|
Base (chemistry)
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word base, known as Arrhenius bases, Brønsted bases, and Lewis bases. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acids, as originally proposed by G.-F. Rouelle in the mid-18th century. In 1884, Svante Arrhenius proposed that a base is a substance which dissociates in aqueous solution to form Hydroxide ions OH−. These ions can react with hydrogen ions (H+ according to Arrhenius) from the dissociation of acids to form water in an acid–base reaction An acid–base reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs between an acid and a base. It can be used to determine pH via titration. Several theoretical frameworks provide alternative conceptions of the reaction mechanisms and their applica .... A base was therefore a metal hydroxide such as Sodium hydroxide, NaOH or Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2. Such aqueous hydroxide solutions were also described by certain characteristic properties. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decorative Soaps
Beauty is commonly described as a feature of objects that makes these objects pleasurable to perceive. Such objects include landscapes, sunsets, humans and works of art. Beauty, together with art and taste, is the main subject of aesthetics, one of the major branches of philosophy. As a positive aesthetic value, it is contrasted with ugliness as its negative counterpart. Along with truth and goodness it is one of the transcendentals, which are often considered the three fundamental concepts of human understanding. One difficulty in understanding beauty is because it has both objective and subjective aspects: it is seen as a property of things but also as depending on the emotional response of observers. Because of its subjective side, beauty is said to be "in the eye of the beholder". It has been argued that the ability on the side of the subject needed to perceive and judge beauty, sometimes referred to as the "sense of taste", can be trained and that the verdicts of experts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-ionization Of Water
The self-ionization of water (also autoionization of water, and autodissociation of water) is an ionization reaction in pure water or in an aqueous solution, in which a water molecule, H2O, deprotonates (loses the nucleus of one of its hydrogen atoms) to become a hydroxide ion, OH−. The hydrogen nucleus, H+, immediately protonates another water molecule to form a hydronium cation, H3O+. It is an example of autoprotolysis, and exemplifies the amphoteric nature of water. History and notation The self-ionization of water was first proposed in 1884 by Svante Arrhenius as part of the theory of ionic dissociation which he proposed to explain the conductivity of electrolytes including water. Arrhenius wrote the self-ionization as H2O H+ + OH-. At that time, nothing was yet known of atomic structure or subatomic particles, so he had no reason to consider the formation of an H+ ion from a hydrogen atom on electrolysis as any less likely than, say, the formation of a Na+ ion from a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for polar molecules and the most common solvent used by living things; all the ions and proteins in a cell are dissolved in water within the cell. The quantity of solute that can dissolve in a specific volume of solvent varies with temperature. Major uses of solvents are in paints, paint removers, inks, and dry cleaning. Specific uses for organic solvents are in dry cleaning (e.g. tetrachloroethylene); as paint thinners (toluene, turpentine); as nail polish removers and solvents of glue (acetone, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate); in spot removers (hexane, petrol ether); in detergents ( citrus terpenes); and in perfumes (ethanol). Solvents find various applications in chemical, pharmaceutical, oil, and gas industries, including in chemical syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturated Solution
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution. The extent of the solubility of a substance in a specific solvent is generally measured as the concentration of the solute in a saturated solution, one in which no more solute can be dissolved. At this point, the two substances are said to be at the solubility equilibrium. For some solutes and solvents, there may be no such limit, in which case the two substances are said to be "miscible in all proportions" (or just "miscible"). The solute can be a solid, a liquid, or a gas, while the solvent is usually solid or liquid. Both may be pure substances, or may themselves be solutions. Gases are always miscible in all proportions, except in very extreme situations,J. de Swaan Arons and G. A. M. Diepen (1966): "Gas—Gas Equilibria". ''Journal of Chemical Physics'', vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt (chemistry)
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions. The component ions in a salt compound can be either inorganic, such as chloride (Cl−), or organic, such as acetate (). Each ion can be either monatomic, such as fluoride (F−), or polyatomic, such as sulfate (). Types of salt Salts can be classified in a variety of ways. Salts that produce hydroxide ions when dissolved in water are called ''alkali salts'' and salts that produce hydrogen ions when dissolved in water are called ''acid salts''. ''Neutral salts'' are those salts that are neither acidic nor basic. Zwitterions contain an anionic and a cationic centre in the same molecule, but are not considered salts. Examples of zwitterions are amino acids, many metabolites, peptid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutralization (chemistry)
In chemistry, neutralization or neutralisation (see spelling differences) is a chemical reaction in which acid and a base react quantitatively with each other. In a reaction in water, neutralization results in there being no excess of hydrogen or hydroxide ions present in the solution. The pH of the neutralized solution depends on the acid strength of the reactants. Meaning of "neutralization" In the context of a chemical reaction the term neutralization is used for a reaction between an acid and a base or alkali. Historically, this reaction was represented as :acid + base (alkali) → salt + water For example: :HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O The statement is still valid as long as it is understood that in an aqueous solution the substances involved are subject to dissociation, which changes the ionization state of the substances. The arrow sign, →, is used because the reaction is complete, that is, neutralization is a quantitative reaction. A more general definition is base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydronium
In chemistry, hydronium (hydroxonium in traditional British English) is the common name for the aqueous cation , the type of oxonium ion produced by protonation of water. It is often viewed as the positive ion present when an Arrhenius acid is dissolved in water, as Arrhenius acid molecules in solution give up a proton (a positive hydrogen ion, ) to the surrounding water molecules (). In fact, acids must be surrounded by more than a single water molecule in order to ionize, yielding aqueous and conjugate base. Three main structures for the aqueous proton have garnered experimental support: The Eigen cation, which is a tetrahydrate, H3O+(H2O)3; the Zundel cation, which is a symmetric dihydrate, H+(H2O)2; and the Stoyanov cation, an expanded Zundel cation, which is a hexahydrate: H+(H2O)2(H2O)4. Spectroscopic evidence from well-defined IR spectra overwhelmingly supports the Stoyanov cation as the predominant form. For this reason, it has been suggested that wherever possible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid Strength
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula HA, to dissociate into a proton, H+, and an anion, A-. The dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions. :HA -> H+ + A- Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid (HCl), perchloric acid (HClO4), nitric acid (HNO3) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4). A weak acid is only partially dissociated, with both the undissociated acid and its dissociation products being present, in solution, in equilibrium with each other. :HA H+ + A- Acetic acid (CH3COOH) is an example of a weak acid. The strength of a weak acid is quantified by its acid dissociation constant, K_\ce value. The strength of a weak organic acid may depend on substituent effects. The strength of an inorganic acid is dependent on the oxidation state for the atom to which the proton may be attached. Acid strength is solvent-dependent. For example, hydrogen chloride is a strong acid in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjugate Base
A conjugate acid, within the Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, is a chemical compound formed when an acid donates a proton () to a base—in other words, it is a base with a hydrogen ion added to it, as in the reverse reaction it loses a hydrogen ion. On the other hand, a conjugate base is what is left over after an acid has donated a proton during a chemical reaction. Hence, a conjugate base is a species formed by the removal of a proton from an acid, as in the reverse reaction it is able to gain a hydrogen ion. Because some acids are capable of releasing multiple protons, the conjugate base of an acid may itself be acidic. In summary, this can be represented as the following chemical reaction: :acid + base conjugate\ base + conjugate\ acid Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted and Martin Lowry introduced the Brønsted–Lowry theory, which proposed that any compound that can transfer a proton to any other compound is an acid, and the compound that accepts the proton is a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkoxide
In chemistry, an alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They are written as , where R is the organic substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, when R is not bulky, good nucleophiles and good ligands. Alkoxides, although generally not stable in protic solvents such as water, occur widely as intermediates in various reactions, including the Williamson ether synthesis. Transition metal alkoxides are widely used for coatings and as catalysts. Enolates are unsaturated alkoxides derived by deprotonation of a bond adjacent to a ketone or aldehyde. The nucleophilic center for simple alkoxides is located on the oxygen, whereas the nucleophilic site on enolates is delocalized onto both carbon and oxygen sites. Ynolates are also unsaturated alkoxides derived from acetylenic alcohols. Phenoxides are close relatives of the alkoxides, in which the alkyl group is replaced by a derivative of be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the Earth's crust consists of oxides. Even materials considered pure elements often develop an oxide coating. For example, aluminium foil develops a thin skin of Al2O3 (called a passivation layer) that protects the foil from further corrosion.Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd Edn.), Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. . Stoichiometry (the measurable relationship between reactants and chemical equations of a equation or reaction) Oxides are extraordinarily diverse in terms of stoichiometries and in terms of the structures of each stoichiometry. Most elements form oxides of more than one stoichiometry. A well known example is carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
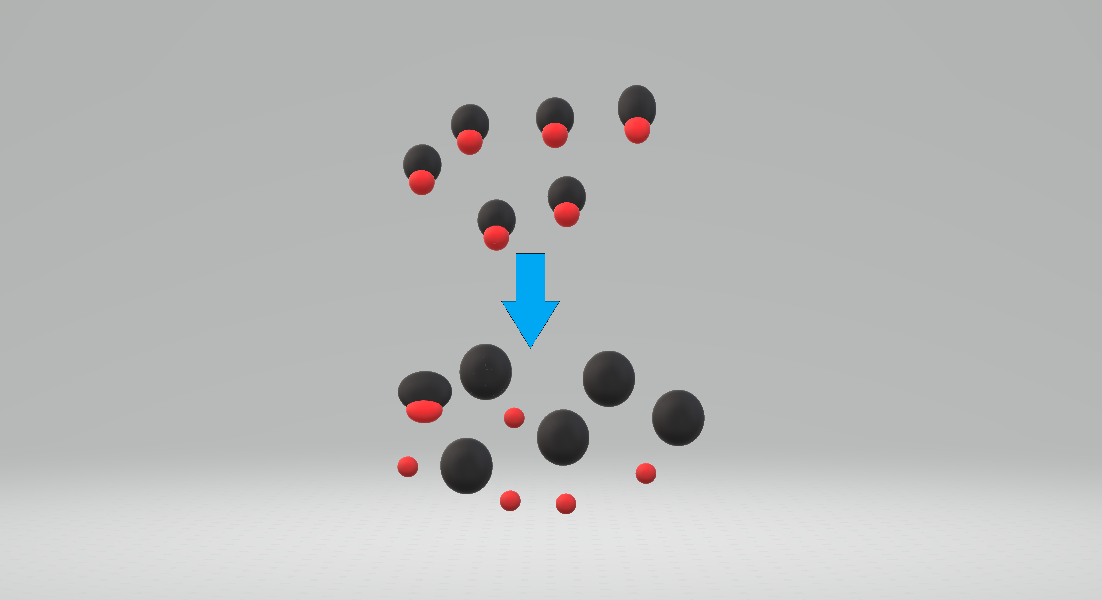
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry refers to the relationship between the quantities of reactants and products before, during, and following chemical reactions. Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products, leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of the products can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated. This is illustrated in the image here, where the balanced equation is: : Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. This particular chemical equation is an example of complete combustion. St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |