|
Balanol
Balanol is a fungal metabolite produced by the fungus '' Verticillium balanoides''. It is a potent inhibitor of the serine/threonine kinases protein kinase A (PKA) and protein kinase C (PKC), binding in a similar manner with that of ATP. Balanol was discovered in 1993 in the search for novel inhibitors of PKC, a member of a family of serine/threonine kinases whose overactivation is associated with numerous human diseases of signal transduction including cancer. However, much of the research on balanol focuses on how chemical modifications of the molecular structure affect binding to PKA. Indeed, balanol, its chemically altered analogs, and their interactions with PKA in particular are used to illuminate the roles of selectivity and protein flexibility in the inhibition of kinases. For instance, the X-ray crystal structure of balanol in complex with PKA was used in order to confer selectivity and to improve pharmacological efficacy of inhibitors of the ''H. sapiens'' Akt (PKB), ano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism. The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, catalytic activity of their own (usually as a cofactor to an enzyme), defense, and interactions with other organisms (e.g. pigments, odorants, and pheromones). A primary metabolite is directly involved in normal "growth", development, and reproduction. Ethylene exemplifies a primary metabolite produced large-scale by industrial microbiology. A secondary metabolite is not directly involved in those processes, but usually has an important ecological function. Examples include antibiotics and pigments such as resins and terpenes etc. Some antibiotics use primary metabolites as precursors, such as actinomycin, which is created from the primary metabolite tryptophan. Some sugars are metabolites, such as fructose or glucose, which are both p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
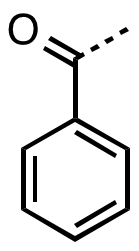
Benzophenone
Benzophenone is the organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2CO, generally abbreviated Ph2CO. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. Benzophenone is a widely used building block in organic chemistry, being the parent diarylketone. Uses Benzophenone can be used as a photo initiator in UV(Ultra-violet)-curing applications such as inks, imaging, and clear coatings in the printing industry. Benzophenone prevents ultraviolet ( UV) light from damaging scents and colors in products such as perfumes and soaps. Benzophenone can also be added to plastic packaging as a UV blocker to prevent photo-degradation of the packaging polymers or its contents. Its use allows manufacturers to package the product in clear glass or plastic (such as a PETE water bottle). Without it, opaque or dark packaging would be required. In biological applications, benzophenones have been used extensively as photophysical probes to identify and map peptide–protein interactions. Benzophenone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzamides
Benzamide is a organic compound with the chemical formula of C6H5C(O)NH2. It is the simplest amide derivative of benzoic acid Benzoic acid is a white (or colorless) solid organic compound with the formula , whose structure consists of a benzene ring () with a carboxyl () substituent. It is the simplest aromatic carboxylic acid. The name is derived from gum benzoin, wh .... In powdered form, it appears as a white solid, while in crystalline form, it appears as colourless crystals. It is slightly soluble in water, and soluble in many organic solvents. It is a natural alkaloid found in the herbs of Berberis pruinosa. Chemical derivatives A number of substituted benzamides are commercial drugs, including: See also * References External links Physical characteristics {{Authority control Phenyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Kinase Inhibitors
A protein kinase inhibitor is a type of enzyme inhibitor that blocks the action of one or more protein kinases. Protein kinases are enzymes that phosphorylate (add a phosphate, or PO4, group) to a protein and can modulate its function. The phosphate groups are usually added to serine, threonine, or tyrosine amino acids on the protein: most kinases act on both serine and threonine, the tyrosine kinases act on tyrosine, and a number (dual-specificity kinases) act on all three. There are also protein kinases that phosphorylate other amino acids, including histidine kinases that phosphorylate histidine residues. Phosphorylation regulates many biological processes, and protein kinase inhibitors can be used to treat diseases due to hyperactive protein kinases (including mutant or overexpressed kinases in cancer) or to modulate cell functions to overcome other disease drivers. Clinical use Kinase inhibitors such as dasatinib are often used in the treatment of cancer and inflammation. So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Kinase G
cGMP-dependent protein kinase or protein kinase G (PKG) is a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase that is activated by cGMP. It phosphorylates a number of biologically important targets and is implicated in the regulation of smooth muscle relaxation, platelet function, sperm metabolism, cell division, and nucleic acid synthesis. Genes and proteins PKG are serine/threonine kinases that are present in a variety of eukaryotes ranging from the unicellular organism ''Paramecium'' to humans. Two PKG genes, coding for PKG type I (PKG-I) and type II (PKG-II), have been identified in mammals. The N-terminus of PKG-I is encoded by two alternatively spliced exons that specify for the PKG-Iα and PKG-Iβ isoforms. PKG-Iβ is activated at ~10-fold higher cGMP concentrations than PKG-Iα. The PKG-I and PKG-II are homodimers of two identical subunits (~75 kDa and ~85 kDa, respectively) and share common structural features. Each subunit is composed of three functional domains: * (1) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inhibition Constant
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a molecule which produces a signal by binding to a site on a target protein. The binding typically results in a change of conformational isomerism (conformation) of the target protein. In DNA-ligand binding studies, the ligand can be a small molecule, ion, or protein which binds to the DNA double helix. The relationship between ligand and binding partner is a function of charge, hydrophobicity, and molecular structure. Binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals forces. The association or docking is actually reversible through dissociation. Measurably irreversible covalent bonding between a ligand and target molecule is atypical in biological systems. In contrast to the definition of ligand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staurosporine
Staurosporine (antibiotic AM-2282 or STS) is a natural product originally isolated in 1977 from the bacterium '' Streptomyces staurosporeus''. It was the first of over 50 alkaloids to be isolated with this type of bis-indole chemical structure. The chemical structure of staurosporine was elucidated by X-ray analysis of a single crystal and the absolute stereochemical configuration by the same method in 1994. Staurosporine was discovered to have biological activities ranging from anti-fungal to anti-hypertensive. The interest in these activities resulted in a large investigative effort in chemistry and biology and the discovery of the potential for anti-cancer treatment. Biological activities The main biological activity of staurosporine is the inhibition of protein kinases through the prevention of ATP binding to the kinase. This is achieved through the stronger affinity of staurosporine to the ATP-binding site on the kinase. Staurosporine is a prototypical ATP-competitive kinase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzoyl
In organic chemistry, benzoyl (, ) is the functional group with the formula C6H5CO-. It can be viewed as benzaldehyde missing one hydrogen. The term "benzoyl" should not be confused with benzyl, which has the formula C6H5CH2. The benzoyl group is given the symbol "Bz". Benzyl is commonly abbreviated "Bn". Sources Benzoyl chloride is a favored source of benzoyl groups, being used to prepare benzoyl ketones, benzamides (benzoyl amides), and benzoate esters. The source of many naturally occurring benzoyl compounds is the thioester benzoyl-CoA. Irradiation of benzil generates benzoyl radicals, which have the formula PhCO. Benzoyl compounds Many ketones contain the benzoyl group. They have the formula C6H5CO–R, an important example being benzophenone. Benzoyl esters and amides are common in organic chemistry. The esters are used as a protecting groups in organic synthesis, which can be easily removed by hydrolysis in dilute basic solution. Benzoyl-β-D-glucoside is a natural su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azepane
Azepane is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)6NH. It is a colorless liquid. A cyclic secondary amine, it is a precursor to several drugs and pesticides. It is produced by partial hydrogenolysis of hexamethylene diamine. Like many amines, it reacts with carbon dioxide. See also * Azepine Azepines are unsaturated heterocycles of seven atoms, with a nitrogen replacing a carbon at one position. See also * Azepane * Benzazepines Benzazepines are heterocyclic chemical compounds consisting of a benzene ring fused to an azepine ring ... References {{reflist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-dimensional Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (2D NMR) is a set of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) methods which give data plotted in a space defined by two frequency axes rather than one. Types of 2D NMR include correlation spectroscopy (COSY), J-spectroscopy, exchange spectroscopy (EXSY), and nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy (NOESY). Two-dimensional NMR spectra provide more information about a molecule than one-dimensional NMR spectra and are especially useful in determining the structure of a molecule, particularly for molecules that are too complicated to work with using one-dimensional NMR. The first two-dimensional experiment, COSY, was proposed by Jean Jeener, a professor at the Université Libre de Bruxelles, in 1971. This experiment was later implemented by Walter P. Aue, Enrico Bartholdi and Richard R. Ernst, who published their work in 1976. Fundamental concepts Each experiment consists of a sequence of radio frequency (RF) pulses with d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verticillium
''Verticillium'' is a genus of fungi in the division Ascomycota, and are an anamorphic form of the family Plectosphaerellaceae. The genus used to include diverse groups comprising saprobes and parasites of higher plants, insects, nematodes, mollusc eggs, and other fungi, thus the genus used to have a wide-ranging group of taxa characterised by simple but ill-defined characters. The genus, currently thought to contain 51 species, may be broadly divided into three ecologically based groups - mycopathogens, entomopathogens, and plant pathogens and related saprotrophs. However, the genus has undergone recent revision into which most entomopathogenic and mycopathogenic isolates fall into a new group called '' Lecanicillium''. At least five species are known to cause a wilt disease in plants called verticillium wilt: ''V. dahliae'', ''V. longisporum'', ''V. albo-atrum'', ''V. nubilum'', and ''V. tricorpus''. A sixth species, ''V. theobromae'', causes fruit or crown rot, a non-wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon-13 NMR
Carbon-13 (C13) nuclear magnetic resonance (most commonly known as carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy or 13C NMR spectroscopy or sometimes simply referred to as carbon NMR) is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to carbon. It is analogous to proton NMR ( NMR) and allows the identification of carbon atoms in an organic molecule just as proton NMR identifies hydrogen atoms. 13C NMR detects only the isotope. The main carbon isotope, is not detected. Although much less sensitive than 1H NMR spectroscopy, 13C NMR spectroscopy is widely used for characterizing organic and organometallic compounds. Chemical shifts 13C NMR chemical shifts follow the same principles as those of 1H, although the typical range of chemical shifts is much larger than for 1H (by a factor of about 20). The chemical shift reference standard for 13C is the carbons in tetramethylsilane (TMS), whose chemical shift is considered to be 0.0 ppm. ImageSize = width:540 height:440 AlignBar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |