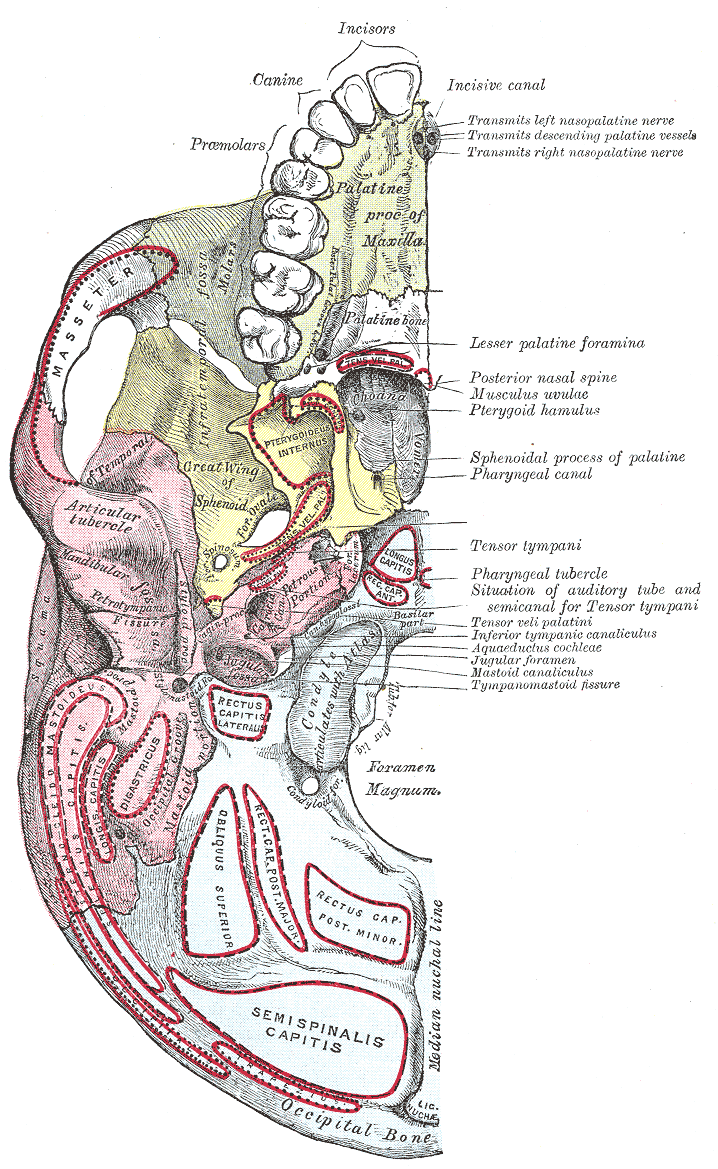
|
Basicranium
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria. Structure Structures found at the base of the skull are for example: Bones There are five bones that make up the base of the skull: *Ethmoid bone *Sphenoid bone *Occipital bone The occipital bone () is a neurocranium, cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobe ... *Frontal bone *Temporal bone Sinuses *Occipital sinus *Superior sagittal sinus *Superior petrosal sinus Foramina of the skull *Foramen cecum (frontal bone), Foramen cecum *Optic foramen *Foramen lacerum *Foramen rotundum *Foramen magnum *Foramen ovale (skull), Foramen ovale *Jugular foramen *Internal auditory meatus *Mastoid foramen *Sphenoidal emissary foramen *Foramen s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foramen Lacerum
The foramen lacerum ( la, lacerated piercing) is a triangular hole in the base of skull. It is located between the sphenoid bone, the apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone, and the basilar part of the occipital bone. Structure The foramen lacerum ( la, lacerated piercing) is a triangular hole in the base of skull. It is located between 3 bones: * the sphenoid bone, forming the anterior border. * the apex of petrous part of the temporal bone, forming the posterolateral border. * the basilar part of occipital bone, forming the posteromedial border. It is the junction point of 3 sutures of the skull: * the petroclival (petrooccipital) suture. * the sphenopetrosal suture. * the sphenooccipital suture. It is situated anteromedial to the carotid canal. Development The foramen lacerum fills with cartilage after birth. Function The foramen lacerum transmits many structures, including: * the artery of the pterygoid canal. * the recurrent artery of the foramen laceru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenopetrosal Suture
The sphenopetrosal fissure (or sphenopetrosal suture) is the cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the petrous portion of the temporal bone. It is in the middle cranial fossa The middle cranial fossa, deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull. It is separated from the posterior fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest. It is bounded in front by the pos .... External links Skull {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenofrontal Suture
The sphenofrontal suture is the cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone The frontal bone is a bone in the human skull. The bone consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, .... Additional images File:Gray164.png, The skull from the side. File:Gray190.png, The skull from the front. File:Gray193.png, Base of the skull. Upper surface. References External links * * Bones of the head and neck Cranial sutures Human head and neck Joints Joints of the head and neck Skeletal system Skull {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontoethmoidal Suture
The frontoethmoidal suture is the suture between the ethmoid bone and the frontal bone. It is located in the anterior cranial fossa The anterior cranial fossa is a depression in the floor of the cranial base which houses the projecting frontal lobes of the brain. It is formed by the orbital part of frontal bone, orbital plates of the Frontal bone, frontal, the cribriform plate .... References External links * Bones of the head and neck Cranial sutures Human head and neck Joints Joints of the head and neck Skeletal system Skull {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foramen Spinosum
The foramen spinosum is a hole located in the greater wing of the sphenoid. It is located posterolateral to the foramen ovale and anterior to the sphenoidal spine. It allows the passage of the middle meningeal artery, middle meningeal vein and usually the meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve (sometimes it passes through the foramen ovale). The foramen spinosum is often used as a landmark in neurosurgery, due to its close relations with other cranial foramina. It was first described by Jakob Benignus Winslow in the 18th century. Structure The foramen spinosum is a foramen in the sphenoid bone of the skull. It connects the middle cranial fossa to the infratemporal fossa. It is located posterolateral to the foramen ovale, and anterior to the sphenoidal spine. Variation The foramen spinosum varies in size and location. The foramen is rarely absent, usually unilaterally, in which case the middle meningeal artery enters the cranial cavity through the foramen ovale. It ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenoidal Emissary Foramen
In the base of the skull, in the great wings of the sphenoid bone, medial to the foramen ovale, a small aperture, the sphenoidal emissary foramen, may occasionally be seen (it is often absent) opposite the root of the pterygoid process. When present, it opens below near the scaphoid fossa. Vesalius was the first to describe and illustrate this foramen, and it thus sometimes bears the name of foramen Vesalii (meaning foramen of Vesalius). Other names include foramen venosum and canaliculus sphenoidalis. Importance If at all present, the sphenoidal emissary foramen gives passage to a small vein (vein of Vesalius) that connects the pterygoid plexus with the cavernous sinus. The importance of this passage lies in the fact that an infected thrombus from an extracranial source may reach the cavernous sinus. The mean area of the foramen is small, which may suggest that it plays a minor role in the dynamics of blood circulation in the venous system of the head. Structure The sphenoidal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastoid Foramen
The mastoid foramen is a hole in the posterior border of the temporal bone. It transmits an emissary vein between the sigmoid sinus and the suboccipital venous plexus, and a small branch of the occipital artery, the posterior meningeal artery to the dura mater. Structure The mastoid foramen is a hole in the posterior border of the temporal bone of the skull. The opening of the mastoid foramen is an average of 18 mm from the asterion, and around 34 mm from the external auditory meatus. It is typically very narrow. This may be around 2 mm. Variation The position and size of this foramen are very variable. It is not always present. Sometimes, it is duplicated on one side or both sides. Sometimes, it is situated in the occipital bone, or in the suture between the temporal bone and the occipital bone. Function The mastoid foramen transmits: * an emissary vein between the sigmoid sinus and the suboccipital venous plexus or the posterior auricular vein. * a small branch of the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Auditory Meatus
The internal auditory meatus (also meatus acusticus internus, internal acoustic meatus, internal auditory canal, or internal acoustic canal) is a canal within the petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull between the posterior cranial fossa and the inner ear. Structure The opening to the meatus is called the porus acusticus internus or internal acoustic opening. It is located inside the posterior cranial fossa of the skull, near the center of the posterior surface of the petrous part of the temporal bone. The size varies considerably. Its outer margins are smooth and rounded. The canal which comprises the internal auditory meatus is short (about 1 cm) and runs laterally into the bone. The lateral (outer) aspect of the canal is known as the fundus. The fundus is subdivided by two thin crests of bone to form three separate canals, through which course the facial and vestibulocochlear nerve branches. The falciform crest first divides the meatus into superior and inferior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jugular Foramen
A jugular foramen is one of the two (left and right) large foramina (openings) in the base of the skull, located behind the carotid canal. It is formed by the temporal bone and the occipital bone. It allows many structures to pass, including the inferior petrosal sinus, three cranial nerves, the sigmoid sinus, and meningeal arteries. Structure The jugular foramen is formed in front by the petrous portion of the temporal bone, and behind by the occipital bone. It is generally slightly larger on the right side than on the left side. Contents The jugular foramen may be subdivided into three compartments, each with their own contents. * The ''anterior'' compartment transmits the inferior petrosal sinus. * The ''intermediate'' compartment transmits the glossopharyngeal nerve, the vagus nerve, and the accessory nerve. * The ''posterior'' compartment transmits the sigmoid sinus (becoming the internal jugular vein), and some meningeal branches from the occipital artery and ascending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |