|
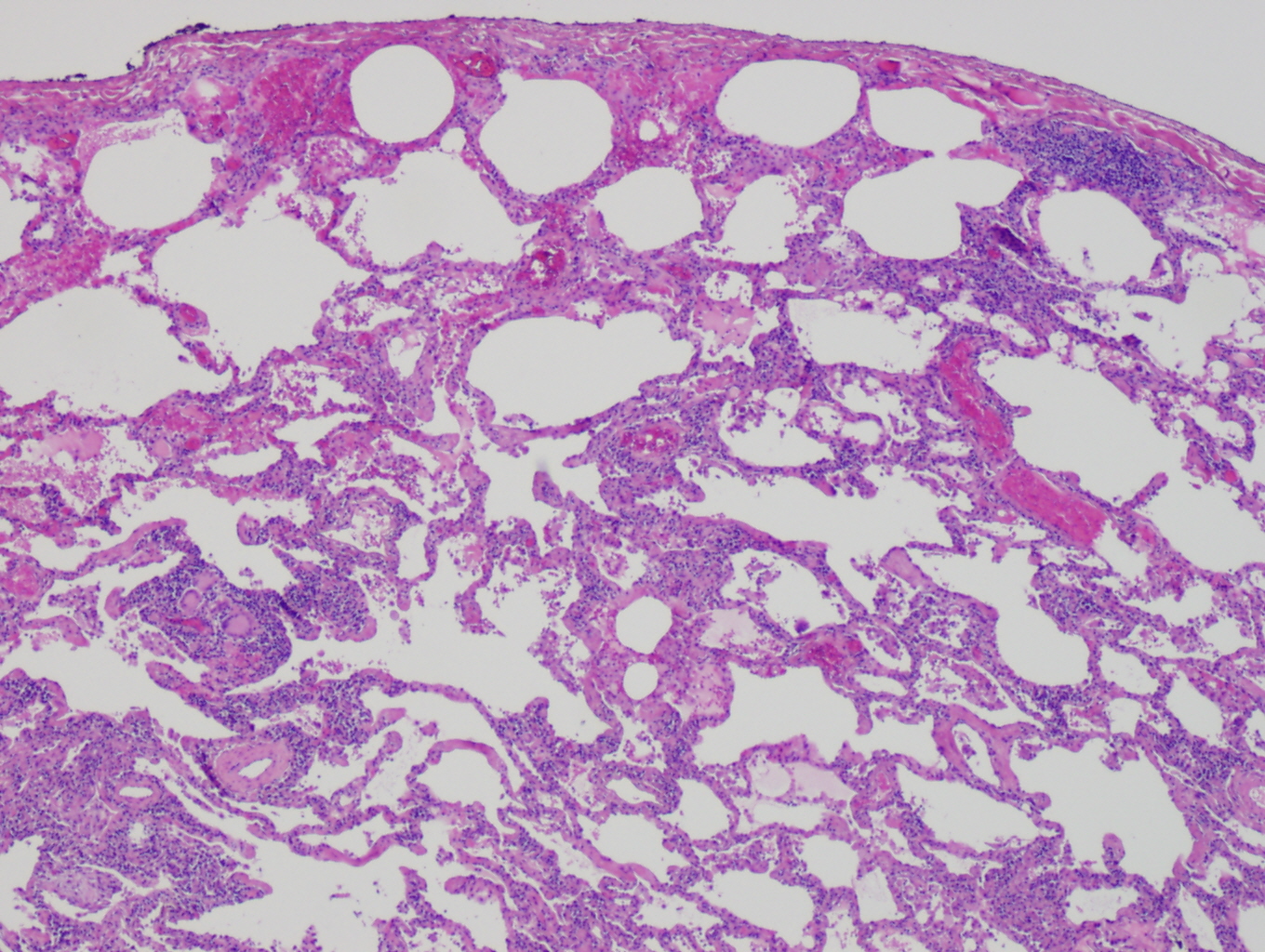
Bagassosis
Bagassosis, an interstitial lung disease, is a type of hypersensitivity pneumonitis attributed to exposure to moldy molasses or bagasse dust. Signs and symptoms Some symptoms and signs of Bagassosis include breathlessness, cough, haemoptysis, slight fever. Acute diffuse bronchiolitis may also occur. An xray may show mottling of lungs or a shadow. Cause Bagassosis has been shown to be due to a thermophilic actinomycetes The Actinomycetales is an order of Actinomycetota. A member of the order is often called an actinomycete. Actinomycetales are generally gram-positive and anaerobic and have mycelia in a filamentous and branching growth pattern. Some actinomycete ... for which the name thermoactinomycetes sacchari was suggested. Prevention The following are precautionary measures that can be taken to avoid the spread of bagassosis: # Dust control-prevention /suppression of dust such as wet process, enclosed apparatus, exhaust ventilation etc. should be used # Personal protectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagasse
Bagasse ( ) is the dry pulpy fibrous material that remains after crushing sugarcane or sorghum stalks to extract their juice. It is used as a biofuel for the production of heat, energy, and electricity, and in the manufacture of pulp and building materials. Agave bagasse is similar, but is the material remnants after extracting blue agave sap. Etymology The word comes from ''bagage'' (French) and ''bagazo'' (Spanish), meaning ''refuse'' or ''trash''. It originally referred to the material left after pressing olives, palm nuts, and grapes. The word eventually came to be used in the context of processing of plants such as sugarcane and sugar beets. Today, it usually refers to by-products of the sugarcane mill. Description Bagasse is the solid by-product when the liquid components are extracted from plants. Much of the core of those plants is a heterogeneous "pith" fibre. This fibre is primarily parenchyma tissue, along with bast, rind, or stem fibers of the sclerenchyma. Here's an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
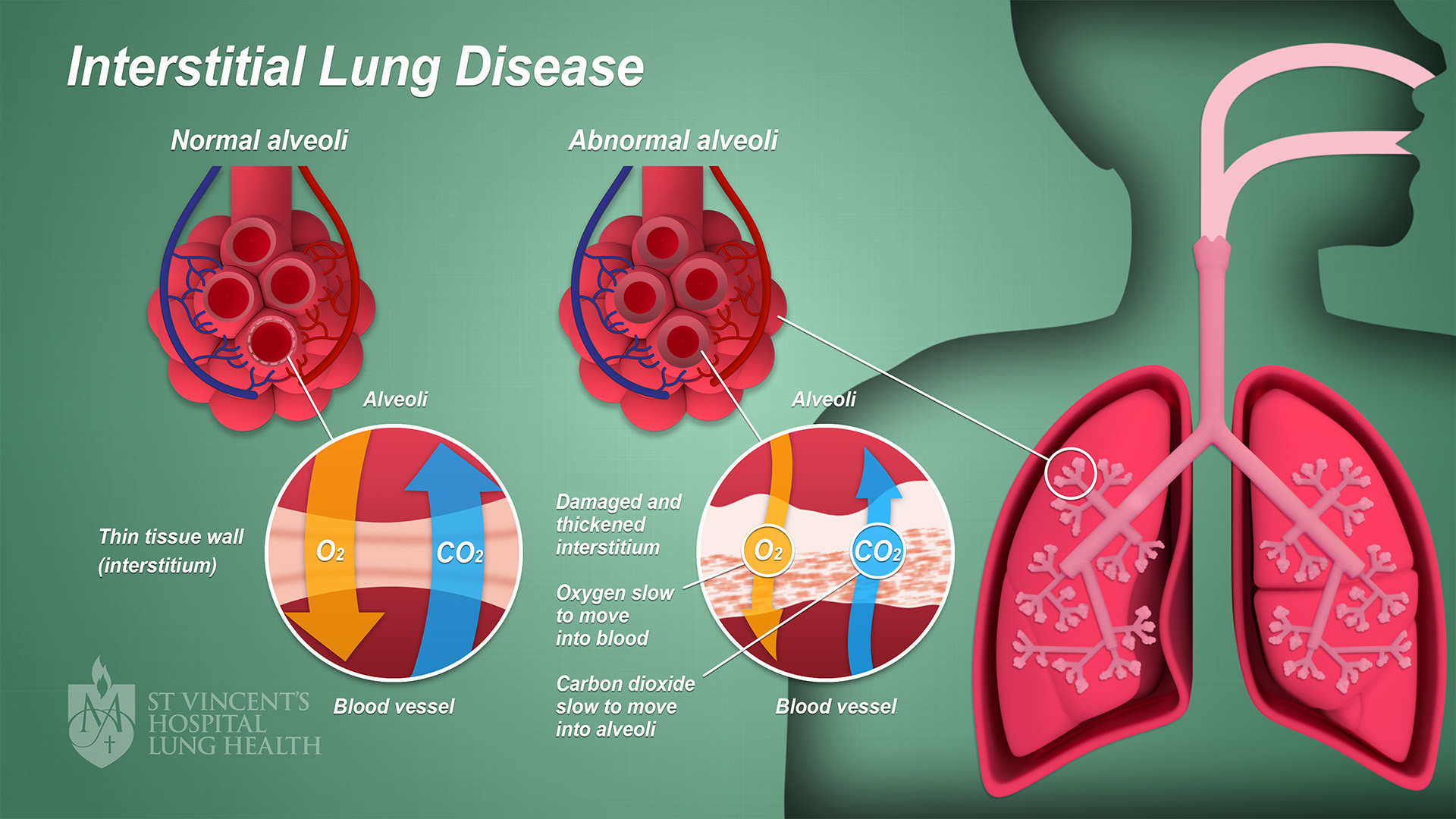
Interstitial Lung Disease
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue and space around the alveoli (air sacs)) of the lungs. It concerns alveolar epithelium, pulmonary capillary endothelium, basement membrane, and perivascular and perilymphatic tissues. It may occur when an injury to the lungs triggers an abnormal healing response. Ordinarily, the body generates just the right amount of tissue to repair damage, but in interstitial lung disease, the repair process is disrupted, and the tissue around the air sacs (alveoli) becomes scarred and thickened. This makes it more difficult for oxygen to pass into the bloodstream. The disease presents itself with the following symptoms: shortness of breath, nonproductive coughing, fatigue, and weight loss, which tend to develop slowly, over several months. The average rate of survival for someone with this disease is between three and five years. The term ILD i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) or extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA) is a syndrome caused by the repetitive inhalation of antigens from the environment in susceptible or sensitized people. Common antigens include molds, bacteria, bird droppings, bird feathers, agricultural dusts, bioaerosols and chemicals from paints or plastics. People affected by this type of lung inflammation (pneumonitis) are commonly exposed to the antigens by their occupations, hobbies, the environment and animals. The inhaled antigens produce a hypersensitivity immune reaction causing inflammation of the airspaces (alveoli) and small airways (bronchioles) within the lung. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis may eventually lead to interstitial lung disease. Signs and symptoms Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) can be categorized as acute, subacute, and chronic based on the duration of the illness. Acute In the acute form of HP dose of antigen exposure tends to be very high but only for a short duration. Symptoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molasses
Molasses () is a viscous substance resulting from refining sugarcane or sugar beets into sugar. Molasses varies in the amount of sugar, method of extraction and age of the plant. Sugarcane molasses is primarily used to sweeten and flavour foods. Molasses is a major constituent of fine commercial brown sugar. It is also one of the primary ingredients used to distill rum. Sweet sorghum syrup is colloquially called ''sorghum molasses'' in the southern United States. Molasses has a stronger flavour than most alternative syrups. Name The word molasses comes from ''melaço'' in Portuguese, a derivative (intensifier) of ''mel'' (honey) with Latinate roots. Cognates include Ancient Greek μέλι (''méli'') (honey), Latin ''mel'', Spanish ''melaza'' (molasses), Romanian ''miere'' or ''melasă'', and French ''miel'' (honey). Cane molasses Cane molasses is an ingredient used in baking and cooking. It was popular in the Americas before the twentieth century, when it was plentiful and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breathlessness
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that consists of qualitatively distinct sensations that vary in intensity", and recommends evaluating dyspnea by assessing the intensity of its distinct sensations, the degree of distress and discomfort involved, and its burden or impact on the patient's activities of daily living. Distinct sensations include effort/work to breathe, chest tightness or pain, and "air hunger" (the feeling of not enough oxygen). The tripod position is often assumed to be a sign. Dyspnea is a normal symptom of heavy physical exertion but becomes pathological if it occurs in unexpected situations, when resting or during light exertion. In 85% of cases it is due to asthma, pneumonia, cardiac ischemia, interstitial lung disease, congestive heart failure, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haemoptysis
Hemoptysis is the coughing up of blood or blood-stained mucus from the bronchi, larynx, trachea, or lungs. In other words, it is the airway bleeding. This can occur with lung cancer, infections such as tuberculosis, bronchitis, or pneumonia, and certain cardiovascular conditions. Hemoptysis is considered massive at . In such cases, there are always severe injuries. The primary danger comes from choking, rather than blood loss. Diagnosis * Past history, history of present illness, family history ** history of tuberculosis, bronchiectasis, chronic bronchitis, mitral stenosis, etc. ** history of cigarette smoking, occupational diseases by exposure to silica dust, etc. * Blood ** duration, frequency, amount ** Amounts of blood: large amounts of blood, or is there blood-streaked sputum ** Probable source of bleeding: Is the blood coughed up, or vomited? * Bloody sputum ** color, characters: blood-streaked, fresh blood, frothy pink, bloody gelatinous. * Accompanying symptoms ** fever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermophilic
A thermophile is an organism—a type of extremophile—that thrives at relatively high temperatures, between . Many thermophiles are archaea, though they can be bacteria or fungi. Thermophilic eubacteria are suggested to have been among the earliest bacteria. Thermophiles are found in various geothermally heated regions of the Earth, such as hot springs like those in Yellowstone National Park (see image) and deep sea hydrothermal vents, as well as decaying plant matter, such as peat bogs and compost. Thermophiles can survive at high temperatures, whereas other bacteria or archaea would be damaged and sometimes killed if exposed to the same temperatures. The enzymes in thermophiles function at high temperatures. Some of these enzymes are used in molecular biology, for example the ''Taq'' polymerase used in PCR. "Thermophile" is derived from the el, θερμότητα (''thermotita''), meaning heat, and el, φίλια (''philia''), love. Classification Thermophiles can be c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinomycetes
The Actinomycetales is an order of Actinomycetota. A member of the order is often called an actinomycete. Actinomycetales are generally gram-positive and anaerobic and have mycelia in a filamentous and branching growth pattern. Some actinomycetes can form rod- or coccoid-shaped forms, while others can form spores on aerial hyphae. Actinomycetales bacteria can be infected by bacteriophages, which are called actinophages. Actinomycetales can range from harmless bacteria to pathogens with resistance to antibiotics. Reproduction Actinomycetales have 2 main forms of reproduction: spore formation and hyphae fragmentation. During reproduction, Actinomycetales can form conidiophores, sporangiospores, and oidiospores. In reproducing through hyphae fragmentation, the hyphae formed by Actinomycetales can be a fifth to half the size of fungal hyphae, and bear long spore chains. Presence and associations Actinomycetales can be found mostly in soil and decaying organic matter, as well as in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |