|
Balloon Satellite
A balloon satellite is inflated with gas after it has been put into orbit. It is also occasionally referred to as a "satelloon", which is a trademarked name owned by Gilmore Schjeldahl's G.T. Schjeldahl Company. List of balloon satellites abbreviations: * pcr = passive communications reflector, satellite reflects microwave signals. * ado = atmospheric density observations * spc = solar pressure calculations, estimate impact of solar wind on orbit. * tri = satellite triangulation, measuring the Earth's surface. * SC = Sensors and camera for earth curvature images Echo 1 and Echo 2 balloon satellites The first flying body of this type was Echo 1, which was launched into a high orbit on August 12, 1960, by the United States. It originally had a spherical shape measuring , with a thin metal-coated plastic shell made of Mylar. It served for testing as a "passive" communication and geodetic satellite. Its international COSPAR number was 6000901 (9th satellite launched in 1960, 1s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as a planet, moon, asteroid, or Lagrange point. Normally, orbit refers to a regularly repeating trajectory, although it may also refer to a non-repeating trajectory. To a close approximation, planets and satellites follow elliptic orbits, with the center of mass being orbited at a focal point of the ellipse, as described by Kepler's laws of planetary motion. For most situations, orbital motion is adequately approximated by Newtonian mechanics, which explains gravity as a force obeying an inverse-square law. However, Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, which accounts for gravity as due to curvature of spacetime, with orbits following geodesics, provides a more accurate calculation and understanding of the exact mechanics of orbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spherical
A sphere () is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the centre of the sphere, and is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental object in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres roll smoothly in any direction, so most balls used in sports and toys are spherical, as are ball bearings. Basic terminology As mentioned earlier is the sphere's r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelsat I
Intelsat I (nicknamed Early Bird for the proverb "The early bird catches the worm") was the first commercial communications satellite to be placed in geosynchronous orbit, on April 6, 1965. It was built by the Space and Communications Group of Hughes Aircraft Company (later Hughes Space and Communications Company, and now Boeing Satellite Systems) for COMSAT, which activated it on June 28, 1965. It was based on the Syncom series of satellites that Hughes had previously built for NASA to demonstrate that communications via synchronous-orbit satellite were feasible. Its booster was a Thrust Augmented Delta (Delta D). After a series of maneuvers, it reached its geosynchronous orbital position over the Atlantic Ocean at 28° West longitude, where it was put into service. It helped provide the first live TV coverage of a spacecraft splashdown, that of Gemini 6 in December 1965. Originally slated to operate for 18 months, Early Bird was in active service for 4 years and 4 months, bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telstar 1
Telstar 1 was a communications satellite launched by NASA on July 10, 1962. It was the satellite that allowed the first live broadcast of television images between the United States and Europe. Telstar 1 remained active for only 7 months before it prematurely failed due to Starfish Prime, a high-altitude nuclear test conducted by the United States. Although the satellite is no longer operational, it remains in Earth orbit. History The idea of transmitting information by means of satellites was hardly new. As early as October 1945, the mathematician and visionary Arthur C. Clarke published an article talking about it in the specialized magazine Wireless World. His idea was to take advantage of the immensity of space to transmit information, using a satellite system for this purpose. During the Cold War, the shock caused by the successful launch of the first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, by the Soviets increased the United States' interest in aerospace research. Soon thereafte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explorer Program
The Explorers program is a NASA exploration program that provides flight opportunities for physics, geophysics, heliophysics, and astrophysics investigations from space. Launched in 1958, Explorer 1 was the first spacecraft of the United States to achieve orbit. Over 90 space missions have been launched since. Starting with Explorer 6, it has been operated by NASA, with regular collaboration with a variety of other institutions, including many international partners. Launchers for the Explorer program have included Juno I, Juno II, various Thor, Scout, Delta and Pegasus launch vehicles, and Falcon 9. The program has three classes: Medium-Class Explorers (MIDEX), Small Explorers (SMEX), and University-Class Explorers (UNEX), with select Missions of Opportunity operated with other agencies. History Early Explorer satellites The Explorer program began as a U.S. Army proposal (Project Orbiter) to place a "civilian" artificial satellite into orbit during the International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pageos
PAGEOS (PAssive Geodetic Earth Orbiting Satellite) was a balloon satellite which was launched by NASA in June 1966. Design PAGEOS had a diameter of exactly , consisted of a thick mylar plastic film coated with vapour deposited aluminium enclosing a volume of and was used for the Weltnetz der Satellitentriangulation (Worldwide Satellite Triangulation Network) – a global cooperation organized by Hellmut Schmid (Switzerland & USA) 1969-1973. Finished in 1974, the network connected 46 stations (3000–5000 km distance) of all continents with an accuracy of 3–5 m (approx. 20 times better than terrestrial triangulations at that time). Orbit The PAGEOS spacecraft was placed into a polar orbit (inclination 85–86°) with a height of approx. 4000 km, which had gradually lowered during its 9 years of operation. The satellite partly disintegrated in July 1975, which was followed by a second break-up that occurred in January 1976 resulting in the release of a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
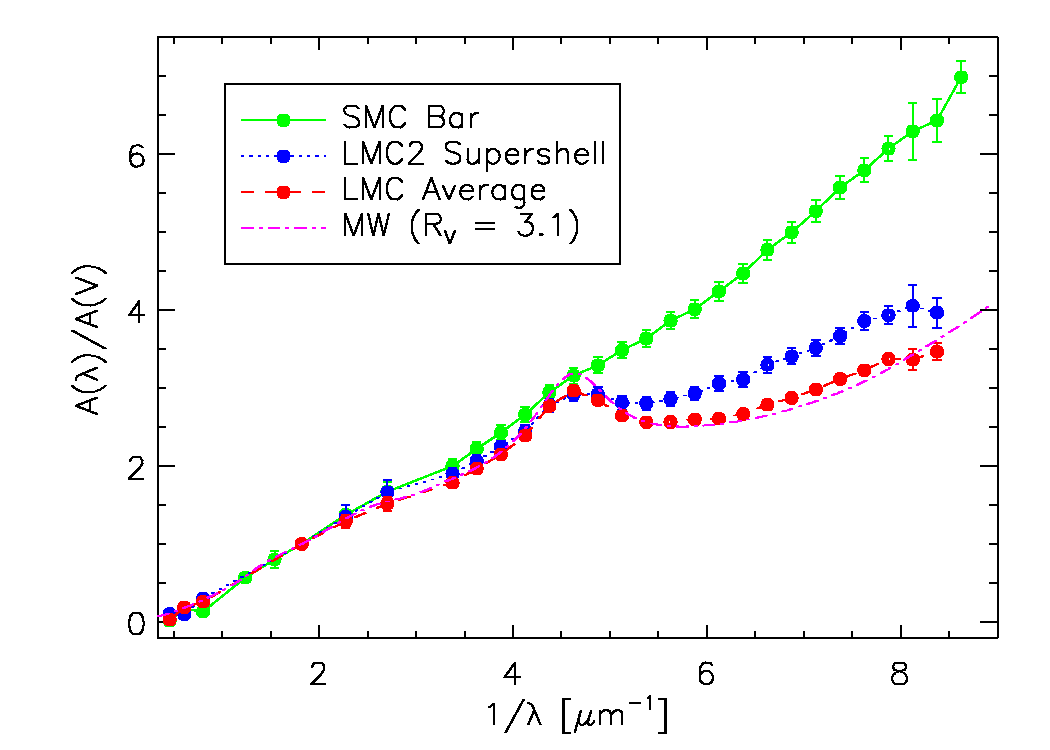
Extinction (astronomy)
In astronomy, extinction is the absorption and scattering of electromagnetic radiation by dust and gas between an emitting astronomical object and the observer. Interstellar extinction was first documented as such in 1930 by Robert Julius Trumpler. However, its effects had been noted in 1847 by Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve, and its effect on the colors of stars had been observed by a number of individuals who did not connect it with the general presence of galactic dust. For stars that lie near the plane of the Milky Way and are within a few thousand parsecs of the Earth, extinction in the visual band of frequencies (photometric system) is roughly 1.8 magnitudes per kiloparsec. For Earth-bound observers, extinction arises both from the interstellar medium (ISM) and the Earth's atmosphere; it may also arise from circumstellar dust around an observed object. Strong extinction in earth's atmosphere of some wavelength regions (such as X-ray, ultraviolet, and infrared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phases Of The Moon
Concerning the lunar month of ~29.53 days as viewed from Earth, the lunar phase or Moon phase is the shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion, which can be expressed quantitatively using areas or angles, or described qualitatively using the terminology of the 4 major phases: new moon, first quarter, full moon, last quarter and 4 minor phases: waxing crescent, waxing gibbous, waning gibbous, and waning crescent. The lunar phases gradually change over a synodic month (~29.53 days) as the Moon's orbital positions around Earth and Earth around the Sun shift. The visible side of the Moon is variously sunlit, depending on the position of the Moon in its orbit. Thus, this face's sunlit portion can vary from 0% (at new moon) to 100% (at full moon). Each of the 4 major lunar phases (see below) is ~7.4 days, with +/− 19 hours in variation (6.58–8.24 days) due to the elliptical shape of the Moon's orbit. Phases of the Moon There are four ''principal'' (primary/major) lunar phases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
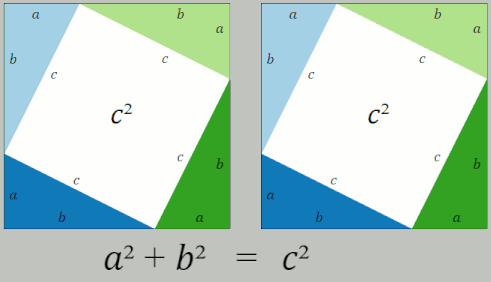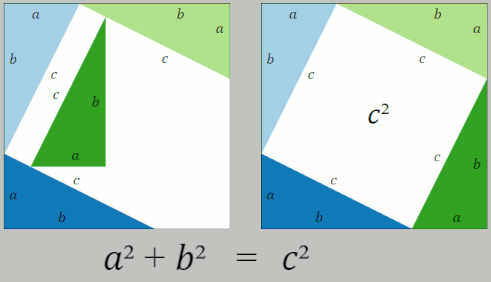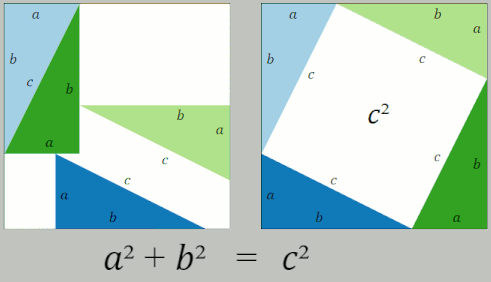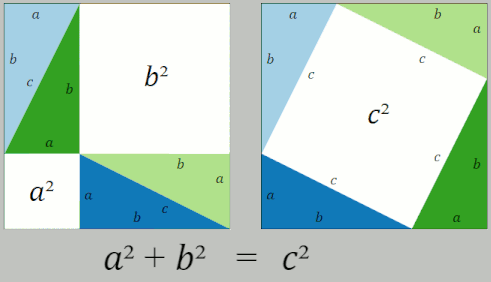
Pythagorean Theorem
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras' theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry between the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. This theorem can be written as an equation relating the lengths of the sides ''a'', ''b'' and the hypotenuse ''c'', often called the Pythagorean equation: :a^2 + b^2 = c^2 , The theorem is named for the Greek philosopher Pythagoras, born around 570 BC. The theorem has been proven numerous times by many different methods – possibly the most for any mathematical theorem. The proofs are diverse, including both geometric proofs and algebraic proofs, with some dating back thousands of years. When Euclidean space is represented by a Cartesian coordinate system in analytic geometry, Euclidean distance satisfies the Pythagorean relation: the squared dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, natural satellite, moons, comets and galaxy, galaxies – in either observational astronomy, observational (by analyzing the data) or theoretical astronomy. Examples of topics or fields astronomers study include planetary science, Sun, solar astronomy, the Star formation, origin or stellar evolution, evolution of stars, or the galaxy formation and evolution, formation of galaxies. A related but distinct subject is physical cosmology, which studies the Universe as a whole. Types Astronomers usually fall under either of two main types: observational astronomy, observational and theoretical astronomy, theoretical. Observational astronomers make direct observations of Astronomical object, celestial objects and analyze the data. In contrast, theoretical astronomers create and investigate C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Station (communications)
A ground station, Earth station, or Earth terminal is a terrestrial radio station designed for extraplanetary telecommunication with spacecraft (constituting part of the ground segment of the spacecraft system), or reception of radio waves from astronomical radio sources. Ground stations may be located either on the surface of the Earth, or in its atmosphere. Earth stations communicate with spacecraft by transmitting and receiving radio waves in the super high frequency (SHF) or extremely high frequency (EHF) bands (e.g. microwaves). When a ground station successfully transmits radio waves to a spacecraft (or vice versa), it establishes a telecommunications link. A principal telecommunications device of the ground station is the parabolic antenna. Ground stations may have either a fixed or itinerant position. Article 1 § III of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) Radio Regulations describes various types of stationary and mobile ground stations, and their interrel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COSPAR
The Committee on Space Research (COSPAR) was established on October 3, 1958 by the International Council for Scientific Unions (ICSU). Among COSPAR's objectives are the promotion of scientific research in space on an international level, with emphasis on the free exchange of results, information, and opinions, and providing a forum, open to all scientists, for the discussion of problems that may affect space research. These objectives are achieved through the organization of symposia, publication, and other means. COSPAR has created a number of research programmes on different topics, a few in cooperation with other scientific Unions. The long-term project COSPAR international reference atmosphere started in 1960; since then it has produced several editions of the high-atmosphere code CIRA. The code "IRI" of the URSI-COSPAR working group on the International Reference Ionosphere was first edited in 1978 and is yearly updated. General Assembly Every second year, COSPAR c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |