviations for grammatical terms that are used in linguistic interlinear glossing of oral languages in English. The list provides conventional glosses as established by standard inventories of glossing abbreviations such as the Leipzig Glossing rules, the most widely known standard. These will generally be the glosses used on Wikipedia. Synonymous glosses are listed as alternatives for reference purposes. In a few cases, long and short standard forms are listed, intended for texts where that gloss is rare or common. Conventions * Grammatical abbreviations are generally written in full or small caps to visually distinguish them from the translations of lexical words. For instance, capital or small-cap (frequently abbreviated to ) glosses a grammatical past-tense morpheme, while lower-case 'past' would be a literal translation of a word with that meaning. Similarly, (small) cap might be a locative suffix used in nominal inflections, prototypically in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aymara Language
Aymara (; also ) is an Aymaran language spoken by the Aymara people of the Bolivian Andes. It is one of only a handful of Native American languages with over one million speakers.The other native American languages with more than one million speakers are Nahuatl, Quechua languages, and Guaraní. Aymara, along with Spanish and Quechua, is an official language in Bolivia and Peru. It is also spoken, to a much lesser extent, by some communities in northern Chile, where it is a recognized minority language. Some linguists have claimed that Aymara is related to its more widely spoken neighbor, Quechua. That claim, however, is disputed. Although there are indeed similarities, like the nearly identical phonologies, the majority position among linguists today is that the similarities are better explained as areal features rising from prolonged cohabitation, rather than natural genealogical changes that would stem from a common protolanguage. Aymara is an agglutinating and, to a cert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ditransitive Verb
In grammar, a ditransitive (or bitransitive) verb is a transitive verb whose contextual use corresponds to a subject (grammar), subject and two object (grammar), objects which refer to a Thematic relation, theme and a recipient. According to certain linguistics considerations, these objects may be called ''direct'' and ''indirect'', or ''primary'' and ''secondary''. This is in contrast to monotransitive verbs, whose contextual use corresponds to only one object. In languages which mark grammatical case, it is common to differentiate the objects of a ditransitive verb using, for example, the accusative case for the direct object, and the dative case for the indirect object (but this morphological alignment is not unique; see below). In languages without morphological case (such as English for the most part) the objects are distinguished by word order and/or context. In English English has a number of generally ditransitive verbs, such as ''give'', ''grant'', and ''tell'' and many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflexive Verb
In grammar, a reflexive verb is, loosely, a verb whose direct object is the same as its subject; for example, "I wash myself". More generally, a reflexive verb has the same semantic agent and patient (typically represented syntactically by the subject and the direct object). For example, the English verb ''to perjure'' is reflexive, since one can only perjure ''oneself''. In a wider sense, the term refers to any verb form whose grammatical object is a reflexive pronoun, regardless of semantics; such verbs are also more broadly referred to as pronominal verbs, especially in grammars of the Romance languages. Other kinds of pronominal verbs are reciprocal (''they killed each other''), passive (''it is told''), subjective, idiomatic. The presence of the reflexive pronoun changes the meaning of a verb, e.g. Spanish ''abonar'' to pay, ''abonarse'' to subscribe. There are languages that have explicit morphology or syntax to transform a verb into a reflexive form. In many languages, ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intransitive
In grammar, an intransitive verb is a verb whose context does not entail a direct object. That lack of transitivity distinguishes intransitive verbs from transitive verbs, which entail one or more objects. Additionally, intransitive verbs are typically considered within a class apart from modal verbs and defective verbs. Examples In the following sentences, verbs are used without a direct object: *"Rivers flow." *"I sneezed." *"My dog ran." *"Water evaporates when it's hot." *"You've grown since I last saw you!" *"I wonder how old I will be when I die." The following sentences contain transitive verbs (they entail one or more objects): *"We watched ''a movie'' last night." *"She's making ''promises''." *"When I said that, my sister smacked ''me''." *"Santa gave ''me'' ''a present''." *"He continuously clicked ''his pen'' and it was incredibly annoying to me." Some verbs, called ambitransitive verbs, may entail objects but do not always require one. Such a verb may be used as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colognian Language
Colognian or Kölsch (; natively ''Kölsch Platt'') is a small set of very closely related dialects, or variants, of the Ripuarian group of dialects of the Central German group. These dialects are spoken in the area covered by the Archdiocese and former Electorate of Cologne reaching from Neuss in the north to just south of Bonn, west to Düren and east to Olpe in northwest Germany. Name In the Ripuarian dialects, ''"kölsch"'' is an adjective meaning "from Cologne" or "pertaining to Cologne", thus equivalent to ''"Colognian"''. Its nominalized forms (''ene Kölsche'', ''de Kölsche'' etc.) denote the inhabitants of Cologne. The word ''"Kölsch"'', without an article, refers to either the dialect or the local Kölsch beer. Hence the humorous Colognian saying: "Ours is the only language you can drink!" Speakers In Cologne, it is actively spoken by about 250,000 people, roughly one quarter of the population. Almost all speakers are also fluent in standard or high German. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinelandic Regiolect
The terms Rhinelandic, Rhenish, and Rhinelandic regiolect refer to the vernacular lect spoken in the so-called Rhineland of West Germany. This linguistic region is approximately formed of the West of North Rhine-Westphalia, the North of Rhineland-Palatinate and several smaller adjacent areas, including some areas in neighbouring countries. Although there is such a thing as a Rhinelandic accent, and the regiolect uses it, the Rhinelandic variety is not simply German spoken with an accent. Indeed, it differs from Standard German in several thousand commonly used additional words, phrases, and idioms, and some grammatical constructions. Like other German regiolects, there is not a strict definition of what constitutes Rhinelandic; it can be spoken in a way very close to the standard idiom, but if locals talk to each other, it is mostly unintelligible to inhabitants of other German-speaking regions. Linguists classify the Rhinelandic regiolect as a dialectal variety of Standard Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applicative Voice
The applicative voice (; abbreviated or ) is a grammatical voice that promotes an oblique argument of a verb to the core object argument. It is generally considered a valency-increasing morpheme. The Applicative is often found in agglutinative languages, such as the Bantu languages and Austronesian languages. Other examples include Nuxalk, Ubykh, and Ainu. Behavior Prototypically, applicatives apply to intransitive verbs. Dixon, R.M.W. & Alexandra Y. Aikhenvald (eds) (1999). ''The Amazonian Languages''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. They can also be called "advancements" or "object promotion" because they bring a peripheral object to the centre as a direct object. This object is sometimes called the applied object. For transitive verbs, the resulting verb can be ditransitive, or the original object is no longer expressed. If the original object is no longer expressed, it is not a valency-increasing operationPayne, Thomas E. (1997). Describing morphosyntax: A guide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibeto-Burman Languages
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non-Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people speak Tibeto-Burman languages. The name derives from the most widely spoken of these languages, Burmese and the Tibetic languages, which also have extensive literary traditions, dating from the 12th and 7th centuries respectively. Most of the other languages are spoken by much smaller communities, and many of them have not been described in detail. Though the division of Sino-Tibetan into Sinitic and Tibeto-Burman branches (e.g. Benedict, Matisoff) is widely used, some historical linguists criticize this classification, as the non-Sinitic Sino-Tibetan languages lack any shared innovations in phonology or morphology to show that they comprise a clade of the phylogenetic tree. History During the 18th century, several scholars noticed parallels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
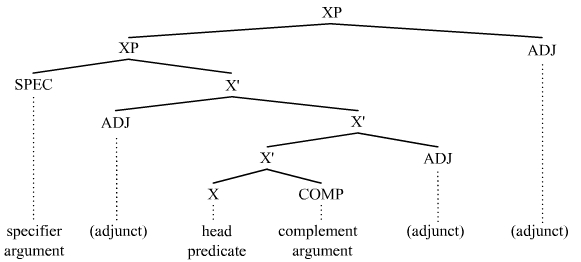
Core Argument
In linguistics, an argument is an expression that helps complete the meaning of a predicate, the latter referring in this context to a main verb and its auxiliaries. In this regard, the ''complement'' is a closely related concept. Most predicates take one, two, or three arguments. A predicate and its arguments form a ''predicate-argument structure''. The discussion of predicates and arguments is associated most with (content) verbs and noun phrases (NPs), although other syntactic categories can also be construed as predicates and as arguments. Arguments must be distinguished from adjuncts. While a predicate needs its arguments to complete its meaning, the adjuncts that appear with a predicate are optional; they are not necessary to complete the meaning of the predicate. Most theories of syntax and semantics acknowledge arguments and adjuncts, although the terminology varies, and the distinction is generally believed to exist in all languages. Dependency grammars sometimes call arg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quechua Language
Quechua (, ; ), usually called ("people's language") in Quechuan languages, is an Indigenous languages of the Americas, indigenous language family spoken by the Quechua peoples, primarily living in the Peruvian Andes. Derived from a common ancestral language, it is the most widely spoken Pre-Columbian era, pre-Columbian language family of the Americas, with an estimated 8–10 million speakers as of 2004.Adelaar 2004, pp. 167–168, 255. Approximately 25% (7.7 million) of Peruvians speak a Quechuan language. It is perhaps most widely known for being the main language family of the Inca Empire. The Spanish encouraged its use until the Peruvian War of Independence, Peruvian struggle for independence of the 1780s. As a result, Quechua variants are still widely spoken today, being the co-official language of many regions and the second most spoken language family in Peru. History Quechua had already expanded across wide ranges of the central Andes long before the expansion of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)