|
Baeocystin
Baeocystin is a zwitterionic alkaloid and analog of psilocybin. It is found as a minor compound in most psilocybin mushrooms together with psilocybin, norbaeocystin, aeruginascin, and psilocin. Baeocystin is an ''N''-demethylated derivative of psilocybin, and a phosphorylated derivative of 4-HO-NMT (4-hydroxy- ''N''-methyltryptamine). The structures at right illustrate baeocystin in its zwitterionic form. Baeocystin was first isolated from the mushroom '' Psilocybe baeocystis'', and later from '' P. semilanceata'', '' Panaeolus renenosus'', '' Panaeolus subbalteatus'', and '' Copelandia chlorocystis''. It was first synthesized by Troxler ''et al''. in 1959. Little information exists with regard to human pharmacology, but in the book ''Magic Mushrooms Around the World'', author Jochen Gartz reports being aware of a study in which "10 mg of baeocystin were found to be about as psychoactive as a similar amount of psilocybin." Gartz also reported in a research paper that a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norbaeocystin
Norbaeocystin is a psilocybin mushroom alkaloid and analog of psilocybin. It is found as a minor compound in most psilocybin mushrooms together with psilocin, psilocybin, aeruginascin, and baeocystin, from which it is a derivative. Norbaeocystin is a N-demethylated derivative of baeocystin (itself a N-demethylated derivative of psilocybin), and a phosphorylated derivative of 4-hydroxytryptamine. The latter is notable as a positional isomer of serotonin, which is 5-hydroxytryptamine. See also * Aeruginascin * Baeocystin * Norpsilocin * Psilocybin Psilocybin ( , ) is a naturally occurring psychedelic prodrug compound produced by more than 200 species of fungi. The most potent are members of the genus ''Psilocybe'', such as '' P. azurescens'', '' P. semilanceata'', and '' P.&nbs ... References Tryptamine alkaloids Organophosphates Psychedelic tryptamines {{hallucinogen-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norbaeocystin
Norbaeocystin is a psilocybin mushroom alkaloid and analog of psilocybin. It is found as a minor compound in most psilocybin mushrooms together with psilocin, psilocybin, aeruginascin, and baeocystin, from which it is a derivative. Norbaeocystin is a N-demethylated derivative of baeocystin (itself a N-demethylated derivative of psilocybin), and a phosphorylated derivative of 4-hydroxytryptamine. The latter is notable as a positional isomer of serotonin, which is 5-hydroxytryptamine. See also * Aeruginascin * Baeocystin * Norpsilocin * Psilocybin Psilocybin ( , ) is a naturally occurring psychedelic prodrug compound produced by more than 200 species of fungi. The most potent are members of the genus ''Psilocybe'', such as '' P. azurescens'', '' P. semilanceata'', and '' P.&nbs ... References Tryptamine alkaloids Organophosphates Psychedelic tryptamines {{hallucinogen-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
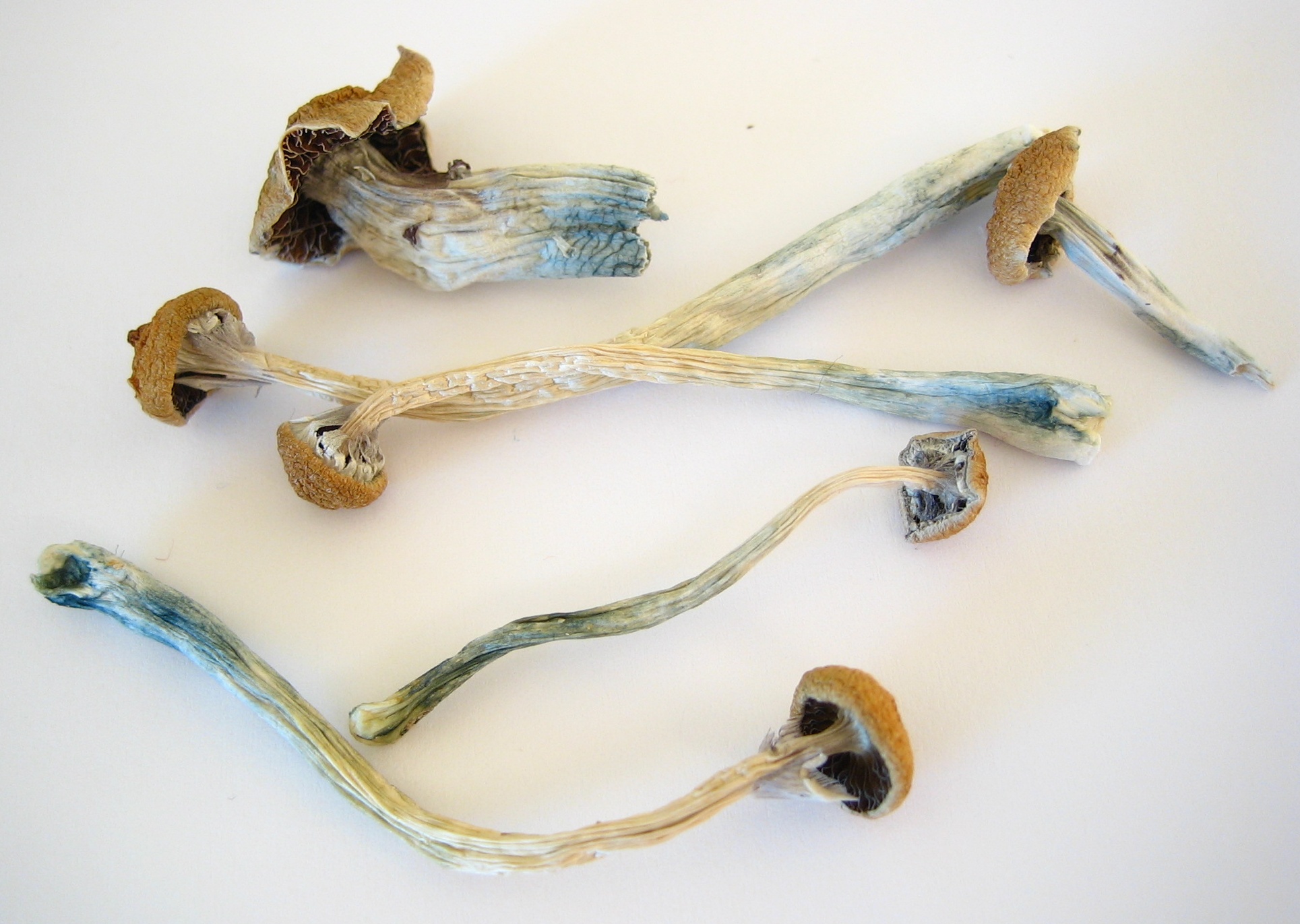
Psilocybe Baeocystis
''Psilocybe baeocystis'' is a psilocybin mushroom of the family Hymenogastraceae. It contains the hallucinogenic compounds psilocybin, psilocin and baeocystin. The species is commonly known by various names such as bottle caps, knobby tops, blue bells, olive caps. Etymology and history *From the Greek words ''baeo'' (little) and ''kystis'' (bladder) *1945 ''P. baeocystis'' is first collected in Eugene, Oregon. *1958 ''P. baeocystis'' is formally described and published by Singer and Smith. *1962 Psilocin is first reported in this species. *1967-68 Baeocystin and norbaeocystin are discovered and named. *1981 Testing again reveals psilocybin, psilocin, baeocystin and norbaeocystin. Description *Pileas: The cap is in diameter and conic to obtusely conic to convex. The cap margin is turned inwards when young, rarely becoming plane in age, often distinctly rippled, translucent-striate and bruising and aging greenish-bluish about the margin. It is dark olive brown to buff brown in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psilocybe Semilanceata
''Psilocybe semilanceata'', commonly known as the liberty cap, is a species of fungus which produces the Psychoactive drug, psychoactive compounds psilocybin, psilocin and baeocystin. It is both one of the most widely distributed psilocybin mushrooms in nature, and one of the most potency (pharmacology), potent. The mushrooms have a distinctive conical to bell-shaped pileus (mycology), cap, up to in diameter, with a small Umbo (mycology), nipple-like protrusion on the top. They are yellow to brown, covered with radial grooves when moist, and fade to a lighter color as they mature. Their stipe (mycology), stipes tend to be slender and long, and the same color or slightly lighter than the cap. The lamella (mycology), gill attachment to the stipe is adnexed (narrowly attached), and they are initially cream-colored before tinting purple to black as the spores mature. The spores are dark purplish-brown in spore print, mass, ellipsoid in shape, and measure 10.5–15 by 6.5–8.5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-HO-NMT
Norpsilocin (4-HO-NMT) is tryptamine alkaloid recently discovered in 2017 in the psychedelic mushroom ''Psilocybe cubensis''. It is hypothesized to be a dephosphorylated metabolite of baeocystin. Norpsilocin was found to be a full agonist of 5-HT2A receptor. It is also more potent than psilocin. See also * Norbaeocystin Norbaeocystin is a psilocybin mushroom alkaloid and analog of psilocybin. It is found as a minor compound in most psilocybin mushrooms together with psilocin, psilocybin, aeruginascin, and baeocystin, from which it is a derivative. Norbaeocystin ... References Tryptamine alkaloids Secondary amines {{Alkaloid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psilocybin
Psilocybin ( , ) is a naturally occurring psychedelic prodrug compound produced by more than 200 species of fungi. The most potent are members of the genus ''Psilocybe'', such as '' P. azurescens'', '' P. semilanceata'', and '' P. cyanescens'', but psilocybin has also been isolated from about a dozen other genera. Psilocybin is itself biologically inactive but is quickly converted by the body to psilocin, which has mind-altering effects similar, in some aspects, to those of LSD, mescaline, and DMT. In general, the effects include euphoria, visual and mental hallucinations, changes in perception, a distorted sense of time, and perceived spiritual experiences. It can also cause adverse reactions such as nausea and panic attacks. Imagery found on prehistoric murals and rock paintings of modern-day Spain and Algeria suggests that human usage of psilocybin mushrooms predates recorded history. In Mesoamerica, the mushrooms had long been consumed in spiritual and div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psilocybin
Psilocybin ( , ) is a naturally occurring psychedelic prodrug compound produced by more than 200 species of fungi. The most potent are members of the genus ''Psilocybe'', such as '' P. azurescens'', '' P. semilanceata'', and '' P. cyanescens'', but psilocybin has also been isolated from about a dozen other genera. Psilocybin is itself biologically inactive but is quickly converted by the body to psilocin, which has mind-altering effects similar, in some aspects, to those of LSD, mescaline, and DMT. In general, the effects include euphoria, visual and mental hallucinations, changes in perception, a distorted sense of time, and perceived spiritual experiences. It can also cause adverse reactions such as nausea and panic attacks. Imagery found on prehistoric murals and rock paintings of modern-day Spain and Algeria suggests that human usage of psilocybin mushrooms predates recorded history. In Mesoamerica, the mushrooms had long been consumed in spiritual and div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panaeolus Subbalteatus
''Panaeolus cinctulus'', syn. ''Panaeolus subbalteatus'', commonly known as the banded mottlegill, weed Panaeolus or is a very common, widely distributed psilocybin mushroom. According to American naturalist and mycologist David Arora, ''Panaeolus cinctulus'' is the most common psilocybin mushroom in California. During the early 1900s, these species were referred to as the "weed Panaeolus" because they were commonly found in beds of the commercially grown, grocery-store mushroom ''Agaricus bisporus''. Mushroom farmers had to weed it out from the edible mushrooms because of its hallucinogenic properties. Name The descriptor ''subbalteatus'' comes from the Latin words ''sub'' ('somewhat') and ''balteat'' ('girdled'), a reference to the dark outer band of the cap. Description *Cap: , hemispherical to convex when young to broadly umbonate or plane in age, smooth, hygrophanous, striking cinnamon-brown when moist, soot-black when wet which disappears as the mushroom completely drie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeruginascin
Aeruginascin or ''N,N,N''-trimethyl-4-phosphoryloxytryptamine is an indoleamine derivative which occurs naturally within the mushroom '' Inocybe aeruginascens'' and '' Pholiotina cyanopus''. Aeruginascin is the ''N''-trimethyl analogue of psilocybin. It is closely related to the frog skin toxin bufotenidine (5-HTQ), a potent 5-HT3 receptor agonist, but the aeruginascin metabolite 4-HO-TMT shows strong binding at the 5-HT2 receptors similar to psilocin Psilocin (also known as 4-HO-DMT, 4-hydroxy DMT, psilocine, psilocyn, or psilotsin) is a substituted tryptamine alkaloid and a serotonergic psychedelic substance. It is present in most psychedelic mushrooms together with its phosphorylated cou .... The first scientific literature about the pharmacological effects of aeruginascin is from a study published by Gartz in 1989. Across 23 analyzed cases of accidental hallucinogenic mushroom poisonings, people who had ingested the mushroom ''Inocybe aeruginascens'' reported only eup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
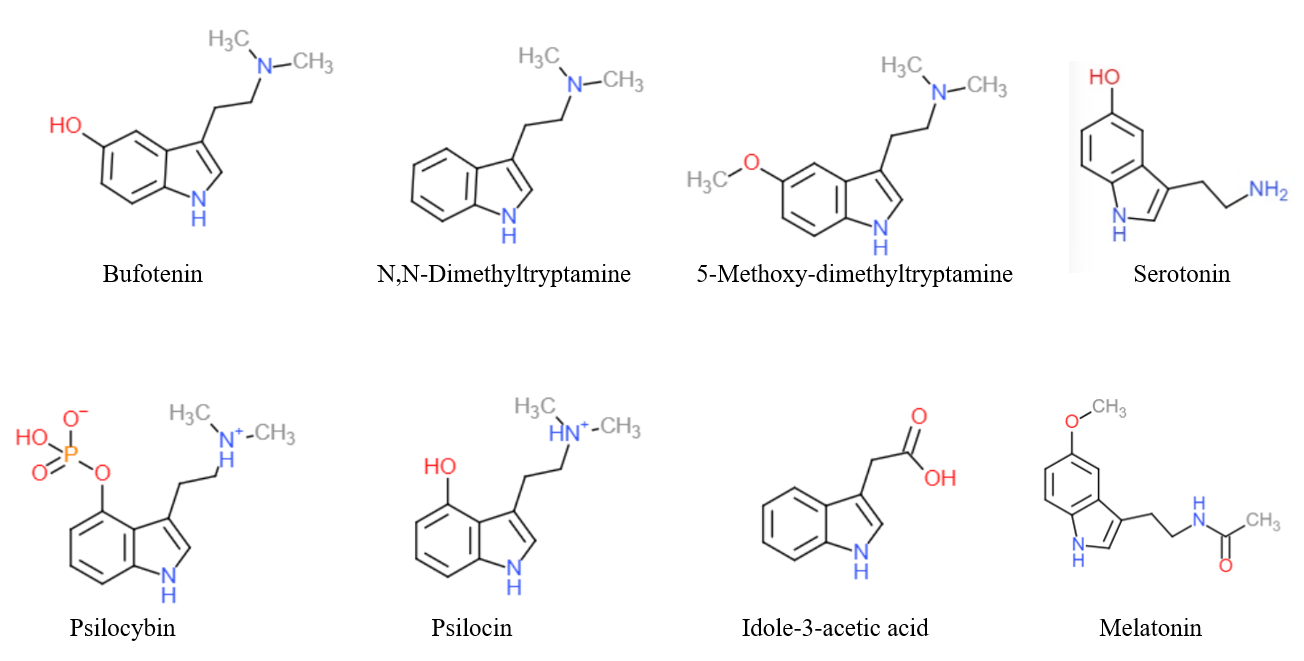
Tryptamine Alkaloids
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid, tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole ─ a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the first one being the heterocyclic nitrogen). The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and others. Tryptamine has been shown to activate trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain, and regulates the activity of dopaminergic, serotonergic and glutamatergic systems. In the human gut, symbiotic bacteria convert dietary tryptophan to tryptamine, which activates 5-HT4 receptors and regulates gastrointestinal motility. Multiple tryptamine-derived drugs have been developed to treat migraines, while trace amine-associated receptors are being explored as a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psilocin
Psilocin (also known as 4-HO-DMT, 4-hydroxy DMT, psilocine, psilocyn, or psilotsin) is a substituted tryptamine alkaloid and a serotonergic psychedelic substance. It is present in most psychedelic mushrooms together with its phosphorylated counterpart psilocybin. Psilocin is a Schedule I drug under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances. Acting on the 5-HT2A receptors, psilocin modulates the production and reuptake of serotonin. The mind-altering effects of psilocin are highly variable and subjective and resemble those of LSD and DMT. Chemistry Psilocin and its phosphorylated cousin, psilocybin, were first isolated and named in 1958 by Swiss chemist Albert Hofmann. Hofmann obtained the chemicals from laboratory-grown specimens of the entheogenic mushroom '' Psilocybe mexicana''. Hofmann also succeeded in finding synthetic routes to these chemicals. Psilocin can be obtained by dephosphorylation of natural psilocybin under strongly acidic or under alkaline conditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacology
Pharmacology is a branch of medicine, biology and pharmaceutical sciences concerned with drug or medication action, where a drug may be defined as any artificial, natural, or endogenous (from within the body) molecule which exerts a biochemical or physiological effect on the cell, tissue, organ, or organism (sometimes the word ''pharmacon'' is used as a term to encompass these endogenous and exogenous Biological activity, bioactive species). More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur between a living organism and chemicals that affect normal or abnormal biochemical function. If substances have medicinal properties, they are considered Pharmaceutical drug, pharmaceuticals. The field encompasses drug composition and properties,functions,sources,synthesis and drug design, molecular and cellular mechanism of action, mechanisms, organ/systems mechanisms, signal transduction/cellular communication, molecular diagnostics, drug interaction, interactions, chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |