|
Baulk Road
Baulk road is the name given to a type of railway track or 'rail road' that is formed using rails carried on continuous timber bearings, as opposed to the more familiar 'cross-sleeper' track that uses closely spaced sleepers or ties to give intermittent support to stronger rails. Baulk road was popularised by Isambard Kingdom Brunel for his broad gauge railways in the UK, but has also been used for other railways and can still be found in modified form in special locations on present day railways. Development Brunel sought an improved design for the railway track needed for the Great Western Railway (GWR), authorised by Act of Parliament in 1835 to link London and Bristol. He refused to accept received wisdom without challenge. The gauge that had been adopted by most railways at that time had been fine for small mineral trucks on a horse-drawn tramway, but he wanted something more stable for his high-speed railway. The large diameter wheels used in stage coaches gave bett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baulk Road Crossing
Baulk may refer to: * , areas on various types of billiard table * , a wall of intact earth in an archaeological excavation * Baulk road, a type of railway track * Baulking :* Water polo#Baulking, Baulking, tactic used in water polo to trick a goalkeeper into thinking that the player is shooting :* Baulking, a village in Oxfordshire England * Baulk Head to Mullion, a coastal site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in Cornwall, England See also * Balk (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Blacker Vignoles
Charles Blacker Vignoles (31 May 1793 – 17 November 1875) was an influential British railway engineer, and eponym of the Vignoles rail. Early life He was born at Woodbrook, County Wexford, Ireland in May 1793 the son of Capt. Charles Henry Vignoles and Camilla, née Hutton. In 1794 Charles was promoted to a Captaincy in the 43rd Foot and posted to the West Indies with his wife and son. He was severely wounded in the unsuccessful storming of Point-à-Pitre, Guadeloupe and taken prisoner; whilst prisoners both he and Camilla contracted yellow fever. They were cared for by a M. Courtois, a merchant on the island. Henry died on 8 June 1794, Camilla a few days later. Charles, then thirteen months old survived, was cared for by M. Courtois who sent for Charles' uncle, Capt. George Henry Hutton (1765–1827) — later Lt. Gen — who reached Gaudeloupe some ten months later. Charles was appointed an Ensign in the 43rd Foot with effect from 25 Oct 1794, at the age of 2½. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakwater (structure)
A breakwater is a permanent structure constructed at a coastal area to protect against tides, currents, waves, and storm surges. Part of a coastal management system, breakwaters are installed to minimize erosion, and to protect anchorages, helping isolate vessels within them from marine hazards such as prop washes and wind-driven waves. A breakwater, also known in some contexts as a jetty, may be connected to land or freestanding, and may contain a walkway or road for vehicle access. On beaches where longshore drift threatens the erosion of beach material, smaller structures on the beach, usually perpendicular to the water's edge, may be installed. Their action on waves and current is intended to slow the longshore drift and discourage mobilisation of beach material. In this usage they are more usually referred to as groynes. Purposes Breakwaters reduce the intensity of wave action in inshore waters and thereby provide safe harbourage. Breakwaters may also be small structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Coode (engineer)
Sir John Coode (11 November 1816 – 2 March 1892), English civil engineer, known for harbour works. Life He was born at Bodmin on 11 November 1816. He was educated at Bodmin Grammar School and after leaving school entered his father's office. His natural tastes, however, were not for law but for engineering ; he was therefore articled to James Meadows Rendel of Plymouth, and on completion of his pupilage he worked for some years for that gentleman and on the Great Western Railway. In 1844, he set up in business for himself in Westminster as a consulting engineer, and remained there till 1847. In that year he was appointed resident engineer in charge of the great works at Portland harbour, which had been designed by Rendel. On the death of the latter in 1856, Coode was appointed engineer-in-chief, and retained that post until the completion of the work in 1872. This harbour provided the largest area of deep water of any artificial harbour in Great Britain, and was a work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paddington Platform 1 Baulk Road
Paddington is an area within the City of Westminster, in Central London. First a medieval parish then a metropolitan borough, it was integrated with Westminster and Greater London in 1965. Three important landmarks of the district are Paddington station, designed by the engineer Isambard Kingdom Brunel and opened in 1847; St Mary's Hospital; and the former Paddington Green Police Station (once the most important high-security police station in the United Kingdom). A major project called Paddington Waterside aims to regenerate former railway and canal land between 1998 and 2018, and the area is seeing many new developments. Offshoot districts (historically within Paddington) are Maida Vale, Westbourne and Bayswater including Lancaster Gate. History The earliest extant references to ''Padington'' (or "Padintun", as in the ''Saxon Chartularies'', 959), historically a part of Middlesex, appear in documentation of purported tenth-century land grants to the monks of Westminster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
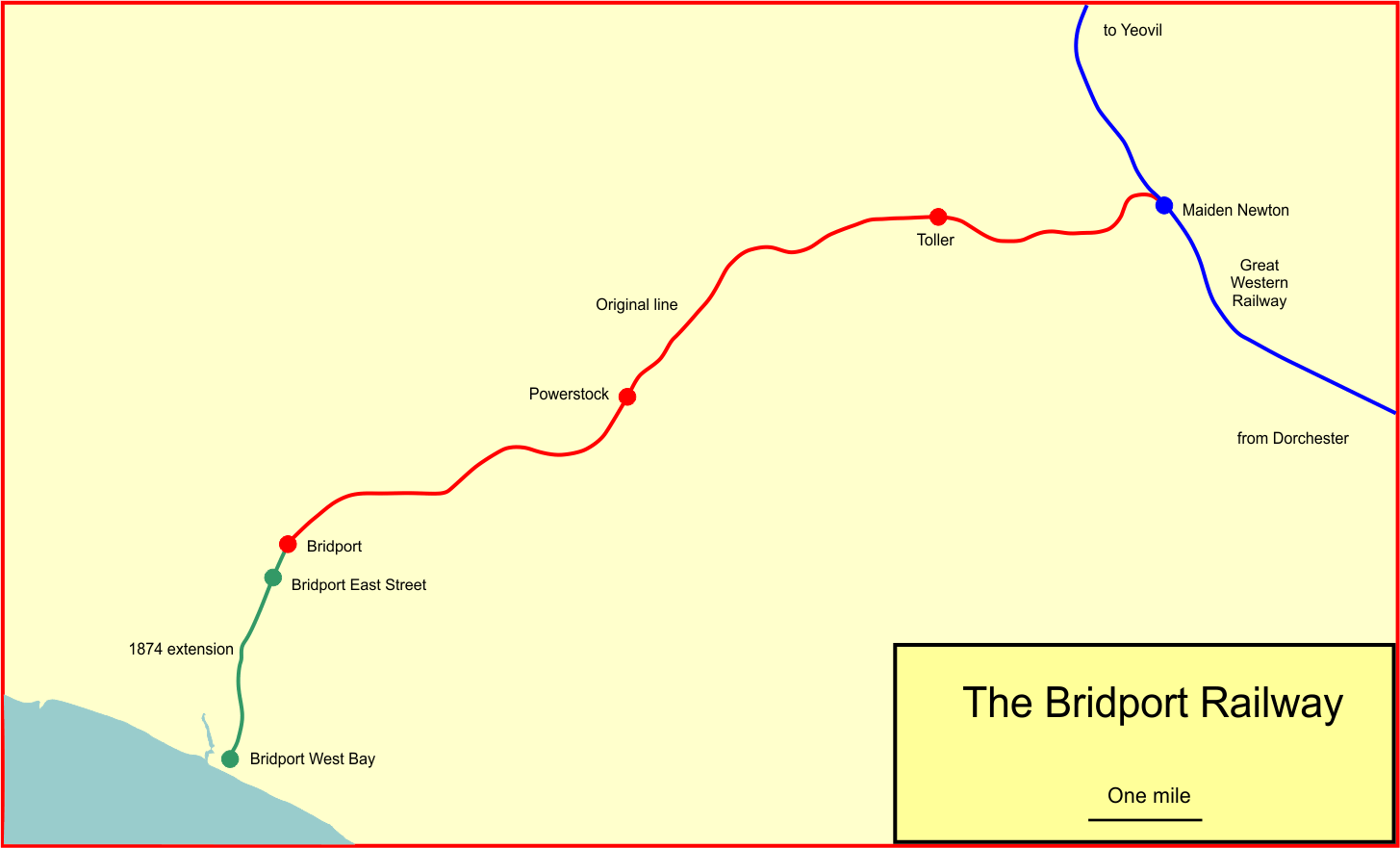
Bridport Railway
The Bridport Railway was a railway branch line that operated in the county of Dorset in England. It connected Bridport with the main line network at Maiden Newton, and opened on 12 November 1857. It was extended to West Bay in 1884, but the extension was not well used and it closed to passengers in 1930. The remaining branch closed in 1975. Origins During the 1840s a number of railway schemes had been proposed, that would have put Bridport on a main line from London to Exeter. This included the Bridport and Exeter Railway, and schemes to extend the London and South Western Railway to Exeter from Dorchester. As late as 1853 there was a firm proposal to build such a line, but it fell through and the present-day route via Yeovil was adopted instead. Dismayed at being abandoned from the main line system, businessmen in Bridport observed that the Great Western Railway (GWR) was making plans to extend its partly built line, the Wilts, Somerset and Weymouth Railway (WS&WR) from Cast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol And Exeter Railway
The Bristol & Exeter Railway (B&ER) was an English railway company formed to connect Bristol and Exeter. It was built on the broad gauge and its engineer was Isambard Kingdom Brunel. It opened in stages between 1841 and 1844. It was allied with the Great Western Railway (GWR), which built its main line between London and Bristol, and in time formed part of a through route between London and Cornwall. It became involved in the gauge wars, a protracted and expensive attempt to secure territory against rival companies supported by the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) which used the narrow gauge, later referred to as ''standard gauge''. At first it contracted with the GWR for that company to work the line, avoiding the expense of acquiring locomotives, but after that arrangement expired in 1849, the B&ER operated its own line. It opened a number of branches within the general area it served: to Clevedon, Cheddar, Wells, Weston-super-Mare, Chard, Yeovil and Tiverton. The B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clevedon Pier
Clevedon Pier is a seaside pier in the town of Clevedon, Somerset, England on the east shore of the Severn Estuary. It was described by Sir John Betjeman, as "the most beautiful pier in England" and was designated a Grade I listed building in 2001. The pier was built during the 1860s to attract tourists and provide a ferry port for rail passengers to South Wales. The pier is long and consists of eight spans supported by steel rails covered by wooden decking, with a pavilion on the pier head. The pier opened in 1869 and served as an embarkation point for paddle steamer excursions for almost 100 years. Two of the spans collapsed during stress testing in 1970 and demolition was proposed, but local fund raising and heritage grants allowed the pier to be dismantled for restoration and reassembled. It reopened in 1989, and ten years later was awarded the Pier of the Year from the National Piers Society, and a Civic Trust Award. The pier now offers a landing stage for steamers and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New South Wales Government Railways
The New South Wales Government Railways (NSWGR) was the agency of the Government of New South Wales that administered rail transport in New South Wales, Australia, between 1855 and 1932. Management The agency was managed by a range of different commission structures between 1857 and 1932, which reported to either the Minister for Public Works or the Minister for Transport. The inaugural Chief Commissioner was Ben Martindale and, following the enactment of the he became Commissioner of Railways. John Rae succeeded Martindale in 1861, and in 1877 Charles Goodchap was appointed Commissioner. The set up a corporate body of three railway commissioners to manage the railways and remove them from political influence, resulting in the resignation of Goodchap. This Board of Railway Commissioners of New South Wales was in place from 22 October 1888 to 4 April 1907, and was replaced by a sole Chief Commissioner of Railways and Tramways until 22 March 1932, when a panel arrangement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Wales Railway
The South Wales Railway ( cy, Rheilffordd De Cymru) was a main line railway which opened in stages from 1850, connecting the Great Western Railway from Gloucester to South Wales. It was constructed on the broad gauge. An original aspiration was to reach Fishguard to engender an Irish ferry transit and transatlantic trade, but the latter did not materialise for many years, and never became an important sector of the business. Neyland was the western terminus of the line until 1906. The company amalgamated with the Great Western Railway in 1863 and the track was converted to narrow (standard) gauge in 1873. In 1922–1923, most of the independent Welsh railways were constituents of the new enlarged Great Western Railway, enabling rationalisation and benefits of scale. Nearly all of the original main line of the South Wales Railway remains in use at present (2020). Proposals The prospectus of the South Wales Railway was issued in the summer of 1844. It proposed a railway with capital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wycombe Railway
The Wycombe Railway was a British railway between and that connected with the Great Western Railway at both ends; there was one branch, to . History The Wycombe Railway Company was incorporated by an act of Parliament passed in 1846. The act authorised the construction of a single line railway from the Great Western Railway's Maidenhead railway station, then located close to the site of the current Taplow railway station. In 1852 construction started; the first section to be built was between Maidenhead and High Wycombe, and opened for passenger services on 1 August 1854. It linked the town of High Wycombe with the Great Western Main Line, and the Great Western Railway operated the services for the Wycombe Railway company. The GWR had been built to Isambard Kingdom Brunel's broad gauge of , so the Wycombe Railway was also built to this gauge. In 1862, the Wycombe Railway opened an extension from High Wycombe via Princes Risborough to Thame. In 1863, it opened a branch line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |